
Formaldehyde [HCHO] undergoes Cannizzaro reaction: Give reason.
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism gives the method to get one molecule of alcohol and one molecule of carboxylic acid from two molecules of a given aldehyde. The reaction is executed by a nucleophilic acyl substitution on one aldehyde where the leaving group attacks another aldehyde.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Cannizzaro reaction is a chemical reaction which is named after Stanislao Cannizzaro and it involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol. In 1853, he succeeded in obtaining benzyl alcohol and potassium benzoate from benzaldehyde.
The Cannizzaro reaction is basically a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of an aldehyde lacking a hydrogen atom in the alpha position or an alpha-hydrogen. For example, formaldehyde (HCHO) has no alpha hydrogen, so it can undergo Cannizzaro reaction. But acetaldehyde \[(C{H_3}CHO)\] has an alpha hydrogen, so it does not undergo this reaction.
$2HCHO\xrightarrow{{NaOH}}HCO{O^ - }N{A^ + } + C{H_3}OH$
One molecule of aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol, while a second one is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Let us look at the mechanism clearly.
STEP 1: The reaction initiated by the nucleophilic attack of a hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of a formaldehyde molecule by giving a hydrate anion, which can be further deprotonated in a strongly alkaline medium to give a dianion. Here, the hydroxide behaves as a base.
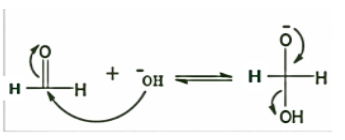
STEP 2: Now a hydride anion is transferred either from the dianionic species to the carbonyl carbon of another formaldehyde molecule. The strong electron donating effect of \[{O^ - }\] groups facilitates the hydride transfer and the reaction goes on. That is why, it is the rate determining step of the reaction.
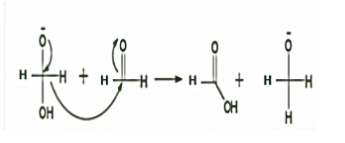
STEP 3: Here, one molecule is oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other one got reduced to an alcohol. It indicates that hydrogen is transferred from the second formaldehyde molecule. The overall order of the reaction can be either 3 or 4. The reaction occurs very slowly when electron-donating groups are present but occurs at faster rates when electron withdrawing groups are present.
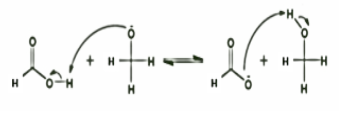
Note:The applicability of Cannizzaro reaction in organic synthesis is limited as the yield is not more than \[50\% \] for either acid or alcohol formed. In case of aldehydes that do have \[\alpha \] -hydrogens, the aldol condensation reaction takes place preferentially. When a mixture of formaldehyde and a non-enolizable aldehyde reacts with a strong base, the latter is reduced to alcohol while formaldehyde is oxidized to formic acid. This is known as the cross Cannizzaro reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Cannizzaro reaction is a chemical reaction which is named after Stanislao Cannizzaro and it involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol. In 1853, he succeeded in obtaining benzyl alcohol and potassium benzoate from benzaldehyde.
The Cannizzaro reaction is basically a chemical reaction which involves the base-induced disproportionation of an aldehyde lacking a hydrogen atom in the alpha position or an alpha-hydrogen. For example, formaldehyde (HCHO) has no alpha hydrogen, so it can undergo Cannizzaro reaction. But acetaldehyde \[(C{H_3}CHO)\] has an alpha hydrogen, so it does not undergo this reaction.
$2HCHO\xrightarrow{{NaOH}}HCO{O^ - }N{A^ + } + C{H_3}OH$
One molecule of aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol, while a second one is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Let us look at the mechanism clearly.
STEP 1: The reaction initiated by the nucleophilic attack of a hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon of a formaldehyde molecule by giving a hydrate anion, which can be further deprotonated in a strongly alkaline medium to give a dianion. Here, the hydroxide behaves as a base.

STEP 2: Now a hydride anion is transferred either from the dianionic species to the carbonyl carbon of another formaldehyde molecule. The strong electron donating effect of \[{O^ - }\] groups facilitates the hydride transfer and the reaction goes on. That is why, it is the rate determining step of the reaction.

STEP 3: Here, one molecule is oxidized to carboxylic acid and the other one got reduced to an alcohol. It indicates that hydrogen is transferred from the second formaldehyde molecule. The overall order of the reaction can be either 3 or 4. The reaction occurs very slowly when electron-donating groups are present but occurs at faster rates when electron withdrawing groups are present.

Note:The applicability of Cannizzaro reaction in organic synthesis is limited as the yield is not more than \[50\% \] for either acid or alcohol formed. In case of aldehydes that do have \[\alpha \] -hydrogens, the aldol condensation reaction takes place preferentially. When a mixture of formaldehyde and a non-enolizable aldehyde reacts with a strong base, the latter is reduced to alcohol while formaldehyde is oxidized to formic acid. This is known as the cross Cannizzaro reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




