
Find the left hand limit and right hand limit of the function$f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Define the function for the values of $x < 2$and$x > 2$. Compute their limits using the properties of absolute value and the fact that the limit of a constant function is the constant.
These limits will be the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Finding the left hand and right hand limits of a function$f(x)$at a point$x = a$means finding the limit of $f(x)$ at $x < a$and finding the limit of $f(x)$ at $x > a$respectively where $a$ is any real number.
The left hand limit of $f(x)$ at $x < a$ is denoted by$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x)$ if it exists.
Similarly, the right hand limit of$f(x)$ at $x > a$is denoted by $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x)$ if it exists.
Therefore, to find the left and right hand limits we need to define the value of$f(x)$ at $x > a$and at $x < a$ respectively.
In the given question, we have
$a = 2$ and $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$
Therefore, we will determine the value of $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x < 2$ and $x > 2$
Let’s recall the behaviour of the absolute value function.
For a real number $x$
If $x < 0$, then $|x| = - x$ and
if $x > 0$, then $|x| = x$
Consider the graph of the absolute value function.
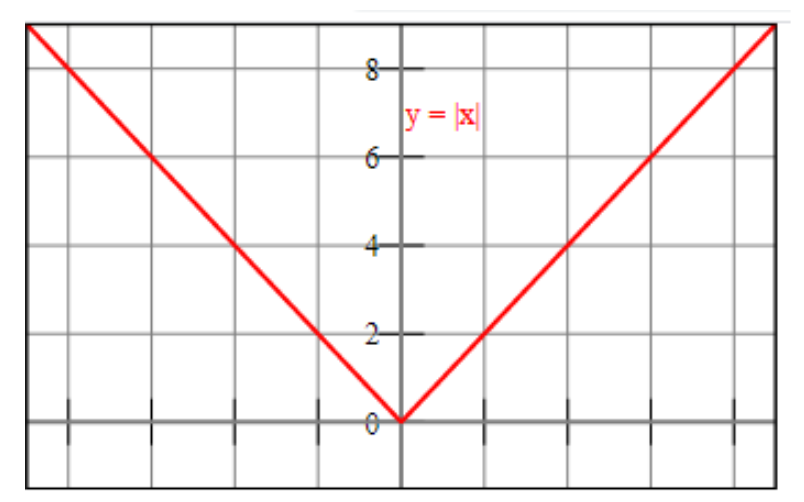
Thus, when $x < 2$,
\[
x - 2 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow |x - 2| = - (x - 2) \\
\]
Therefore, $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}} = \dfrac{{ - (x - 2)}}{{x - 2}} = - 1$
Thus, $f(x)$ is a constant function when $x < 2$
We know that the limit of a constant function is equal to the constant.
This implies that \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} ( - 1) = - 1\].
That is, the left hand limit of the given function $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$ is $ - 1$
Similarly, we need to find the right hand limit of $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$
Now, when $x > 2$
\[
x - 2 > 0 \\
\Rightarrow |x - 2| = x - 2 \\
\]
Therefore, we have $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}} = \dfrac{{x - 2}}{{x - 2}} = 1$
Below is the graph of the function$f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$
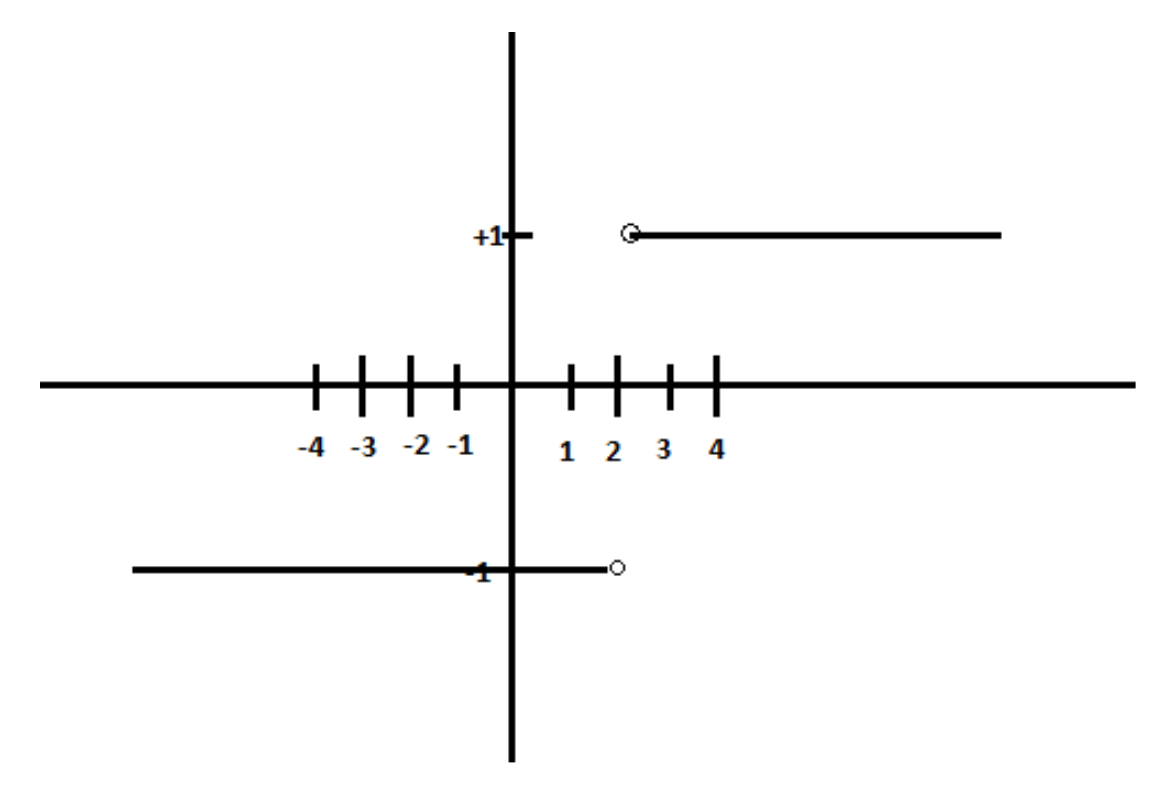
Thus, $f(x)$ is a constant function when $x > 2$ as well.
Let us compute the right hand limit of $f(x)$.
\[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} (1) = 1\].
Thus, the right hand limit of the given function is 1.
Hence the left hand and right hand limits of the function $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$ are $ - 1$ and $1$ respectively.
