
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose foci are $\left( 4,2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,2 \right)$ with eccentricity 2.
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We first define the general equation of hyperbola and its different parts. We then equate that with the given values of foci and eccentricity. Using the values, we find out the common characteristics of the conic and also the equation of the hyperbola.
Complete step by step answer:
We define the general equation of hyperbola and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$. The difference between two foci is $2ae$.
Now for our given hyperbola foci are $\left( 4,2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,2 \right)$ with eccentricity 2. The difference between two foci are $\left| 8-4 \right|=4$ unit. So, $2ae=4\Rightarrow ae=2$.
Equating the y coordinate of the foci we get $\beta =2$.
Equating the x coordinate of the foci we get $\alpha \pm ae=4,8$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=2\]. So, $2a=2\Rightarrow a=1$.
The general formula of eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
Putting values, we get \[2=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{1}^{2}}}}\]. Solving we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{1}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 1+{{b}^{2}}={{2}^{2}}=4 \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=3 \\
\end{align}\]
From the equation $\alpha \pm ae=4,8$, we get the value of $\alpha =6$.
We now place all the values of $\alpha ,\beta ,a,b$ in $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ to find the equation.
The equation is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}}{1}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-2 \right)}^{2}}}{3}=1\Rightarrow 3{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( y-2 \right)}^{2}}=3$.
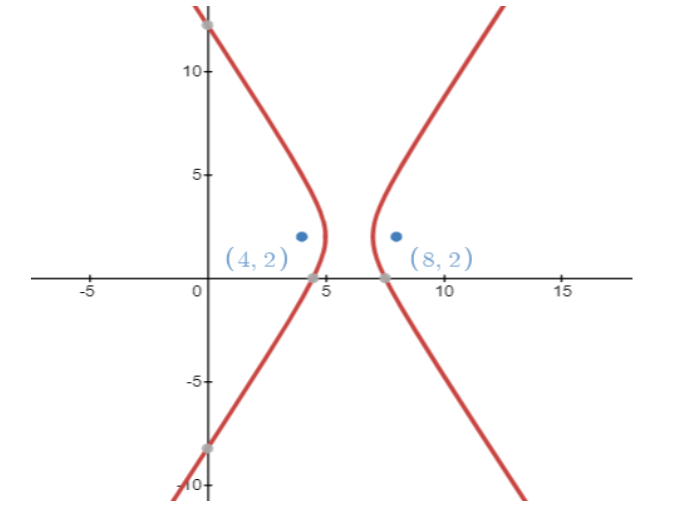
Note: We need to remember that the foci are on the axis of the hyperbola. So, they are on the same line and that’s why we found the distance of the foci as the difference of their y coordinates. When we get the square values of a and b we don’t need to solve as in the equation they are already in their square form.
Complete step by step answer:
We define the general equation of hyperbola and its different parts.
General equation of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
The centre will be $\left( \alpha ,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of vertices are $\left( \alpha \pm a,\beta \right)$. Coordinates of foci are $\left( \alpha \pm ae,\beta \right)$. Equations of the directrices are $x=\alpha \pm \dfrac{a}{e}$. The difference between two foci is $2ae$.
Now for our given hyperbola foci are $\left( 4,2 \right)$ and $\left( 8,2 \right)$ with eccentricity 2. The difference between two foci are $\left| 8-4 \right|=4$ unit. So, $2ae=4\Rightarrow ae=2$.
Equating the y coordinate of the foci we get $\beta =2$.
Equating the x coordinate of the foci we get $\alpha \pm ae=4,8$.
The eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=2\]. So, $2a=2\Rightarrow a=1$.
The general formula of eccentricity of the ellipse is \[e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}\].
Putting values, we get \[2=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{1}^{2}}}}\]. Solving we get
\[\begin{align}
& 2=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{1}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 1+{{b}^{2}}={{2}^{2}}=4 \\
& \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}=3 \\
\end{align}\]
From the equation $\alpha \pm ae=4,8$, we get the value of $\alpha =6$.
We now place all the values of $\alpha ,\beta ,a,b$ in $\dfrac{{{\left( x-\alpha \right)}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-\beta \right)}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ to find the equation.
The equation is $\dfrac{{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}}{1}-\dfrac{{{\left( y-2 \right)}^{2}}}{3}=1\Rightarrow 3{{\left( x-6 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( y-2 \right)}^{2}}=3$.

Note: We need to remember that the foci are on the axis of the hyperbola. So, they are on the same line and that’s why we found the distance of the foci as the difference of their y coordinates. When we get the square values of a and b we don’t need to solve as in the equation they are already in their square form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




