
Find the circumcenter of the triangle whose sides are $3x - y - 5 = 0$, $x + 2y - 4 = 0$, $5x + 3y + 1 = 0$
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Solve the given equations pairwise to obtain the vertices of the triangle. Substitute the coordinates of the vertices in the general equation of a circle ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}$ with $(h,k)$ as its centre. Solve the equations thus obtained to get $(h,k)$ which is the required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the equation of the lines which form the sides of the triangle.
They are $3x - y - 5 = 0$, $x + 2y - 4 = 0$, $5x + 3y + 1 = 0$.
We need to find the circumcenter of the triangle.
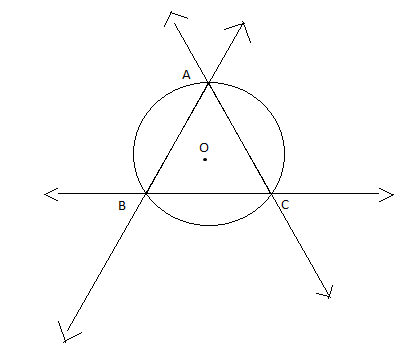
In the above figure, consider O as the circumcenter of $\vartriangle ABC$.
Consider the system of linear equations
$3x - y - 5 = 0......(1)$
$x + 2y - 4 = 0.....(2)$
$5x + 3y + 1 = 0....(3)$
As can be understood from the figure, every pair of lines has a point of intersection and these 3 points of intersection form the vertices of the triangle.
From (1), we get \[3x - 5 = y \Rightarrow y = 3x - 5\]
From (2), we get $2y = - x + 4 \Rightarrow y = - \dfrac{x}{2} + 2$
Therefore,
\[
3x - 5 = - \dfrac{x}{2} + 2 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{7x}}{2} = 7 \\
\Rightarrow x = 2 \\
\]
Substituting\[x = 2\]in\[y = 3x - 5\], we get\[y = 3(2) - 5 = 1\]
Thus, we get one of the vertices of the triangle. Call this vertex as A.
$A \equiv (2,1)$
Similarly, by solving the remaining equations in pairs, we get the other two vertices.
$B \equiv (1, - 2)$ and $C \equiv ( - 2,3)$
Now, these vertices of $\vartriangle ABC$lie on the circle and we need only 3 points to construct a circle.
The centre of the circle formed by the vertices A, B, C is the required circumcenter.
We will construct the equation of the circle using A, B, and C.
Let $(h,k)$be the circumcenter.
Then the equation of the circle with radius r and centre $(h,k)$ is given by ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}....(4)$
As the points A, B, and C lie on the circle, they will satisfy equation (4).
$A \equiv (2,1) \Rightarrow {(2 - h)^2} + {(1 - k)^2} = {r^2}.....(5)$
$B \equiv (1, - 2) \Rightarrow {(1 - h)^2} + {( - 2 - k)^2} = {r^2}.....(6)$
$C \equiv ( - 2,3) \Rightarrow {( - 2 - h)^2} + {(3 - k)^2} = {r^2}....(7)$
Comparing the equations (5) and (6), we get
\[
{(2 - h)^2} + {(1 - k)^2} = {(1 - h)^2} + {( - 2 - k)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 4 - 4h + {h^2} + 1 - 2k + {k^2} = 1 - 2h + {h^2} + 4 + 4k + {k^2} \\
\Rightarrow - 2h - 6k = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2h + 6k = 0....(8) \\
\]
Similarly, from (6) and (7), we get
$3h - 5k = - 4.....(9)$
Solving (8) and (9), we get $(h,k) \equiv (\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7},\dfrac{2}{7})$
Hence, the circumcenter is $(\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7},\dfrac{2}{7})$.
Note: In the given $\vartriangle ABC$, the line passing through the circumcenter and the vertex A is the perpendicular bisector of its opposite side BC. This holds true for all the vertices.
In fact, the circumcenter of a triangle is defined as the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given the equation of the lines which form the sides of the triangle.
They are $3x - y - 5 = 0$, $x + 2y - 4 = 0$, $5x + 3y + 1 = 0$.
We need to find the circumcenter of the triangle.

In the above figure, consider O as the circumcenter of $\vartriangle ABC$.
Consider the system of linear equations
$3x - y - 5 = 0......(1)$
$x + 2y - 4 = 0.....(2)$
$5x + 3y + 1 = 0....(3)$
As can be understood from the figure, every pair of lines has a point of intersection and these 3 points of intersection form the vertices of the triangle.
From (1), we get \[3x - 5 = y \Rightarrow y = 3x - 5\]
From (2), we get $2y = - x + 4 \Rightarrow y = - \dfrac{x}{2} + 2$
Therefore,
\[
3x - 5 = - \dfrac{x}{2} + 2 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{7x}}{2} = 7 \\
\Rightarrow x = 2 \\
\]
Substituting\[x = 2\]in\[y = 3x - 5\], we get\[y = 3(2) - 5 = 1\]
Thus, we get one of the vertices of the triangle. Call this vertex as A.
$A \equiv (2,1)$
Similarly, by solving the remaining equations in pairs, we get the other two vertices.
$B \equiv (1, - 2)$ and $C \equiv ( - 2,3)$
Now, these vertices of $\vartriangle ABC$lie on the circle and we need only 3 points to construct a circle.
The centre of the circle formed by the vertices A, B, C is the required circumcenter.
We will construct the equation of the circle using A, B, and C.
Let $(h,k)$be the circumcenter.
Then the equation of the circle with radius r and centre $(h,k)$ is given by ${(x - h)^2} + {(y - k)^2} = {r^2}....(4)$
As the points A, B, and C lie on the circle, they will satisfy equation (4).
$A \equiv (2,1) \Rightarrow {(2 - h)^2} + {(1 - k)^2} = {r^2}.....(5)$
$B \equiv (1, - 2) \Rightarrow {(1 - h)^2} + {( - 2 - k)^2} = {r^2}.....(6)$
$C \equiv ( - 2,3) \Rightarrow {( - 2 - h)^2} + {(3 - k)^2} = {r^2}....(7)$
Comparing the equations (5) and (6), we get
\[
{(2 - h)^2} + {(1 - k)^2} = {(1 - h)^2} + {( - 2 - k)^2} \\
\Rightarrow 4 - 4h + {h^2} + 1 - 2k + {k^2} = 1 - 2h + {h^2} + 4 + 4k + {k^2} \\
\Rightarrow - 2h - 6k = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 2h + 6k = 0....(8) \\
\]
Similarly, from (6) and (7), we get
$3h - 5k = - 4.....(9)$
Solving (8) and (9), we get $(h,k) \equiv (\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7},\dfrac{2}{7})$
Hence, the circumcenter is $(\dfrac{{ - 6}}{7},\dfrac{2}{7})$.
Note: In the given $\vartriangle ABC$, the line passing through the circumcenter and the vertex A is the perpendicular bisector of its opposite side BC. This holds true for all the vertices.
In fact, the circumcenter of a triangle is defined as the point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




