
How do you find core and valence electrons?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint The answer to this question is based on the general concept of chemistry which includes the writing of the electronic configuration of the given atom and this gives the information about the core and the valence point.
Complete answer:
In the classes of chemistry, we have dealt with the topics which tell the basic composition and structure of an atom and also the properties of an atom.
Now, we shall see how to identify the valence and core electrons by recalling the definition about the atom and also the relating terms of atoms.
- An atom is composed of a central nucleus in which the positively charged protons and neutral neutrons are concentrated in and also the negatively charged species called the electrons are revolving around the orbit of the nucleus of an atom.
- The core electrons are those electrons which are in the inner shell of an atom that are near to the nucleus and valence electrons are those which are the outermost electrons that are the electrons present in the outermost orbit.
- Valence electrons participate in the bonding and core electrons do not participate in the bonding.
If we consider an example of Carbon with an atomic number 6 and the atomic symbol$C$which has the electronic configuration $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}$, the core electrons is in the 1s orbital and there are 2 electrons and the valence electrons is in 2s and 2p orbital which are 4 in number.
The diagram which depicts valence and core electrons is shown below,
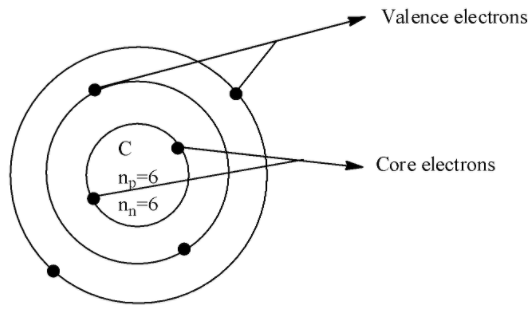
Thus, in this way we can find the core and valence electrons of the given atom.
Note: Note that apart from core and valence electrons there is also lone pair of electrons which also participates in bonding but does not form the covalent bond and the lone pair of electrons can be understood by writing the Lewis structure.
Complete answer:
In the classes of chemistry, we have dealt with the topics which tell the basic composition and structure of an atom and also the properties of an atom.
Now, we shall see how to identify the valence and core electrons by recalling the definition about the atom and also the relating terms of atoms.
- An atom is composed of a central nucleus in which the positively charged protons and neutral neutrons are concentrated in and also the negatively charged species called the electrons are revolving around the orbit of the nucleus of an atom.
- The core electrons are those electrons which are in the inner shell of an atom that are near to the nucleus and valence electrons are those which are the outermost electrons that are the electrons present in the outermost orbit.
- Valence electrons participate in the bonding and core electrons do not participate in the bonding.
If we consider an example of Carbon with an atomic number 6 and the atomic symbol$C$which has the electronic configuration $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{2}}$, the core electrons is in the 1s orbital and there are 2 electrons and the valence electrons is in 2s and 2p orbital which are 4 in number.
The diagram which depicts valence and core electrons is shown below,

Thus, in this way we can find the core and valence electrons of the given atom.
Note: Note that apart from core and valence electrons there is also lone pair of electrons which also participates in bonding but does not form the covalent bond and the lone pair of electrons can be understood by writing the Lewis structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




