
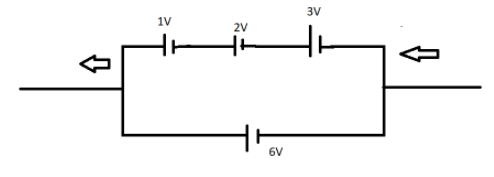
Find the emf of the circuit.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Electromotive force, emf, electrical energy per unit, which is transmitted by a power source, such as a generator or battery. The electrical charge in the generator is transferred from one form to the other as the unit operates on the electrical charge. One terminal is charged positively, the other is charged negatively. The electric power is the work carried out on an electrical charge unit or the energy produced by the electrical charge unit. Any energy source able to move electric load through a circuit is characteristic of electrical force.
Complete step by Step Solution: In electromagnetic induction, emf, the electromagnetic work that will take place at an electrical charge (electron in this instance) as it is moving around the ring, can be described around the closed loop of conductor. The scale-scale field of the electric potential is not specified because of a rotating electrical vector field for a time-varying magnetic flux that connects a circle, but an emf nevertheless acts as a virtual electrical potential around the circle.
Since the cells are connected in series, therefore,
${R_ {emf}} = 1 + 2 + 3$
${R_ {emf}} = 6V$
Resultant emf is $6V$ which is in parallel with the other battery
Hence, emf of the circuit will be $6V$
Note: The generation by a time-dependent magnetic field of a circulating electric field is electro-magnetic induction. Time-dependent magnetic fields can be produced either by shifting a magnet relative to a circuit, shifting a circuit relative to another circuit or changing an electrical current on a permanent circuit (at least one of them is expected to be holding an electrical current). The effect of modifying the electric power on the circuit itself is called auto-induction; it is known as reciprocal induction on another circuit. The electromagnetically induced emf is solely calculated for a given circuit by the rate of change of the magnetic flux by the circuit in compliance with Faraday’s induction laws. As flux connexions are modified, an emf is induced into a coil or conductor.
Complete step by Step Solution: In electromagnetic induction, emf, the electromagnetic work that will take place at an electrical charge (electron in this instance) as it is moving around the ring, can be described around the closed loop of conductor. The scale-scale field of the electric potential is not specified because of a rotating electrical vector field for a time-varying magnetic flux that connects a circle, but an emf nevertheless acts as a virtual electrical potential around the circle.
Since the cells are connected in series, therefore,
${R_ {emf}} = 1 + 2 + 3$
${R_ {emf}} = 6V$
Resultant emf is $6V$ which is in parallel with the other battery
Hence, emf of the circuit will be $6V$
Note: The generation by a time-dependent magnetic field of a circulating electric field is electro-magnetic induction. Time-dependent magnetic fields can be produced either by shifting a magnet relative to a circuit, shifting a circuit relative to another circuit or changing an electrical current on a permanent circuit (at least one of them is expected to be holding an electrical current). The effect of modifying the electric power on the circuit itself is called auto-induction; it is known as reciprocal induction on another circuit. The electromagnetically induced emf is solely calculated for a given circuit by the rate of change of the magnetic flux by the circuit in compliance with Faraday’s induction laws. As flux connexions are modified, an emf is induced into a coil or conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




