
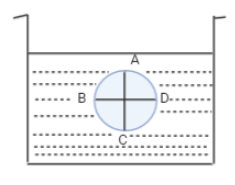
Figure shows a container filled with a liquid of density ρ. Four points A, B, C and D lie on the diametrically opposite points of a circle as shown. Points A and C lie on the vertical line and points B and D lie on the horizontal line. The incorrect statement is (${p_A},{p_B},{p_C}and{p_D}$ are absolute pressure at the respective points)
A. ${p_D} = {p_B}$
B. ${p_A} < {p_B} = {p_D} < {p_C}$
C. ${p_D} = {p_B} = \dfrac{{{p_C} - {p_A}}}{2}$
D. ${p_D} = {p_B} = \dfrac{{{p_C} + {p_A}}}{2}$

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We know that Pascal’s law states that pressure is the same at all points in a horizontal plane and it increases with increase in depth from the surface of the liquid. The total pressure at a certain depth is equal to the sum of atmospheric pressure and pressure due to the height.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure shows a container which is filled with a liquid of density $\rho $ . The four points A, B, C and D lie on the diametrically opposite points of a circle that is shown in the figure i.e., A and C are the endpoints of one diameter and B and D are the endpoints of another diameter.
According to Pascal’s law, pressure is the same at all points on a horizontal plane in a stationary liquid i.e., a liquid which is in a rest position. Hence, pressure at D $\left( {{p_D}} \right)$ is the same as pressure at B $\left( {{p_B}} \right)$ since both the points B and D lie on the same horizontal line. Therefore, option A is correct.
Also, we know that pressure at a point inside the liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid. Thus, pressure at A is less than pressure at B as B is at a higher depth than A and pressure at D is less than pressure at C as C is at a higher depth than D. Due to symmetry i.e., all the four points lie at the quarter of a circle. Hence, ${p_A} < {p_B} = {p_D} < {p_C}$ Therefore, option B is also correct.
The total pressure in a liquid at a depth $d = {P_o} + \rho gd$ .
Pressure at C $\left( {{p_o}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho g\left( {h + 2r} \right)$ where ${P_o}$ is the atmospheric pressure, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the liquid column from the upper surface of the liquid to point A and 2r is the distance between point A and C. r is the radius of the circle. [eqn.1]
Pressure at A $\left( {{p_A}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho gh$ [eqn.2]
Now, we add eqn.1 and eqn.2
${p_A} + {p_C} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho g\left( {2r} \right) + {P_o} + \rho gh$
${p_C} + {p_A} = 2{P_o} + 2\rho gh + 2\rho gr$
$\dfrac{{{p_C} + {p_A}}}{2} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ [eqn.3]
Pressure at B $\left( {{p_B}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho g\left( {h + r} \right)$
${p_B} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ and ${p_D} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ as both lie at the same line. [eqn.4]
From eqn.3 and eqn.4, we get
$\dfrac{{{p_C} + {p_A}}}{2} = {p_B} = {p_D}$
Thus, option C is incorrect.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note: We should remember that pressure in a liquid is the same at all points at the same depth from the given surface and pressure increases with the increase in the depth of liquid from the surface.Moreover, the pressure is thrust per unit area, hence it is directly proportional to thrust and inversely proportional to area. The units used for pressure is pounds per square inch, Newtons per square meter, or Pascals.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure shows a container which is filled with a liquid of density $\rho $ . The four points A, B, C and D lie on the diametrically opposite points of a circle that is shown in the figure i.e., A and C are the endpoints of one diameter and B and D are the endpoints of another diameter.
According to Pascal’s law, pressure is the same at all points on a horizontal plane in a stationary liquid i.e., a liquid which is in a rest position. Hence, pressure at D $\left( {{p_D}} \right)$ is the same as pressure at B $\left( {{p_B}} \right)$ since both the points B and D lie on the same horizontal line. Therefore, option A is correct.
Also, we know that pressure at a point inside the liquid increases with the depth from the free surface of the liquid. Thus, pressure at A is less than pressure at B as B is at a higher depth than A and pressure at D is less than pressure at C as C is at a higher depth than D. Due to symmetry i.e., all the four points lie at the quarter of a circle. Hence, ${p_A} < {p_B} = {p_D} < {p_C}$ Therefore, option B is also correct.
The total pressure in a liquid at a depth $d = {P_o} + \rho gd$ .
Pressure at C $\left( {{p_o}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho g\left( {h + 2r} \right)$ where ${P_o}$ is the atmospheric pressure, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the liquid column from the upper surface of the liquid to point A and 2r is the distance between point A and C. r is the radius of the circle. [eqn.1]
Pressure at A $\left( {{p_A}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho gh$ [eqn.2]
Now, we add eqn.1 and eqn.2
${p_A} + {p_C} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho g\left( {2r} \right) + {P_o} + \rho gh$
${p_C} + {p_A} = 2{P_o} + 2\rho gh + 2\rho gr$
$\dfrac{{{p_C} + {p_A}}}{2} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ [eqn.3]
Pressure at B $\left( {{p_B}} \right) = {P_o} + \rho g\left( {h + r} \right)$
${p_B} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ and ${p_D} = {P_o} + \rho gh + \rho gr$ as both lie at the same line. [eqn.4]
From eqn.3 and eqn.4, we get
$\dfrac{{{p_C} + {p_A}}}{2} = {p_B} = {p_D}$
Thus, option C is incorrect.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note: We should remember that pressure in a liquid is the same at all points at the same depth from the given surface and pressure increases with the increase in the depth of liquid from the surface.Moreover, the pressure is thrust per unit area, hence it is directly proportional to thrust and inversely proportional to area. The units used for pressure is pounds per square inch, Newtons per square meter, or Pascals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




