
How do you find the domain and range of sine, cosine, and tangent?
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find the Domain and range of sine, cosine and tangent. To do so, we first learn about Domain and Range, then we learn about the function sine, cosine and tangent, how they define, where they are defined, where they take value, depending on these values we will find the Domain and Range.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three functions, we have to find the Domain and range of them.
To answer this we will first learn about the Domain and range definition.
Domain of any function is the collection of all those values on which function is defined.
We know sine function is graphed as
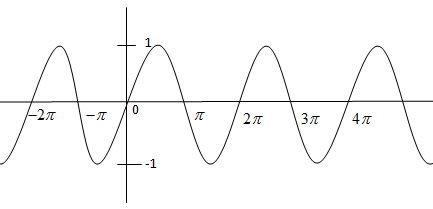
So, we can see that it is defined along all real values of ‘x’, so it mean Domain of sine consists of all real values.
So, Domain of sine is whole $R\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$ .
Similarly, if we look at the graph of cosine function, we see –
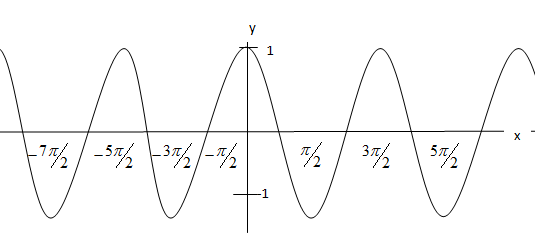
So, cosine is defined for all values of ‘x’. so, clearly Domain of cosine is constant as a whole real line.
So, Domain of $\cos ine=\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$ or R.
Lastly for the Domain of the tangent function, if we see the graph of it we get –
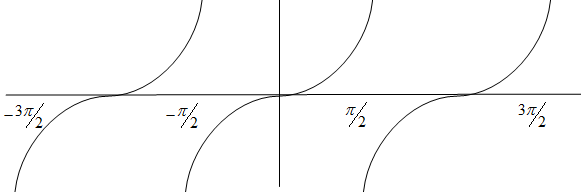
So, we can see that apart from the odd integral multiple of $\pi $ , the tangent is defined at every other value of ‘x’.
Mean tangent is not defined only on $\left( 2x+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
So, Domain of tangent is $\left( -\infty ,\infty \right) - \left\{ x:x=\left( 2x+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2},n\in N \right\}$ .
Now, range is the collection of those values which were taken by the function.
So, if we see the graph again then we can see sine take value between -1 and 1, so the range of sine is $\left( -1,1 \right)$ .
Similarly,
The range of cosine is $\left( -1,1 \right)$ .
Lastly, we look at the graph of the tangent then we see that the tangent takes all the value along the y-axis.
So, the range of tangents takes on a whole real value.
So, range of tangent $\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$
Note: While finding Domain and range we have to look if we have skipped all points that should not belong to the set.
In the similar way we can find the Domain and range of other trigonometric function secant, cosecant and cotangent.
We have Domain of secant in all real values except the odd integral multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Similarly,
Domain of cosecant is all real value except the integral multiples of $\pi $ .
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three functions, we have to find the Domain and range of them.
To answer this we will first learn about the Domain and range definition.
Domain of any function is the collection of all those values on which function is defined.
We know sine function is graphed as

So, we can see that it is defined along all real values of ‘x’, so it mean Domain of sine consists of all real values.
So, Domain of sine is whole $R\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$ .
Similarly, if we look at the graph of cosine function, we see –

So, cosine is defined for all values of ‘x’. so, clearly Domain of cosine is constant as a whole real line.
So, Domain of $\cos ine=\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$ or R.
Lastly for the Domain of the tangent function, if we see the graph of it we get –
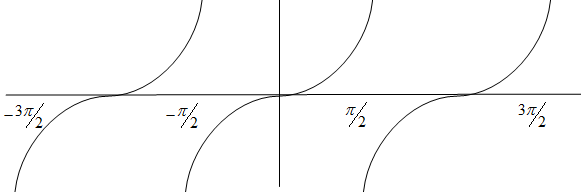
So, we can see that apart from the odd integral multiple of $\pi $ , the tangent is defined at every other value of ‘x’.
Mean tangent is not defined only on $\left( 2x+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
So, Domain of tangent is $\left( -\infty ,\infty \right) - \left\{ x:x=\left( 2x+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2},n\in N \right\}$ .
Now, range is the collection of those values which were taken by the function.
So, if we see the graph again then we can see sine take value between -1 and 1, so the range of sine is $\left( -1,1 \right)$ .
Similarly,
The range of cosine is $\left( -1,1 \right)$ .
Lastly, we look at the graph of the tangent then we see that the tangent takes all the value along the y-axis.
So, the range of tangents takes on a whole real value.
So, range of tangent $\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)$
Note: While finding Domain and range we have to look if we have skipped all points that should not belong to the set.
In the similar way we can find the Domain and range of other trigonometric function secant, cosecant and cotangent.
We have Domain of secant in all real values except the odd integral multiple of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Similarly,
Domain of cosecant is all real value except the integral multiples of $\pi $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




