
For the given reaction,
\[2PbO + C \to Pb + C{O_2}\] name the oxidized substance, reduced substance, reducing agent, and oxidizing agent in this reaction.
Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: For finding the oxidized substance, reduced substance, reducing agent and oxidizing agent in the above reaction first calculate the oxidation states of lead and carbon in the reaction. Observe the change in the oxidation states of lead and carbon in both the reactant side and the product side.
Complete answer:
The above reaction is a redox reaction. We have to find out the oxidized substance, reduced substance, reducing agent, and oxidizing agent in this reaction. For this let us see how the oxidation states of the compounds change during the reaction.
The reaction given is:
\[2\mathop {Pb}\limits^{ + 2} \mathop O\limits^{ - 2} + \mathop C\limits^0 \to \mathop {Pb}\limits^0 + \mathop C\limits^{ + 4} \mathop {{O_2}}\limits^{ - 2} \]
So we can see in the above reaction that there is change in the oxidation state of lead from $ + 2$ to $0$ and carbon changes from $0$ to $ + 4$. The oxidation and reduction is taking place in the following manner.
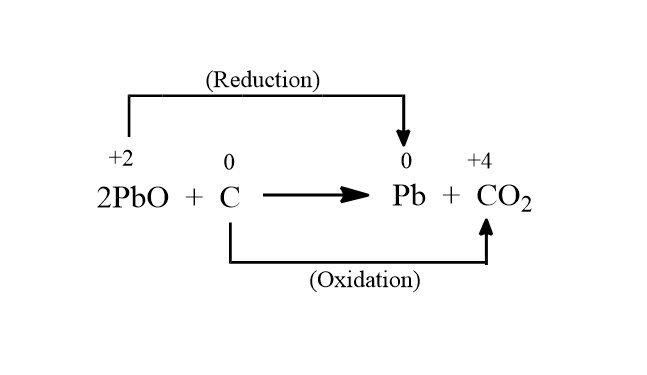
As we can see in the above image Lead oxide is undergoing reduction and changing to lead whereas carbon is undergoing oxidation and changing to carbon dioxide. So by this, we can say that lead is a reduced substance, carbon dioxide is an oxidized substance. Thus lead oxide acts as an oxidizing agent as it is oxidizing carbon to carbon dioxide and itself it is getting reduced. And carbon acts as a reducing agent because it is reducing the lead oxide to lead and it is getting oxidized.
Note:
The above reaction is a thermodynamic reaction taking place in a blast furnace. The reaction takes place at a high temperature of ${100^0}C$. This is an exothermic reaction. Once the reaction starts, the temperature is ${100^0}C$, but as the reaction continues the temperature of the furnace soon rises to about ${1200^0}C$ and the reduction of lead oxide takes place. And for this reaction, Gibbs free energy value is also negative.
Complete answer:
The above reaction is a redox reaction. We have to find out the oxidized substance, reduced substance, reducing agent, and oxidizing agent in this reaction. For this let us see how the oxidation states of the compounds change during the reaction.
The reaction given is:
\[2\mathop {Pb}\limits^{ + 2} \mathop O\limits^{ - 2} + \mathop C\limits^0 \to \mathop {Pb}\limits^0 + \mathop C\limits^{ + 4} \mathop {{O_2}}\limits^{ - 2} \]
So we can see in the above reaction that there is change in the oxidation state of lead from $ + 2$ to $0$ and carbon changes from $0$ to $ + 4$. The oxidation and reduction is taking place in the following manner.

As we can see in the above image Lead oxide is undergoing reduction and changing to lead whereas carbon is undergoing oxidation and changing to carbon dioxide. So by this, we can say that lead is a reduced substance, carbon dioxide is an oxidized substance. Thus lead oxide acts as an oxidizing agent as it is oxidizing carbon to carbon dioxide and itself it is getting reduced. And carbon acts as a reducing agent because it is reducing the lead oxide to lead and it is getting oxidized.
Note:
The above reaction is a thermodynamic reaction taking place in a blast furnace. The reaction takes place at a high temperature of ${100^0}C$. This is an exothermic reaction. Once the reaction starts, the temperature is ${100^0}C$, but as the reaction continues the temperature of the furnace soon rises to about ${1200^0}C$ and the reduction of lead oxide takes place. And for this reaction, Gibbs free energy value is also negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




