
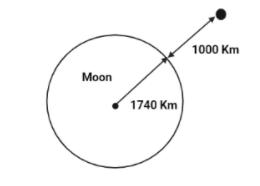
Find the acceleration due to gravity of the moon at a point 1000 km above the moon's surface. The mass of the moon is $7.4 \times {10^2}Kg$ and its radius is $1740Km$.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: For the above question we will equate the gravitational force between the moon and the body to the force exerted on the body.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that there will be a gravitational force exerted between the body and the moon, which is represented by the following formula:
$F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}}$
Where $G$ is the gravitational force,
$M$ is the mass of the moon,
$m$ is the mass of the body,
$r$ is the radius of the moon and
$h$ is the distance between the moon surface and the body
The force exerted on the body is $F = ma$ where $a$ is the acceleration.
Now, this force is equal to the gravitational force. Hence,
$
\dfrac{{GM{m}}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}} = {m}a \\
\dfrac{{GM}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}} = a \\
$
Substituting the values we will get,
$
a = \dfrac{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times 7.14 \times {{10}^{22}}}}{{{{(1740 + 1000)}^2} \times {{10}^6}}} \\
a = \dfrac{{49.358 \times {{10}^{11}}}}{{0.75 \times {{10}^{13}}}} \\
\Rightarrow a = 65.8 \times {10^{ - 2}} \\
\Rightarrow a = 0.65m.{\sec ^{ - 2}} \\
$
Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity of the moon at a point 1000 km above the moon's surface is $0.65m.{\sec ^{ - 2}}$.
Note:
The total gravity on the surface of the Earth is $9.8m.{\sec ^{ - 1}}$. When an object is thrown from a building's roof or a cliff's apex, for example, it travels toward the earth. The gravity on the Moon's surface is about $\dfrac{1}{6}th$ as strong, or about $1.6m.{\sec ^{ - 1}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that there will be a gravitational force exerted between the body and the moon, which is represented by the following formula:
$F = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}}$
Where $G$ is the gravitational force,
$M$ is the mass of the moon,
$m$ is the mass of the body,
$r$ is the radius of the moon and
$h$ is the distance between the moon surface and the body

The force exerted on the body is $F = ma$ where $a$ is the acceleration.
Now, this force is equal to the gravitational force. Hence,
$
\dfrac{{GM{m}}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}} = {m}a \\
\dfrac{{GM}}{{{{(r + h)}^2}}} = a \\
$
Substituting the values we will get,
$
a = \dfrac{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}} \times 7.14 \times {{10}^{22}}}}{{{{(1740 + 1000)}^2} \times {{10}^6}}} \\
a = \dfrac{{49.358 \times {{10}^{11}}}}{{0.75 \times {{10}^{13}}}} \\
\Rightarrow a = 65.8 \times {10^{ - 2}} \\
\Rightarrow a = 0.65m.{\sec ^{ - 2}} \\
$
Therefore, the acceleration due to gravity of the moon at a point 1000 km above the moon's surface is $0.65m.{\sec ^{ - 2}}$.
Note:
The total gravity on the surface of the Earth is $9.8m.{\sec ^{ - 1}}$. When an object is thrown from a building's roof or a cliff's apex, for example, it travels toward the earth. The gravity on the Moon's surface is about $\dfrac{1}{6}th$ as strong, or about $1.6m.{\sec ^{ - 1}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




