
How do you find the missing side of the right triangle with legs: $a = 5$, $b = 12$?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: Here, we are given the dimensions of two legs of the right angle triangle. Therefore, it is obvious that the missing side is the hypotenuse which is the longest sie of the triangle opposite to the right angle. For finding our answer, we will use the Pythagoras law.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the legs of the right angle triangle as $a = 5$ and $b = 12$.
Let the missing side which is hypotenuse is $c$.
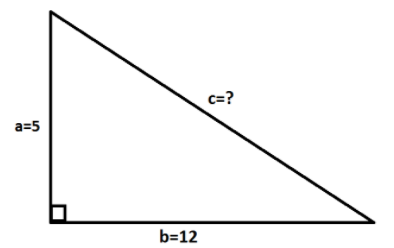
We know that the Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
Therefore, if we apply the Pythagoras theorem in our case, we get
${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$
We are given that $a = 5$ and $b = 12$.
$
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {5^2} + {12^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = 25 + 144 \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = 169 \\
\Rightarrow c = 13 \\
$
Thus, the value of the missing side in the right angle triangle is \[13\].
Note: We have used the Pythagoras theorem to solve this question. There is another theorem which is called the inverse of Pythagoras theorem. The inverse of the Pythagorean Theorem is: If the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. Also, The Pythagorean Theorem is useful for two-dimensional navigation. We can use it and two lengths to find the shortest distance, the distances north and west will be the two legs of the triangle, and the shortest line connecting them will be the diagonal.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the legs of the right angle triangle as $a = 5$ and $b = 12$.
Let the missing side which is hypotenuse is $c$.

We know that the Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
Therefore, if we apply the Pythagoras theorem in our case, we get
${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$
We are given that $a = 5$ and $b = 12$.
$
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {5^2} + {12^2} \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = 25 + 144 \\
\Rightarrow {c^2} = 169 \\
\Rightarrow c = 13 \\
$
Thus, the value of the missing side in the right angle triangle is \[13\].
Note: We have used the Pythagoras theorem to solve this question. There is another theorem which is called the inverse of Pythagoras theorem. The inverse of the Pythagorean Theorem is: If the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. Also, The Pythagorean Theorem is useful for two-dimensional navigation. We can use it and two lengths to find the shortest distance, the distances north and west will be the two legs of the triangle, and the shortest line connecting them will be the diagonal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




