
What is the formula of silver sulphide?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Silver sulphide is an example of an inorganic compound which exists in a form of dense solid which is black in colour. It occurs only in the form of sulphide of silver atoms. Molecular formula of silver sulphide must represent the exact number of silver and sulphide atoms.
Molecular formula of any given compound provides the exact number of atoms of different elements which are present in one mole of compound. Molecular formulas help to determine the chemical and physical nature of compounds depending upon the nature of its constituents.
Complete answer:
Silver sulphide is composed of two components one is a silver atom and another is a sulphide ion.
Atomic number of silver $\left( {Ag} \right)$ is $47$ and the electronic configuration is $\left[ {Kr} \right]4{d^{10}}5{s^1}$. Silver loses its outermost electron from the valence shell to form $\left( {A{g^ + }} \right)$.
Similarly atomic number of sulphur$\left( S \right)$ is $16$ and electronic configuration is $\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^4}$. When a sulphur atom accepts two more electrons to form $\left( {{S^{ - 2}}} \right)$. This $\left( {{S^{ - 2}}} \right)$ is commonly known as sulphide.
Now we write the symbol of silver and sulphide in a row with their valency below them. Now cross matched the valency of both atoms to calculate the formula of silver sulphide.
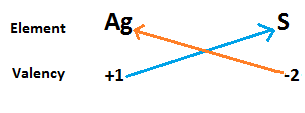
$ \Rightarrow $ From the above diagram we write the chemical formula of silver sulphide as $A{g_2}S$.
Note:
Sulphur atoms also have tendency to extend their valency to $6$ due to presence of $\left( d \right)$ orbitals. Silver sulphide is used as a photosensitizer as well as in the protection of silver from degradation by forming a thin layer of silver sulphide over the surface which inhibits further decomposition.
Molecular formula of any given compound provides the exact number of atoms of different elements which are present in one mole of compound. Molecular formulas help to determine the chemical and physical nature of compounds depending upon the nature of its constituents.
Complete answer:
Silver sulphide is composed of two components one is a silver atom and another is a sulphide ion.
Atomic number of silver $\left( {Ag} \right)$ is $47$ and the electronic configuration is $\left[ {Kr} \right]4{d^{10}}5{s^1}$. Silver loses its outermost electron from the valence shell to form $\left( {A{g^ + }} \right)$.
Similarly atomic number of sulphur$\left( S \right)$ is $16$ and electronic configuration is $\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^4}$. When a sulphur atom accepts two more electrons to form $\left( {{S^{ - 2}}} \right)$. This $\left( {{S^{ - 2}}} \right)$ is commonly known as sulphide.
Now we write the symbol of silver and sulphide in a row with their valency below them. Now cross matched the valency of both atoms to calculate the formula of silver sulphide.

$ \Rightarrow $ From the above diagram we write the chemical formula of silver sulphide as $A{g_2}S$.
Note:
Sulphur atoms also have tendency to extend their valency to $6$ due to presence of $\left( d \right)$ orbitals. Silver sulphide is used as a photosensitizer as well as in the protection of silver from degradation by forming a thin layer of silver sulphide over the surface which inhibits further decomposition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




