
For the complex $\left[ Fe{{\left( CO \right)}_{5}} \right],$ write the hybridization, magnetic character and spin of the complex. (Atomic number: \[Fe=26\] ).
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: We know that, the Hybridization is the concept in which atomic orbitals combine to make a new hybridized orbital which successively influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. We know that the electrons which are present at the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons and the valency of an electron is that the number of electrons during which atom accepts or donate to make a bond.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we find the oxidation state of iron in the complex; we know the oxidation state of carbon monoxide is zero. So the oxidation state of iron in the complex is zero. The outermost electronic configuration of iron is $3{{d}^{3}}4{{s}^{2}}.$ Since carbon monoxide is a strong ligand it pairs up the electrons in the d orbitals and the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}d.$ The below given image clearly shows how the hybridisation takes place in this molecule as,
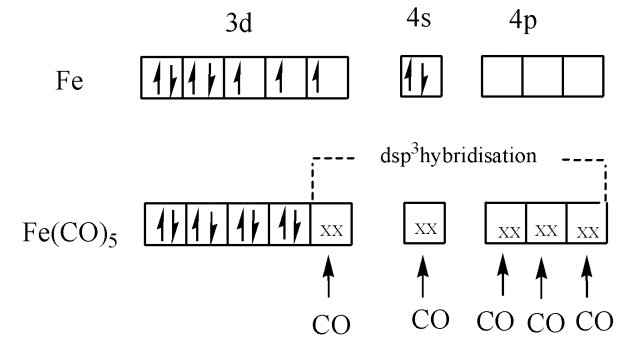
$s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization includes the blending of $3d$ orbitals and $1d$ orbital to frame five $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridized orbitals of equivalent energy. They have trigonal bipyramidal geometry. We can draw the structure of $\left[ Fe{{\left( CO \right)}_{5}} \right]$ as,
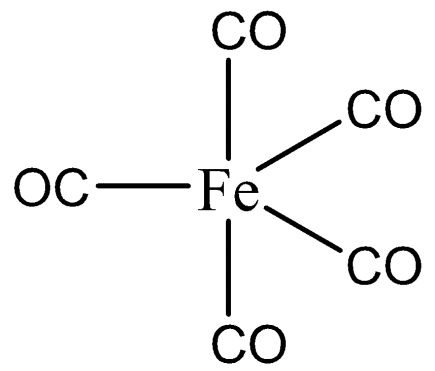
The combination of s, p and d orbital forms three-sided bipyramidal symmetry. Three crossover orbitals lie in the level plane slanted at a point of ${{120}^{0}}$ to one another known as the central orbitals. The leftover two orbitals lie in the vertical plane at $90$ degrees plane of the tropical orbitals known as pivotal orbitals.
Therefore, Hybridisation : $ds{{p}^{3}}$; Magnetic character : Diamagnetic and Spin of the complex : Low spin complex or inner orbital complex.
Note: We have to remember that the spin matching energy alludes to the energy related with combined electrons sharing one orbital and its impact on the particles encompassing it. Electron blending deciding the course of turn relies upon a few laws established by physicists throughout the long term, for example, Hund's law, the Aufbau’s guideline, and Pauli's rejection rule. An outline of the various sorts laws related with the electron pairing principles.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we find the oxidation state of iron in the complex; we know the oxidation state of carbon monoxide is zero. So the oxidation state of iron in the complex is zero. The outermost electronic configuration of iron is $3{{d}^{3}}4{{s}^{2}}.$ Since carbon monoxide is a strong ligand it pairs up the electrons in the d orbitals and the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}d.$ The below given image clearly shows how the hybridisation takes place in this molecule as,

$s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization includes the blending of $3d$ orbitals and $1d$ orbital to frame five $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridized orbitals of equivalent energy. They have trigonal bipyramidal geometry. We can draw the structure of $\left[ Fe{{\left( CO \right)}_{5}} \right]$ as,

The combination of s, p and d orbital forms three-sided bipyramidal symmetry. Three crossover orbitals lie in the level plane slanted at a point of ${{120}^{0}}$ to one another known as the central orbitals. The leftover two orbitals lie in the vertical plane at $90$ degrees plane of the tropical orbitals known as pivotal orbitals.
Therefore, Hybridisation : $ds{{p}^{3}}$; Magnetic character : Diamagnetic and Spin of the complex : Low spin complex or inner orbital complex.
Note: We have to remember that the spin matching energy alludes to the energy related with combined electrons sharing one orbital and its impact on the particles encompassing it. Electron blending deciding the course of turn relies upon a few laws established by physicists throughout the long term, for example, Hund's law, the Aufbau’s guideline, and Pauli's rejection rule. An outline of the various sorts laws related with the electron pairing principles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




