
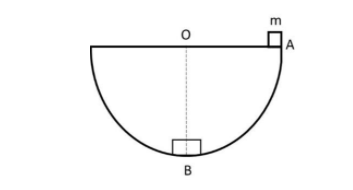
Find out normal reaction at point $B$ when object is released from $A$

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: In this question, first discuss the conservation of energy principle and convert the potential energy of starting into kinetic energy. Then draw the free body diagram and calculate the normal reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that according to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed only can be converted to one form to another form.
When the block is at top position that is at point $A$ then it has zero velocity. We can say then the block is at rest and has no kinetic energy. Then it has only potential energy.
Gradually when the block is released it starts to gain kinetic energy. At point $B$ the kinetic energy becomes maximum and potential energy is minimum. From$A$ to $B$ the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Let us assume the velocity at point $B$ is $v$.
So, the potential energy at point $A$ is $mgr$.
Where $m = $mass of the block
$r = OA = OB = $radius.
And kinetic energy at point $B$ is $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$.
We can say from the law of conservation of energy
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = mgr$
After rearrangement we will get,
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = 2gr$
Now we will draw the free body diagram of the block at $B$.
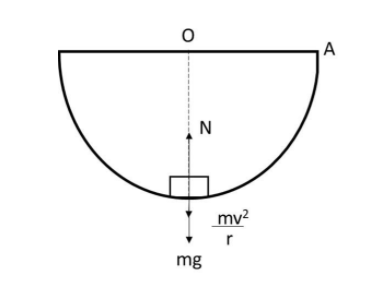
$N$ is the normal reaction here.
The weight acting in the block is $mg$.
As we know the centrifugal force acting on the block is $\dfrac{{n{v^2}}}{r}$.
Now we will be balancing the force in vertical direction and we get
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$
Now we will replace ${v^2} = 2gr$ in this.
We get
$N = mg + \dfrac{{m2gr}}{r}$
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + 2mg$
After simplification we will get,
$\therefore N = 3mg$
So, the normal reaction at point $B$is expressed by $N = 3mg$.
Note:In this question we are careful while drawing the free body diagram keeping in mind the centrifugal component due to rotation. Take the proper height during calculating the potential energy and for the vertical upward direction take positive sign.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that according to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed only can be converted to one form to another form.
When the block is at top position that is at point $A$ then it has zero velocity. We can say then the block is at rest and has no kinetic energy. Then it has only potential energy.
Gradually when the block is released it starts to gain kinetic energy. At point $B$ the kinetic energy becomes maximum and potential energy is minimum. From$A$ to $B$ the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Let us assume the velocity at point $B$ is $v$.
So, the potential energy at point $A$ is $mgr$.
Where $m = $mass of the block
$r = OA = OB = $radius.
And kinetic energy at point $B$ is $\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$.
We can say from the law of conservation of energy
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = mgr$
After rearrangement we will get,
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = 2gr$
Now we will draw the free body diagram of the block at $B$.

$N$ is the normal reaction here.
The weight acting in the block is $mg$.
As we know the centrifugal force acting on the block is $\dfrac{{n{v^2}}}{r}$.
Now we will be balancing the force in vertical direction and we get
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$
Now we will replace ${v^2} = 2gr$ in this.
We get
$N = mg + \dfrac{{m2gr}}{r}$
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + 2mg$
After simplification we will get,
$\therefore N = 3mg$
So, the normal reaction at point $B$is expressed by $N = 3mg$.
Note:In this question we are careful while drawing the free body diagram keeping in mind the centrifugal component due to rotation. Take the proper height during calculating the potential energy and for the vertical upward direction take positive sign.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




