
Explain with diagram the boiling point elevation in terms of vapour pressure lowering.
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: We know that according to Raoult's law, elevation of boiling point of a solution is directly proportional to the lowering in vapour pressure caused by the number of particles of solute present in the solution.
Complete step by step solution:
Elevation in boiling point: The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. For Example, vapour pressure of water is at $373K$ . Therefore, water boils because its vapour pressure at this temperature becomes equal to one atmospheric pressure which is $1.013bar$. The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of sucrose is less than at and therefore the solution will not boil at $373K$ .
In order to make the solution boil, its temperature must be increased so that its vapour pressure becomes equal to . Thus, boiling point of a solution is always higher than the boiling point of the pure solvent in which the solvent is prepared.
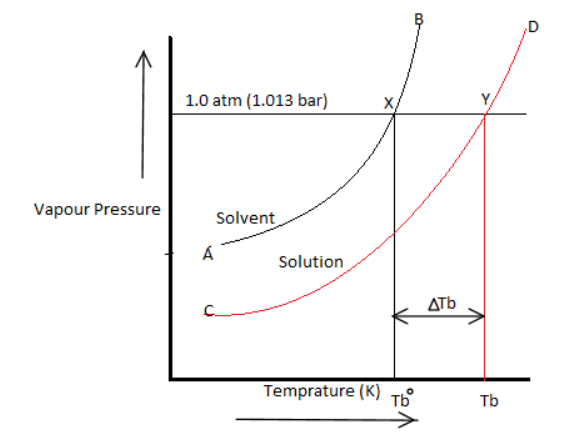
The elevation in boiling point on the addition of a non-volatile solute to a solvent can be easily illustrated graphically as shown above. It is clear from the vapour pressure that the pure solvent becomes equal to atmospheric pressure at ( corresponding to temperature ) while the vapour pressure of the solution becomes equal to atmospheric pressure at ( corresponding to the temperature ).
Note:
Note that for a solution of two liquids A and B, Raoult's law predicts that if no other gases are present, then the total vapor pressure above the solution is equal to the weighted sum of the "pure" vapor pressures and of the two components. Hence, the total pressure above the solution of A and B.
Complete step by step solution:
Elevation in boiling point: The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. For Example, vapour pressure of water is at $373K$ . Therefore, water boils because its vapour pressure at this temperature becomes equal to one atmospheric pressure which is $1.013bar$. The vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of sucrose is less than at and therefore the solution will not boil at $373K$ .
In order to make the solution boil, its temperature must be increased so that its vapour pressure becomes equal to . Thus, boiling point of a solution is always higher than the boiling point of the pure solvent in which the solvent is prepared.

The elevation in boiling point on the addition of a non-volatile solute to a solvent can be easily illustrated graphically as shown above. It is clear from the vapour pressure that the pure solvent becomes equal to atmospheric pressure at ( corresponding to temperature ) while the vapour pressure of the solution becomes equal to atmospheric pressure at ( corresponding to the temperature ).
Note:
Note that for a solution of two liquids A and B, Raoult's law predicts that if no other gases are present, then the total vapor pressure above the solution is equal to the weighted sum of the "pure" vapor pressures and of the two components. Hence, the total pressure above the solution of A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




