
Flame cells are associated with -
(a)Respiration
(b)Excretion
(c)Nutrition
(d)Digestion
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The flame cells are to a flatworm are what a nephron is to a human being. They are associated with the elimination of waste from the body. They are named so because one of the parts of the cell looks like a candle flame.
Complete answer:
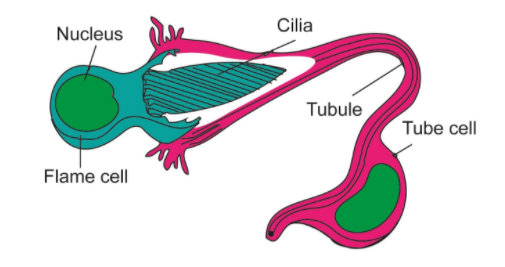
- Flame cells are found in freshwater invertebrates like flatworms (Platyhelminthes), rotifers (Rotifera), and ribbon worms (Nemertea).
- They function as kidneys of the organism. Bundles of flame cells are known as protonephridia.
- The cell contains a nucleated cell body with a cup-shaped projection. The inner surface of the projection is covered by flagella.
- The cup is attached to a tube cell, whose inner surface is coated in cilia, which aid in liquid movement through the tube cell. This tube opens into a nephropore or an excretory bladder.
- Tube cells also contain microvilli that may help in the reabsorption of some ions.
Additional Information: - Platyhelminthes are flattened, soft-bodied, and invertebrate organisms and are either free-living or parasitic. Most of them possess a blind gut, i.e. they have a mouth but no anus.
- Flame cells also maintain the organism’s osmotic and ionic balance.
- The name is derived from the beating of the flagella, which resembles a flame.
- During excretion, molecules enter the tube cells through the gap between the flame cell and tube cell.
So, the correct answer is ‘excretion’.
Note: - Other examples of units responsible for excretion include nephrons in humans, nephridia in annelids, malpighian tubules in arthropods, and solenocytes in cephalochordates.
- Flame cells extract water and waste materials from the mesenchyme, the connective tissue in these organisms.
- Bundles of flame cells are known as protonephridia.
Complete answer:
- Flame cells are found in freshwater invertebrates like flatworms (Platyhelminthes), rotifers (Rotifera), and ribbon worms (Nemertea).
- They function as kidneys of the organism. Bundles of flame cells are known as protonephridia.
- The cell contains a nucleated cell body with a cup-shaped projection. The inner surface of the projection is covered by flagella.
- The cup is attached to a tube cell, whose inner surface is coated in cilia, which aid in liquid movement through the tube cell. This tube opens into a nephropore or an excretory bladder.
- Tube cells also contain microvilli that may help in the reabsorption of some ions.
Additional Information: - Platyhelminthes are flattened, soft-bodied, and invertebrate organisms and are either free-living or parasitic. Most of them possess a blind gut, i.e. they have a mouth but no anus.
- Flame cells also maintain the organism’s osmotic and ionic balance.
- The name is derived from the beating of the flagella, which resembles a flame.
- During excretion, molecules enter the tube cells through the gap between the flame cell and tube cell.

So, the correct answer is ‘excretion’.
Note: - Other examples of units responsible for excretion include nephrons in humans, nephridia in annelids, malpighian tubules in arthropods, and solenocytes in cephalochordates.
- Flame cells extract water and waste materials from the mesenchyme, the connective tissue in these organisms.
- Bundles of flame cells are known as protonephridia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




