
Formula for the following compound Thallium (I) sulphate is $T{l_2}S{O_4}$ .
A.True
B.False
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint:
Thallium has 3 valence electrons (2 in 6s and 1 in 6p) and exhibits mostly (+1) oxidation state while sulphate ($S{O_4}^{ - 2}$) exhibits (-2) oxidation state.
Complete step by step answer:
-Thallium (Tl) has an atomic number of 81 and belongs to the Boron (B) group. It belongs to the 13th group and 6th period. Hence, its electronic configuration is: $\left[ {Xe} \right]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^1}$.
We can see from the configuration that Tl has the ability to lose 1 electron from the outermost subshell of 6p and attain a more stable state, thus exhibiting (+1) oxidation state. It can also lose 3 electrons from the outermost shell (6s and 6p). Thus thallium (Tl) can exhibit (+1) and (+3) oxidation states.
-Thallium (I) sulphate is also known as thallous sulphate is a sulphate salt of thallium in the common (+1) oxidation state as shown by Roman numeral (I).
-It is formed by the reaction of sulphuric acid with thallium metal, which is followed by crystallisation.
-Thallium sulphate is colourless, tasteless, odourless and highly toxic (hence used in insecticides, rodenticides and rat poisons. It gains its toxicity due to $T{l^{ + 1}}$ ion.
-Since the question says the name of the formula to be: Thallium (I) sulphate. The number (I) here shows the oxidation state of thallium atom, which is 1. And we all know that the sulphate has the molecular formula of $S{O_4}^{ - 2}$ and has an oxidation state of (-2). To satisfy or neutralise the (-2) charge of sulphate we will need a (+2) charge, but thallium has (+1) charge. So, we will require 2 atoms of thallium. Hence the molecular formula would be: $T{l_2}S{O_4}$.
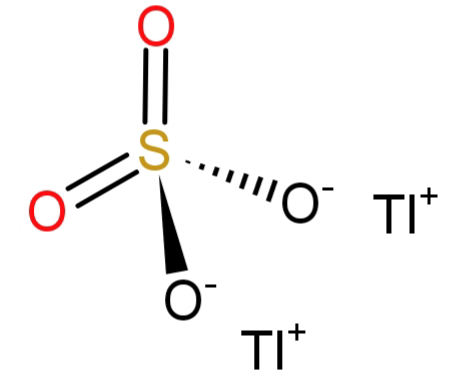
The statement is true and the correct option is: (A) True.
Note:
Although thallium can exhibit (+1) and (+3) oxidation states. It mostly prefers only (+1) because the 2 electrons from 6s subshell are relatively stable and much more difficult to remove than the 6p electron due to inert pair effect.
Thallium has 3 valence electrons (2 in 6s and 1 in 6p) and exhibits mostly (+1) oxidation state while sulphate ($S{O_4}^{ - 2}$) exhibits (-2) oxidation state.
Complete step by step answer:
-Thallium (Tl) has an atomic number of 81 and belongs to the Boron (B) group. It belongs to the 13th group and 6th period. Hence, its electronic configuration is: $\left[ {Xe} \right]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^1}$.
We can see from the configuration that Tl has the ability to lose 1 electron from the outermost subshell of 6p and attain a more stable state, thus exhibiting (+1) oxidation state. It can also lose 3 electrons from the outermost shell (6s and 6p). Thus thallium (Tl) can exhibit (+1) and (+3) oxidation states.
-Thallium (I) sulphate is also known as thallous sulphate is a sulphate salt of thallium in the common (+1) oxidation state as shown by Roman numeral (I).
-It is formed by the reaction of sulphuric acid with thallium metal, which is followed by crystallisation.
-Thallium sulphate is colourless, tasteless, odourless and highly toxic (hence used in insecticides, rodenticides and rat poisons. It gains its toxicity due to $T{l^{ + 1}}$ ion.
-Since the question says the name of the formula to be: Thallium (I) sulphate. The number (I) here shows the oxidation state of thallium atom, which is 1. And we all know that the sulphate has the molecular formula of $S{O_4}^{ - 2}$ and has an oxidation state of (-2). To satisfy or neutralise the (-2) charge of sulphate we will need a (+2) charge, but thallium has (+1) charge. So, we will require 2 atoms of thallium. Hence the molecular formula would be: $T{l_2}S{O_4}$.

The statement is true and the correct option is: (A) True.
Note:
Although thallium can exhibit (+1) and (+3) oxidation states. It mostly prefers only (+1) because the 2 electrons from 6s subshell are relatively stable and much more difficult to remove than the 6p electron due to inert pair effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




