
Explain with example, branched and linear polymers.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Polymers are made up of long, repeating chains of molecules. These have different properties depending on the type of molecules that are bonded and the way in which they are bonded.
Complete answer:
- Let’s first discuss about branched polymers:
- branched polymers have side chains or we can say that these have branches growing out from the main chain.
- During polymerization, the branches result from side reactions.
- It is generally found that the monomers with two or more end groups support branching.
- In branched polymer, the branches should comprise a minimum of one complete monomer unit.
- The common example of branched polymers is low-density polyethylene that is (LDPE) . It has wide applications ranging from plastic bags, textiles, containers, to coatings for various packaging materials.
-There is reduced packing efficiency in branched chains due to which these display lower density.
- The length of the branches differentiates between the short or the long branched polymers. Long branches are found to have comb-like or we can say star-shaped structures.
- let’s see an example of this:
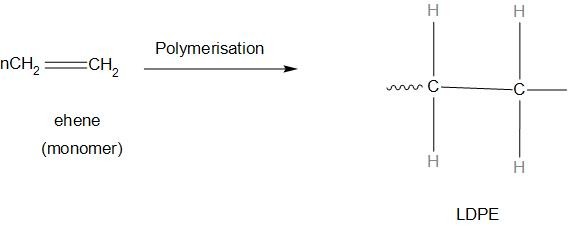
- Let’s discuss about Linear polymer:
- In linear polymers there are the repeating units present which are joined together in a single flexible chain at end to end.
- Generally, linear polymers are more rigid in nature.
-Basically, linear polymers are made from monomers with one end group.
- Three are physical attractions present that keep the polymeric chains together. The attractions present in this are the Vander Waal forces that keep the chains together.
- There are some of the common examples of linear polymers that are, polystyrene, polyamides, PVC, polyethylene etc.
- let’s see an example of this:
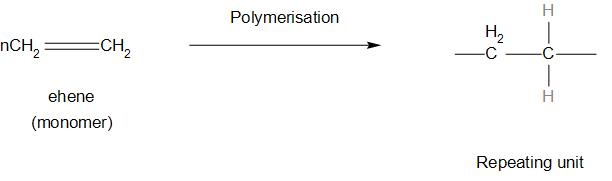
Note:
- When polymers are cut, manipulated or heated these may be toxic. It is found that polymers and their by- products release dangerous vapours and dust when heated.
Complete answer:
- Let’s first discuss about branched polymers:
- branched polymers have side chains or we can say that these have branches growing out from the main chain.
- During polymerization, the branches result from side reactions.
- It is generally found that the monomers with two or more end groups support branching.
- In branched polymer, the branches should comprise a minimum of one complete monomer unit.
- The common example of branched polymers is low-density polyethylene that is (LDPE) . It has wide applications ranging from plastic bags, textiles, containers, to coatings for various packaging materials.
-There is reduced packing efficiency in branched chains due to which these display lower density.
- The length of the branches differentiates between the short or the long branched polymers. Long branches are found to have comb-like or we can say star-shaped structures.
- let’s see an example of this:

- Let’s discuss about Linear polymer:
- In linear polymers there are the repeating units present which are joined together in a single flexible chain at end to end.
- Generally, linear polymers are more rigid in nature.
-Basically, linear polymers are made from monomers with one end group.
- Three are physical attractions present that keep the polymeric chains together. The attractions present in this are the Vander Waal forces that keep the chains together.
- There are some of the common examples of linear polymers that are, polystyrene, polyamides, PVC, polyethylene etc.
- let’s see an example of this:

Note:
- When polymers are cut, manipulated or heated these may be toxic. It is found that polymers and their by- products release dangerous vapours and dust when heated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




