
Find \[A\Delta B\] and draw Venn diagram when:
\[A = \left\{ {a,b,c,d,e} \right\}\] and \[B = \left\{ {a,c,e,g} \right\}\]
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: In this particular question find the elements that are not common to the set A and B because \[A\Delta B\] is a set of all elements which are not in both sets (i.e. uncommon elements).
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now as we know that Venn’s diagram is a diagram representing mathematical or logical sets pictorially as circles or closed curves within an enclosing rectangle (the universal set), and common elements of the set are represented by intersections of the circle or closed curves.
So, now let us first draw the Venn’s diagram for the set A and B.
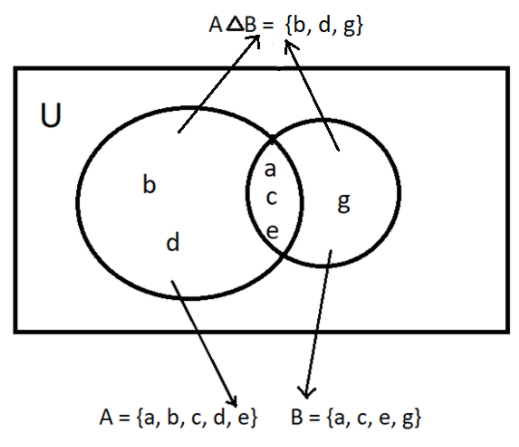
As we can see from the above Venn’s diagram that the element {b, d, g} does not belong to both the sets or in other words each of the elements of set {b, d, g} either belong to set A or set B.
So, \[A\Delta B = \left\{ {b,d,g} \right\}\]
Because \[A\Delta B\] is the set of all elements that are not present in all sets.
Hence, \[A\Delta B = \left\{ {b,d,g} \right\}\].
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept recall is that if there are two sets X and Y then \[X\Delta Y\] will be set having elements that are not present in both the sets X and Y. So, we can directly find the value of \[X\Delta Y\] by applying the formula that is \[X\Delta Y = \left( {X \cup Y} \right) - \left( {X \cap Y} \right)\], where \[\left( {X \cup Y} \right)\] will be the set of all elements of set X and Y. While \[\left( {X \cap Y} \right)\] will be the set of common elements of set X and Y. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution to the problem if the Venn’s diagram is not asked to draw.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now as we know that Venn’s diagram is a diagram representing mathematical or logical sets pictorially as circles or closed curves within an enclosing rectangle (the universal set), and common elements of the set are represented by intersections of the circle or closed curves.
So, now let us first draw the Venn’s diagram for the set A and B.

As we can see from the above Venn’s diagram that the element {b, d, g} does not belong to both the sets or in other words each of the elements of set {b, d, g} either belong to set A or set B.
So, \[A\Delta B = \left\{ {b,d,g} \right\}\]
Because \[A\Delta B\] is the set of all elements that are not present in all sets.
Hence, \[A\Delta B = \left\{ {b,d,g} \right\}\].
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept recall is that if there are two sets X and Y then \[X\Delta Y\] will be set having elements that are not present in both the sets X and Y. So, we can directly find the value of \[X\Delta Y\] by applying the formula that is \[X\Delta Y = \left( {X \cup Y} \right) - \left( {X \cap Y} \right)\], where \[\left( {X \cup Y} \right)\] will be the set of all elements of set X and Y. While \[\left( {X \cap Y} \right)\] will be the set of common elements of set X and Y. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution to the problem if the Venn’s diagram is not asked to draw.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




