
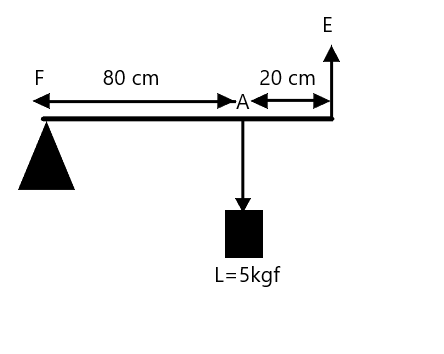
Figure shows a lever in use. To which class of lever does it belong?
(A) Class I
(B) Class II
(C) Class III
(D) Can’t say

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint Classes of lever are only based on the configuration or arrangement of the fulcrum, effort and load, not their exact location.The fulcrum is the pivot point, the effort is where force is applied by external agents and the load is the force the effort aims to move.
Complete step by step answer
A lever is a simple machine which consists of a beam pivoted at a point, commonly called fulcrum. As every machine, levers are built to increase efficiency in doing work. In general, different levers are configured in different ways. It is understood that there are three different classes of lever dependent on the arrangement of their load point, effort point and fulcrum. In any lever, the effort is called input force while the load is called output force. A famous example is a seesaw.
First class lever or commonly class 1 lever: These types of lever have their fulcrum in between their load (or resistance) and their effort. This is to say that the load is acting on one side, of the fulcrum and the effort applied on the other side.
Second class lever or class 2 lever: This is a class of lever whereby the load is in between the fulcrum and the effort, that is to say, that the fulcrum is on one side of the load while the effort is on one side
Third class lever or class 3 lever: This is the class of lever whereby effort is between the load and fulcrum.
Comparing the above definitions with the figure in question, we can conclude that it is a Class 2 lever.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
In application, levers are often used to multiply or amplify force. That is to say, to use a lower force to generate a higher force. Such levers are said to be mechanically advantaged. However, even in such levers, energy is always conserved obeying the fundamental principle of conservation of energy.
Complete step by step answer
A lever is a simple machine which consists of a beam pivoted at a point, commonly called fulcrum. As every machine, levers are built to increase efficiency in doing work. In general, different levers are configured in different ways. It is understood that there are three different classes of lever dependent on the arrangement of their load point, effort point and fulcrum. In any lever, the effort is called input force while the load is called output force. A famous example is a seesaw.
First class lever or commonly class 1 lever: These types of lever have their fulcrum in between their load (or resistance) and their effort. This is to say that the load is acting on one side, of the fulcrum and the effort applied on the other side.
Second class lever or class 2 lever: This is a class of lever whereby the load is in between the fulcrum and the effort, that is to say, that the fulcrum is on one side of the load while the effort is on one side
Third class lever or class 3 lever: This is the class of lever whereby effort is between the load and fulcrum.
Comparing the above definitions with the figure in question, we can conclude that it is a Class 2 lever.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note
In application, levers are often used to multiply or amplify force. That is to say, to use a lower force to generate a higher force. Such levers are said to be mechanically advantaged. However, even in such levers, energy is always conserved obeying the fundamental principle of conservation of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




