
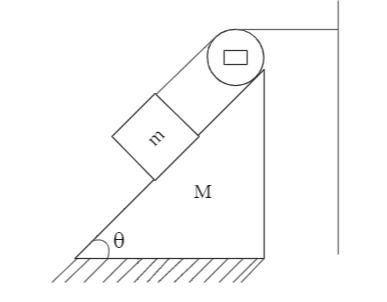
For the arrangement shown in the figure, when the system is released, find the acceleration of the wedge. Pulley and string are ideal and friction is absent.

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint
When the pulley is released, the objects bound to it become free to move. This motion can be determined by applying Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, after analysing the forces using a free-body diagram.
Complete step by step answer
We are provided with a block on the top of a wedge and are asked to find the acceleration of the wedge. We draw the free-body diagram to better understand the forces acting on the block and the wedge:

Let us assume the following variables:
Acceleration of the block is ${a_m}$
Acceleration of the wedge is ${a_M}$
Tension due to the pulley on the block T
Normal reaction on the block due to the wedge N
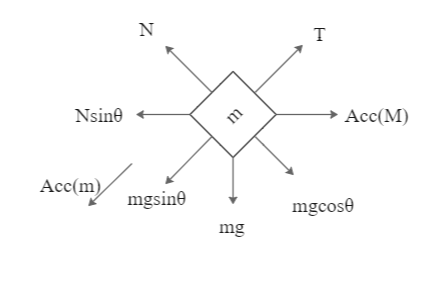
We can see that the wedge will move towards right when the system is released, and the block will slip down the wedge. As the length of the thread remains constant, the distance and hence the acceleration of the block on the wedge will be equal to the acceleration of the wedge on the floor. This implies:
$\Rightarrow {a_m} = {a_M} = a$ … [Eq. 1]
Now, we balance the forces acting on the block as:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - T = m{a_m} - m{a_M}\cos \theta $ [As this is the resultant acceleration that of the block]
This is equivalent to:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - T = ma(1 - \cos \theta )$ [From Eq. 1]
Solving for T, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - ma(1 - \cos \theta ) = T$[Eq. 2]
Also, when balancing the forces vertically, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\cos \theta - N = ma\sin \theta $
Solving for N, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\cos \theta - ma\sin \theta = N$ [Eq. 3]
Now, we balance the forces on the wedge to get:
$\Rightarrow T - T\cos \theta + N\sin \theta = Ma$ [As the normal reaction still acts on the wedge]
$\Rightarrow T(1 - \cos \theta ) + N\sin \theta = Ma$
Putting the values in this equation from Eq. 2 and Eq. 3, we get:
$\Rightarrow [mg\sin \theta - ma(1 - \cos \theta )](1 - \cos \theta ) + [mg\cos \theta - ma\sin \theta ]\sin \theta = Ma$
Opening the brackets and solving for a gives us:
$\Rightarrow Ma = mg\sin \theta - mg\sin \theta \cos \theta - ma{(1 - \cos \theta )^2} + mg\sin \theta \cos \theta - ma{\sin ^2}\theta $
We cancel the equal values to get:
$\Rightarrow Ma = mg\sin \theta - ma{(1 - \cos \theta )^2} - ma{\sin ^2}\theta $
We bring the same variables on one side to get and open the brackets to get:
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma(1 + {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta ) + ma{\sin ^2}\theta = mg\sin \theta $
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma - 2ma\cos \theta + ma({\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta ) = mg\sin \theta $
From the identity${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$, we get:
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma - 2ma\cos \theta + ma = mg\sin \theta $
$\Rightarrow Ma + 2ma(1 - \cos \theta ) = mg\sin \theta $
Solving for a gives us:
$\Rightarrow a[M + 2m(1 - \cos \theta )] = mg\sin \theta $
Hence, the acceleration of the wedge is:
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta }}{{[M + 2m(1 - \cos \theta )]}}$
Note
Drawing a free-body diagram before attempting to solve a Mechanics problem like this is a crucial step because the FBD helps us determine all the forces acting on a body with their directions. It is also important to take in account the inclined plane, as this causes the components of the angle to be the actual participants in the force acting on the object.
When the pulley is released, the objects bound to it become free to move. This motion can be determined by applying Newton’s 2nd Law of motion, after analysing the forces using a free-body diagram.
Complete step by step answer
We are provided with a block on the top of a wedge and are asked to find the acceleration of the wedge. We draw the free-body diagram to better understand the forces acting on the block and the wedge:

Let us assume the following variables:
Acceleration of the block is ${a_m}$
Acceleration of the wedge is ${a_M}$
Tension due to the pulley on the block T
Normal reaction on the block due to the wedge N

We can see that the wedge will move towards right when the system is released, and the block will slip down the wedge. As the length of the thread remains constant, the distance and hence the acceleration of the block on the wedge will be equal to the acceleration of the wedge on the floor. This implies:
$\Rightarrow {a_m} = {a_M} = a$ … [Eq. 1]
Now, we balance the forces acting on the block as:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - T = m{a_m} - m{a_M}\cos \theta $ [As this is the resultant acceleration that of the block]
This is equivalent to:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - T = ma(1 - \cos \theta )$ [From Eq. 1]
Solving for T, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\sin \theta - ma(1 - \cos \theta ) = T$[Eq. 2]
Also, when balancing the forces vertically, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\cos \theta - N = ma\sin \theta $
Solving for N, we get:
$\Rightarrow mg\cos \theta - ma\sin \theta = N$ [Eq. 3]
Now, we balance the forces on the wedge to get:
$\Rightarrow T - T\cos \theta + N\sin \theta = Ma$ [As the normal reaction still acts on the wedge]
$\Rightarrow T(1 - \cos \theta ) + N\sin \theta = Ma$
Putting the values in this equation from Eq. 2 and Eq. 3, we get:
$\Rightarrow [mg\sin \theta - ma(1 - \cos \theta )](1 - \cos \theta ) + [mg\cos \theta - ma\sin \theta ]\sin \theta = Ma$
Opening the brackets and solving for a gives us:
$\Rightarrow Ma = mg\sin \theta - mg\sin \theta \cos \theta - ma{(1 - \cos \theta )^2} + mg\sin \theta \cos \theta - ma{\sin ^2}\theta $
We cancel the equal values to get:
$\Rightarrow Ma = mg\sin \theta - ma{(1 - \cos \theta )^2} - ma{\sin ^2}\theta $
We bring the same variables on one side to get and open the brackets to get:
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma(1 + {\cos ^2}\theta - 2\cos \theta ) + ma{\sin ^2}\theta = mg\sin \theta $
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma - 2ma\cos \theta + ma({\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta ) = mg\sin \theta $
From the identity${\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1$, we get:
$\Rightarrow Ma + ma - 2ma\cos \theta + ma = mg\sin \theta $
$\Rightarrow Ma + 2ma(1 - \cos \theta ) = mg\sin \theta $
Solving for a gives us:
$\Rightarrow a[M + 2m(1 - \cos \theta )] = mg\sin \theta $
Hence, the acceleration of the wedge is:
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta }}{{[M + 2m(1 - \cos \theta )]}}$
Note
Drawing a free-body diagram before attempting to solve a Mechanics problem like this is a crucial step because the FBD helps us determine all the forces acting on a body with their directions. It is also important to take in account the inclined plane, as this causes the components of the angle to be the actual participants in the force acting on the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




