
Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of \[AB\], where \[A\] and \[B\] are the points \[(3,6)\] and \[( - 3,4)\] respectively. Also find its point of intersection with
(i) X-axis and
(ii) Y-axis.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to determine the point of intersection.A perpendicular bisector of a line segment is a line segment perpendicular to and passing through the midpoint of a given line segment. We can find the equation of the perpendicular bisector provided we have the given data regarding both the points of the line segment with the help of formula.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem,
We have to find out the equation of the perpendicular bisector of \[AB\], where \[A\] and \[B\] are the points \[(3,6)\] and \[( - 3,4)\]
Let \[X\] be the point on perpendicular bisector of \[\overline {AB} \] with coordinates \[(x,y)\]
Hence, we can conclude that \[X{A^2} = X{B^2}\]
So \[XA = XB\]
To find out the equation of perpendicular bisector we can use the following formula:
\[\sqrt {{{(x - {x_1})}^2} + {{(y - {y_1})}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(x - {x_2})}^2} + {{(y - {y_2})}^2}} \]
Comparing with the above formula,
\[A = ({x_1},{y_1}) = (3,6)\]
\[B = ({x_2},{y_2}) = ( - 3,4)\]
Substituting the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(x - 3)}^2} + {{(y - 6)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(x + 3)}^2} + {{(y - 4)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 6)^2} = {(x + 3)^2} + {(y - 4)^2}\]
Factoring using the formula \[{a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}\]and \[{a^2} + 2ab + {b^2}\],
\[ \Rightarrow x - 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 12y + 36 = {x^2} + 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 8y + 16\]
Adding and subtracting the values, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow x - 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 12y + 36 - {x^2} - 6x - 9 - {y^2} + 8y - 16 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12x + 4y - 20 = 0\]
Dividing by \[4\],
\[ \Rightarrow 3x + y - 5 = 0\]
Hence the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB is \[3x + y - 5 = 0\].
Now we can proceed to find the point of intersection:
1) On X-axis: The coordinates of any point on X-axis are of the form \[(x,0)\]. In other words, \[y\]-coordinate of every point on the X-axis is zero. So, putting \[y = 0\] in above equation,
\[ \Rightarrow 3x + 0 - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{5}{3}\]
Thus, the perpendicular bisector of AB cuts X-axis at\[(\dfrac{5}{3},0)\]
2) On the Y-Axis: The coordinates of any point on the Y-axis are of the form \[(y,0)\]. In other words, \[x\]-coordinate of every point on the Y-axis is zero. So, putting \[x = 0\] in above equation,
\[ \Rightarrow 3(0) + y - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5\]
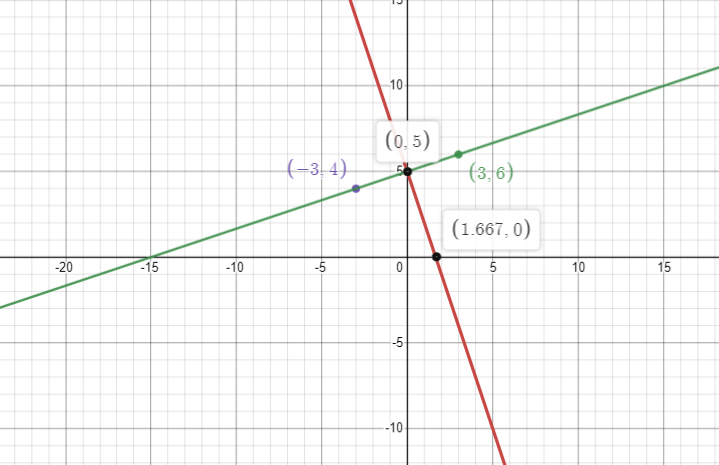
Thus, the perpendicular bisector of AB cuts Y-axis at \[(0,5)\].
The corresponding graph will be:
Note:
1) The perpendicular bisector of a line segment can be constructed using a compass by drawing circles centred at and with radius and connecting their two intersections.
2) Remember to first find the equation which should be in the standard form of the quadratic equation.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given problem,
We have to find out the equation of the perpendicular bisector of \[AB\], where \[A\] and \[B\] are the points \[(3,6)\] and \[( - 3,4)\]
Let \[X\] be the point on perpendicular bisector of \[\overline {AB} \] with coordinates \[(x,y)\]
Hence, we can conclude that \[X{A^2} = X{B^2}\]
So \[XA = XB\]
To find out the equation of perpendicular bisector we can use the following formula:
\[\sqrt {{{(x - {x_1})}^2} + {{(y - {y_1})}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(x - {x_2})}^2} + {{(y - {y_2})}^2}} \]
Comparing with the above formula,
\[A = ({x_1},{y_1}) = (3,6)\]
\[B = ({x_2},{y_2}) = ( - 3,4)\]
Substituting the values,
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{(x - 3)}^2} + {{(y - 6)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{(x + 3)}^2} + {{(y - 4)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {(x - 3)^2} + {(y - 6)^2} = {(x + 3)^2} + {(y - 4)^2}\]
Factoring using the formula \[{a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}\]and \[{a^2} + 2ab + {b^2}\],
\[ \Rightarrow x - 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 12y + 36 = {x^2} + 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 8y + 16\]
Adding and subtracting the values, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow x - 6x + 9 + {y^2} - 12y + 36 - {x^2} - 6x - 9 - {y^2} + 8y - 16 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12x + 4y - 20 = 0\]
Dividing by \[4\],
\[ \Rightarrow 3x + y - 5 = 0\]
Hence the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB is \[3x + y - 5 = 0\].
Now we can proceed to find the point of intersection:
1) On X-axis: The coordinates of any point on X-axis are of the form \[(x,0)\]. In other words, \[y\]-coordinate of every point on the X-axis is zero. So, putting \[y = 0\] in above equation,
\[ \Rightarrow 3x + 0 - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{5}{3}\]
Thus, the perpendicular bisector of AB cuts X-axis at\[(\dfrac{5}{3},0)\]
2) On the Y-Axis: The coordinates of any point on the Y-axis are of the form \[(y,0)\]. In other words, \[x\]-coordinate of every point on the Y-axis is zero. So, putting \[x = 0\] in above equation,
\[ \Rightarrow 3(0) + y - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y - 5 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5\]
Thus, the perpendicular bisector of AB cuts Y-axis at \[(0,5)\].
The corresponding graph will be:

Note:
1) The perpendicular bisector of a line segment can be constructed using a compass by drawing circles centred at and with radius and connecting their two intersections.
2) Remember to first find the equation which should be in the standard form of the quadratic equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




