
Fig shows two amino acids, glycine and valine. Use the space below to make a drawing to show what happens when these two molecules join together to form a dipeptide.
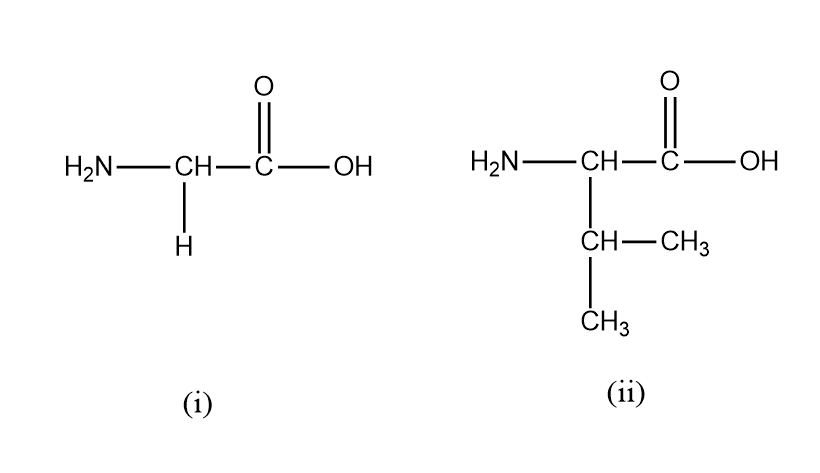
(A) Glycine
(B) valine

Answer
515.7k+ views
Hint :An amino acid is made up of an amino group, a carboxyl group and an R group that is specific to the amino acid. The R group is what determines the characteristics such as the pH of each amino acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The functional group is the carboxyl group and the amino acid. The functional group are the carboxyl groups and the amine group from the amino acids. There are twenty amino acids and the bonds that form between them are known as peptide bonds.
Glycine and valine are two such amino acids that can be joined through a peptide bond. The structure of each are as follows:
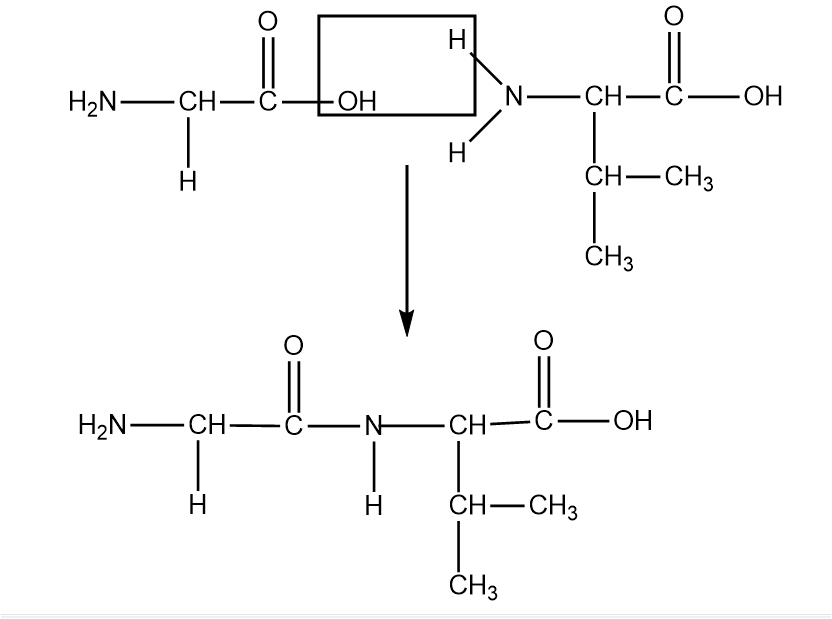
In Glycine, the R group here is H under the central carbon. In Valine the R group here is $ CH(C{H_3})C{H_3} $ under the central carbon. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group and one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. In this case, the OH form the carboxyl group of glycine will bond with the H from the amino group of valine. This will cause a water loss.
Different amino acids can be joined together to make a protein. The order of the amino acids determines which protein will be made.
Note :
When two amino acids are joined together, a dipeptide is formed. A special chemical bond called a peptide bond holds together two amino acids. Protein usually consists of multiple amino acids that are held together by peptide bonds. So, the bigger the protein, the more amino acids and peptide bonds there are.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The functional group is the carboxyl group and the amino acid. The functional group are the carboxyl groups and the amine group from the amino acids. There are twenty amino acids and the bonds that form between them are known as peptide bonds.
Glycine and valine are two such amino acids that can be joined through a peptide bond. The structure of each are as follows:

In Glycine, the R group here is H under the central carbon. In Valine the R group here is $ CH(C{H_3})C{H_3} $ under the central carbon. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group and one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. In this case, the OH form the carboxyl group of glycine will bond with the H from the amino group of valine. This will cause a water loss.
Different amino acids can be joined together to make a protein. The order of the amino acids determines which protein will be made.
Note :
When two amino acids are joined together, a dipeptide is formed. A special chemical bond called a peptide bond holds together two amino acids. Protein usually consists of multiple amino acids that are held together by peptide bonds. So, the bigger the protein, the more amino acids and peptide bonds there are.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




