
How do you find the volume of a rotated region bounded by \[y=\sqrt{x},y=3\], the \[y\] - axis about the \[y\] - axis?
Answer
553.5k+ views
Hint: From the question given, we have been asked to find the volume of a rotated region bounded by \[y=\sqrt{x},y=3\], the \[y\] - axis about the \[y\] - axis. To solve the given question, we have to draw the pictorial representation that is the graph for the given question. By using that we can solve the question given.
Complete step by step answer:
Pictorial representation for the given question is shown below:
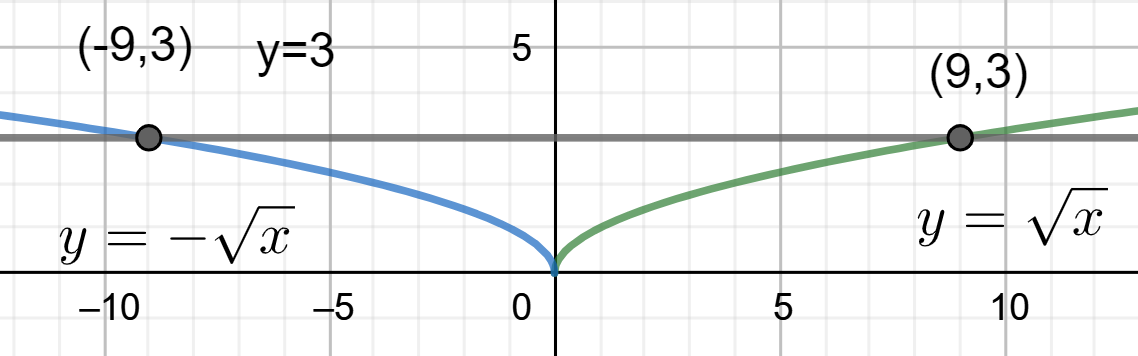
By using the above graph, we have to find the volume bounded by the region.
We know that, circular cross sections of the bounded region have an area \[\pi {{x}^{2}}\]
Or, since \[x={{y}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A\left( y \right)=\pi {{y}^{4}}\]
For a thin enough slice, \[\Delta y\], the volume of the slice approaches \[\Rightarrow S\left( y \right)=\Delta y.A\left( y \right)\]
And the volume of the bounded region will be \[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\pi {{y}^{4}}dy}\]
Therefore, we have to integrate the above equation to get the volume of the bounded region.
By integrating and simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\pi \int\limits_{0}^{3}{{{y}^{4}}dy}\]
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\pi \dfrac{{{y}^{5}}}{5}|_{0}^{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=48.6\pi \]
Therefore, we got the volume of the bounded region.
Note: We should be very careful while drawing the graph that is the pictorial representation of the given question. Also, we should be well aware of the integration concept. Also, we should be very careful while doing the calculation of the integration part of the above problem. Also, we should be well known about the limits that have to be taken to the integration. We should be very careful while applying the limits for the integration. Also, we should use the graph to find the limits for the integration. Similarly we can use integration and differentiation to find the volume or area of any curves which is not specified before.
Complete step by step answer:
Pictorial representation for the given question is shown below:

By using the above graph, we have to find the volume bounded by the region.
We know that, circular cross sections of the bounded region have an area \[\pi {{x}^{2}}\]
Or, since \[x={{y}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A\left( y \right)=\pi {{y}^{4}}\]
For a thin enough slice, \[\Delta y\], the volume of the slice approaches \[\Rightarrow S\left( y \right)=\Delta y.A\left( y \right)\]
And the volume of the bounded region will be \[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\pi {{y}^{4}}dy}\]
Therefore, we have to integrate the above equation to get the volume of the bounded region.
By integrating and simplifying the above equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\pi \int\limits_{0}^{3}{{{y}^{4}}dy}\]
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=\pi \dfrac{{{y}^{5}}}{5}|_{0}^{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow V\left( y \right)=48.6\pi \]
Therefore, we got the volume of the bounded region.
Note: We should be very careful while drawing the graph that is the pictorial representation of the given question. Also, we should be well aware of the integration concept. Also, we should be very careful while doing the calculation of the integration part of the above problem. Also, we should be well known about the limits that have to be taken to the integration. We should be very careful while applying the limits for the integration. Also, we should use the graph to find the limits for the integration. Similarly we can use integration and differentiation to find the volume or area of any curves which is not specified before.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




