
Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD formed by the points A(-2,-2), B(5,1), C(2,4) and D(-1,5).
a) 28 square units
b) 26 square units
c) 24 square units
d) 22 square units
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: A quadrilateral is a polygon having four sides and four vertexes represented on a 2-d geometrical plane. A quadrilateral is also known as a quadrangle, tetragon, and 4-gon. There are basically five basic types of a quadrilateral which differ from each other in respect to the length of the sides and measure of an angle, but they all have four sides, and four vertices are names as Square, Rectangle, Rhombus, Parallelogram, and Trapezoid.
Coordinate of a vertex is the 2-dimensional representation of a point given as\[M\left( {x,y} \right)\], where \[x\]represents the x-coordinates and \[y\]represents the y-coordinates. The area of a quadrilateral polygon is the space occupied by the flat polygon.
In this question, four coordinates of a quadrilateral have been given from which we need to find the area of the quadrilateral. Here, we have divided the quadrilateral into two triangles, and the area of the quadrilateral is the sum of the two triangles.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the coordinates of the quadrilateral are: A(-2,-2), B(5,1), C(2,4), D(-1,5)
We can write the vertex as
\[
A\left( { - 2, - 2} \right) \to A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) \\
B\left( {5,1} \right) \to B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) \\
C\left( {2,4} \right) \to C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) \\
D\left( { - 1,5} \right) \to D\left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) \\
\]
Now draw a diagonal AC which divides the quadrilateral into two triangles ABC and ADC
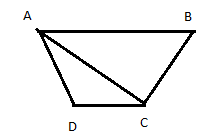
Hence find the area of the triangles ABC and ADC,
\[
\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {y{}_1 - {y_2}} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( {1 - 4} \right) + 5\left( {4 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right) + 2\left( { - 2 - 1} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( { - 3} \right) + 5\left( 6 \right) + 2\left( { - 3} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { + 6 + 30 - 6} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 30 \\
= 15 \\
\]
\[
\vartriangle ACD = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_3} - {y_4}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_4} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_4}\left( {{y_1} - {y_3}} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( {4 - 5} \right) + 2\left( {5 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right) + \left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 2 - 4} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( { - 1} \right) + 2\left( 7 \right) + \left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 6} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {2 + 14 + 6} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{22}}{2} \\
= 11 \\
\]
Hence the area of the quadrilateral will be the sum of the area of triangle ABC and the area of triangle ACD
\[\vartriangle ABC + \vartriangle ACD = 15 + 11 = 26\] Square units
Note:
We can also find the area of the quadrilateral by finding the length of the sides by using the distance formulae, which will be helpful in determining the type of quadrilateral the polygon id, and hence the formulae will be used accordingly.
Coordinate of a vertex is the 2-dimensional representation of a point given as\[M\left( {x,y} \right)\], where \[x\]represents the x-coordinates and \[y\]represents the y-coordinates. The area of a quadrilateral polygon is the space occupied by the flat polygon.
In this question, four coordinates of a quadrilateral have been given from which we need to find the area of the quadrilateral. Here, we have divided the quadrilateral into two triangles, and the area of the quadrilateral is the sum of the two triangles.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the coordinates of the quadrilateral are: A(-2,-2), B(5,1), C(2,4), D(-1,5)
We can write the vertex as
\[
A\left( { - 2, - 2} \right) \to A\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) \\
B\left( {5,1} \right) \to B\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) \\
C\left( {2,4} \right) \to C\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) \\
D\left( { - 1,5} \right) \to D\left( {{x_4},{y_4}} \right) \\
\]
Now draw a diagonal AC which divides the quadrilateral into two triangles ABC and ADC

Hence find the area of the triangles ABC and ADC,
\[
\vartriangle ABC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {y{}_1 - {y_2}} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( {1 - 4} \right) + 5\left( {4 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right) + 2\left( { - 2 - 1} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( { - 3} \right) + 5\left( 6 \right) + 2\left( { - 3} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { + 6 + 30 - 6} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 30 \\
= 15 \\
\]
\[
\vartriangle ACD = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_3} - {y_4}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_4} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_4}\left( {{y_1} - {y_3}} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( {4 - 5} \right) + 2\left( {5 - \left( { - 2} \right)} \right) + \left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 2 - 4} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2\left( { - 1} \right) + 2\left( 7 \right) + \left( { - 1} \right)\left( { - 6} \right)} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {2 + 14 + 6} \right] \\
= \dfrac{{22}}{2} \\
= 11 \\
\]
Hence the area of the quadrilateral will be the sum of the area of triangle ABC and the area of triangle ACD
\[\vartriangle ABC + \vartriangle ACD = 15 + 11 = 26\] Square units
Note:
We can also find the area of the quadrilateral by finding the length of the sides by using the distance formulae, which will be helpful in determining the type of quadrilateral the polygon id, and hence the formulae will be used accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




