
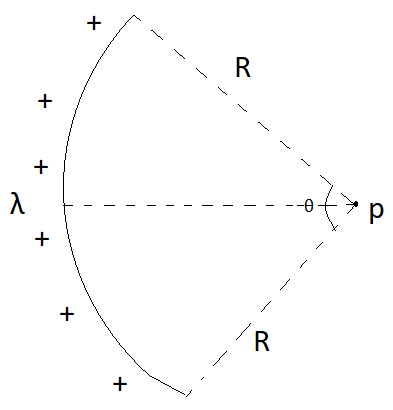
Find the electric field at point P

Answer
552k+ views
Hint: To solve these type of problem we need to take a very small portion of length and by calculating electric field due to this small portion on point P we will integrate over $\theta $ to calculate our required electric field at point P due to an electric charged arc.
Formula used:
Electric field due to a point charge,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{Q}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Complete answer:
From the above diagram we can observe that both half are equal and will exerts same amount of electric field on point P so, we just need to calculate field due to one half and by doing it’s two times we can get our required field at point P
Now, by taking a small section of charge dq in small angle $d\theta $ from point P on upper half and the charge per unit length is given as $\lambda $so,
$\Rightarrow dq=\lambda Rd\theta $ and electric field due to this small portion will be dE at point P, by taking in electric field from both half into consideration and its component along x axis(y axis component will be cancelled) we have,
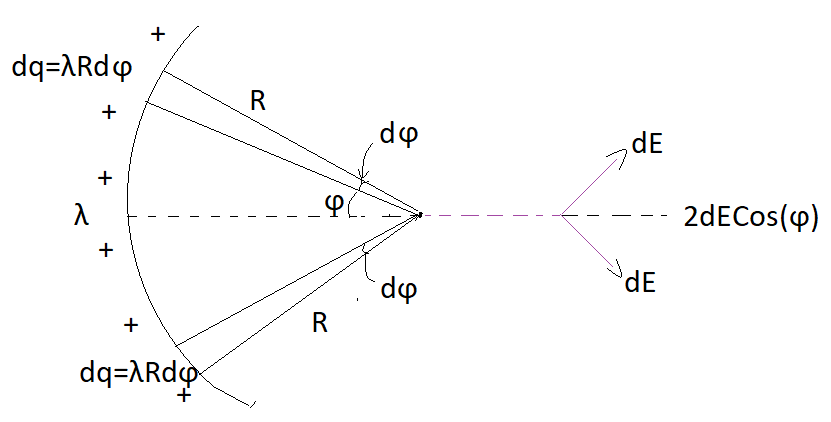
$\Rightarrow dE=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda Rd\phi }{{{R}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow dE=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}d\phi $
Now, net field due to symmetric halfs at point P will be,
$\Rightarrow dE=2dE\cos (\phi )$, now integrating this equation over 0 to $\dfrac{\theta }{2}$ ,
$\Rightarrow E=\int{dE=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\theta }{2}}{2dE\cos (\phi ).d\phi }}$
$\Rightarrow E=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\theta }{2}}{2\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}\cos (\phi ).d\phi }$
$\Rightarrow E=2\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}\left[ \sin (\phi ) \right]\begin{matrix}
\dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
0 \\
\end{matrix}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{R}\sin (\dfrac{\theta }{2})$
$\therefore $ the electric field experienced by point P due to an uniformly charged arc will be given by,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{R}\sin (\dfrac{\theta }{2})$
Note:
In the above problem we are considering a small portion of arc as a point particle and applying formula for electric field by a point particle. This is the standard procedure to calculate electric field at some point due to a uniformly charged body at some distance from it.
Formula used:
Electric field due to a point charge,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{Q}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Complete answer:
From the above diagram we can observe that both half are equal and will exerts same amount of electric field on point P so, we just need to calculate field due to one half and by doing it’s two times we can get our required field at point P
Now, by taking a small section of charge dq in small angle $d\theta $ from point P on upper half and the charge per unit length is given as $\lambda $so,
$\Rightarrow dq=\lambda Rd\theta $ and electric field due to this small portion will be dE at point P, by taking in electric field from both half into consideration and its component along x axis(y axis component will be cancelled) we have,

$\Rightarrow dE=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda Rd\phi }{{{R}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow dE=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}d\phi $
Now, net field due to symmetric halfs at point P will be,
$\Rightarrow dE=2dE\cos (\phi )$, now integrating this equation over 0 to $\dfrac{\theta }{2}$ ,
$\Rightarrow E=\int{dE=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\theta }{2}}{2dE\cos (\phi ).d\phi }}$
$\Rightarrow E=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{\theta }{2}}{2\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}\cos (\phi ).d\phi }$
$\Rightarrow E=2\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{\lambda }{R}\left[ \sin (\phi ) \right]\begin{matrix}
\dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
0 \\
\end{matrix}$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{R}\sin (\dfrac{\theta }{2})$
$\therefore $ the electric field experienced by point P due to an uniformly charged arc will be given by,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{{}^\circ }}}\dfrac{2\lambda }{R}\sin (\dfrac{\theta }{2})$
Note:
In the above problem we are considering a small portion of arc as a point particle and applying formula for electric field by a point particle. This is the standard procedure to calculate electric field at some point due to a uniformly charged body at some distance from it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




