
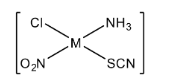
For the square planar compound. How many isomers are possible?
A.$12$
B.$16$
C.$8$
D.$4$

Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: In the square planar compound of type $[M(a)(b)(c)(d)]$ as the name suggests the geometry of the compound is such that all the four atoms are positioned at the corners of the square on the same plane as the central metal atom. Isomers of the compound are compounds with similar formulas but different structures. The type of ligand plays a vital role in complex compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will understand the basics of a coordination compound. Coordination compounds are the compound that possesses multiple metal centers which are surrounded or bounded by ligands. Now in the question, we have given the square planar compound. So here we will consider a general form of the square planar compound as $[Mabcd]$. Here, $M$ is the central metal atom and $a,b,c,d$ are the ligands. In coordination chemistry, ligands are considered as ions or molecules that bind the central metal atom to form a coordination complex. We have the square planar compound as $[M(Cl)(N{H_3})(N{O_2})(SCN)]$. Now we will try to form the maximum number of isomers for the given square planar complex.
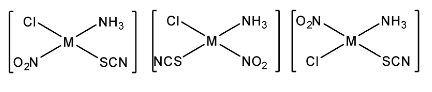
The above are three possible isomers that are formed by changing the positions of unidentate ligands $N{H_3}$ and $Cl$. But $SC{N^ - }$and $N{O_2}^ - $ are ambidentate ligands. Therefore, $SC{N^ - }$ can connect through $S\& N$ and $N{O_2}^ - $can connect through $N$ and $O$. So, similarly, with these connections nine more isomers are possible. Hence, the total number of possible isomers for the given square planar compound is $3 + 9 = 12$.
Therefore, the correct option is (A).
Note: The total number of isomers possible for the square planar complex $[Mabcd]$ is $3$. But due to the presence of Ambidentate ligands which can bind to the central atom with two different atoms which results in more number of possible isomers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will understand the basics of a coordination compound. Coordination compounds are the compound that possesses multiple metal centers which are surrounded or bounded by ligands. Now in the question, we have given the square planar compound. So here we will consider a general form of the square planar compound as $[Mabcd]$. Here, $M$ is the central metal atom and $a,b,c,d$ are the ligands. In coordination chemistry, ligands are considered as ions or molecules that bind the central metal atom to form a coordination complex. We have the square planar compound as $[M(Cl)(N{H_3})(N{O_2})(SCN)]$. Now we will try to form the maximum number of isomers for the given square planar complex.

The above are three possible isomers that are formed by changing the positions of unidentate ligands $N{H_3}$ and $Cl$. But $SC{N^ - }$and $N{O_2}^ - $ are ambidentate ligands. Therefore, $SC{N^ - }$ can connect through $S\& N$ and $N{O_2}^ - $can connect through $N$ and $O$. So, similarly, with these connections nine more isomers are possible. Hence, the total number of possible isomers for the given square planar compound is $3 + 9 = 12$.
Therefore, the correct option is (A).
Note: The total number of isomers possible for the square planar complex $[Mabcd]$ is $3$. But due to the presence of Ambidentate ligands which can bind to the central atom with two different atoms which results in more number of possible isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




