
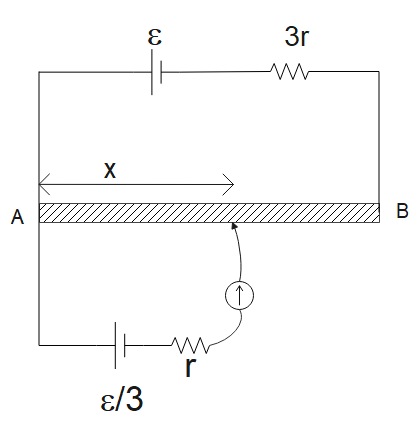
Find the position of Jockey from point A so that there is no deflection in Galvanometer. Length of wire AB is L and its resistance is 12r.
a.) $\dfrac{5L}{12}$ from point “A”
b.) $\dfrac{5L}{6}$ from point “A”
c.) $\dfrac{5L}{12}$ from point “B”
d.) $\dfrac{7L}{12}$ from point “A”

Answer
542.7k+ views
Hint: A galvanometer is a device that detects electrical current and also measures them. Galvanometers have a needle which is basically in the center position, when a current passes through the galvanometer the needle gets deflected either in left or right position, and the top point of needle shows the magnitude of current. When the needle is in center position this means no potential difference is there at that point
Complete answer:
We have been given that the length of wire is “L”
Resistance of wire is “12r”
The current through the wire can be given as
$I=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{12r+3r}$
$I=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{15r}$
Potential drop across the wire can be given as
$\Delta V=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{15r}\times 12r$
$\Delta V=\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5}$
Now potential gradient or voltage per unit length can be given as
$\dfrac{V}{L}=\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}$
Now potential in a wire of length “x” can be given as $\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}\times x$
Now if we want that there should be no deflection in the galvanometer then for this condition the below equation must be satisfied
$\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}\times x=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{3}$
Therefore $x=\dfrac{5L}{12}$
So, we can say that the value of “x” should be $\dfrac{5L}{12}$ from point A
Hence, we can say that option (A) is the correct answer .
Note:
The length that we have found in the question is the length where the galvanometer shows no deflection. We can find this length from any point of reference either from point A and from point B, but the reference point should always be taken from a point where the galvanometer wire is connected. If we take it in some other direction then we might get the length in negative or it can be possible that we get a wrong answer.
Complete answer:
We have been given that the length of wire is “L”
Resistance of wire is “12r”
The current through the wire can be given as
$I=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{12r+3r}$
$I=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{15r}$
Potential drop across the wire can be given as
$\Delta V=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{15r}\times 12r$
$\Delta V=\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5}$
Now potential gradient or voltage per unit length can be given as
$\dfrac{V}{L}=\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}$
Now potential in a wire of length “x” can be given as $\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}\times x$
Now if we want that there should be no deflection in the galvanometer then for this condition the below equation must be satisfied
$\dfrac{4\varepsilon }{5L}\times x=\dfrac{\varepsilon }{3}$
Therefore $x=\dfrac{5L}{12}$
So, we can say that the value of “x” should be $\dfrac{5L}{12}$ from point A
Hence, we can say that option (A) is the correct answer .
Note:
The length that we have found in the question is the length where the galvanometer shows no deflection. We can find this length from any point of reference either from point A and from point B, but the reference point should always be taken from a point where the galvanometer wire is connected. If we take it in some other direction then we might get the length in negative or it can be possible that we get a wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