Note: It is advisable to draw a graph of a function to understand the nature of the function for which the left hand and right hand limits are to be calculated. Functions are best understood with the help of graphs.
These limits will be the required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Finding the left hand and right hand limits of a function$f(x)$at a point$x = a$means finding the limit of $f(x)$ at $x < a$and finding the limit of $f(x)$ at $x > a$respectively where $a$ is any real number.
The left hand limit of $f(x)$ at $x < a$ is denoted by$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x)$ if it exists.
Similarly, the right hand limit of$f(x)$ at $x > a$is denoted by $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x)$ if it exists.
Therefore, to find the left and right hand limits we need to define the value of$f(x)$ at $x > a$and at $x < a$ respectively.
In the given question, we have
$a = 2$ and $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$
Therefore, we will determine the value of $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x < 2$ and $x > 2$
Let’s recall the behaviour of the absolute value function.
For a real number $x$
If $x < 0$, then $|x| = - x$ and
if $x > 0$, then $|x| = x$
Consider the graph of the absolute value function.

Thus, when $x < 2$,
\[
x - 2 < 0 \\
\Rightarrow |x - 2| = - (x - 2) \\
\]
Therefore, $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}} = \dfrac{{ - (x - 2)}}{{x - 2}} = - 1$
Thus, $f(x)$ is a constant function when $x < 2$
We know that the limit of a constant function is equal to the constant.
This implies that \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} ( - 1) = - 1\].
That is, the left hand limit of the given function $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$ is $ - 1$
Similarly, we need to find the right hand limit of $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$
Now, when $x > 2$
\[
x - 2 > 0 \\
\Rightarrow |x - 2| = x - 2 \\
\]
Therefore, we have $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}} = \dfrac{{x - 2}}{{x - 2}} = 1$
Below is the graph of the function$f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$

Thus, $f(x)$ is a constant function when $x > 2$ as well.
Let us compute the right hand limit of $f(x)$.
\[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {2^ - }} (1) = 1\].
Thus, the right hand limit of the given function is 1.
Hence the left hand and right hand limits of the function $f(x) = \dfrac{{|x - 2|}}{{x - 2}}$ at $x = 2$ are $ - 1$ and $1$ respectively.
Note: It is advisable to draw a graph of a function to understand the nature of the function for which the left hand and right hand limits are to be calculated. Functions are best understood with the help of graphs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




