
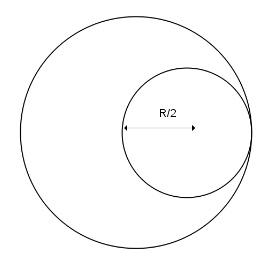
From a solid sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ , a spherical portion of radius $ R/2 $ is removed, as shown in the figure. Taking gravitational potential $ V = 0 $ at $ r = \infty $ , the potential at the center of the cavity thus formed is : ( $ G $ = gravitational constant)
(G= gravitational constant)
(A) $ \dfrac{{ - 2GM}}{{3R}} $
(B) $ \dfrac{{ - 2GM}}{R} $
(C) $ \dfrac{{ - GM}}{{2R}} $
(D) $ \dfrac{{ - GM}}{R} $

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for potential due to gravity of a solid sphere inside the sphere. Subtract the potential due to the sphere that is removed from the gravity from the potential of the complete sphere
Formula used: $ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}(3{R^2} - {r^2}) $ where $ V $ is the potential due to inside a solid sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ at a distance $ r $ away from the center of the sphere.
Complete step by step solution:
We’ve been given that a spherical portion of radius $ R/2 $ is removed from a solid sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ . To solve such questions, we should first calculate the potential due to the complete sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ at the center of the cavity i.e. at a distance of $ R/2 $ . So, we can calculate the potential using the formula
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}(3{R^2} - {r^2}) $
So the potential due to the complete sphere can at $ r = \dfrac{R}{2} $ can be calculated as
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {3{R^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right) $
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {\dfrac{{11{R^2}}}{4}} \right) $
On cancelling $ {R^2} $ , we get
$ V = - \dfrac{{11GM}}{{8R}} $
To find the potential after removing the smaller sphere, we will now calculate the potential at the center of the cavity due to a sphere having the size and mass of the cavity. To find the mass of the sphere the size of the cavity, we will make use of the fact that the sphere has a uniform density given by:
$ \rho = \dfrac{M}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}}} $
So for a sphere of radius $ R/2 $ , the mass $ m $ can be calculated as:
$ m = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^3} $
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \dfrac{{{R^3}}}{8} $
Rewriting the mass in terms of the bigger sphere of mass $ M $ , we can write
$ m = \dfrac{M}{8} $
So the potential due to a sphere the size of the cavity at the center of the cavity $ (r = 0) $ can be calculated as
$ {V_C} = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {3{R^2} - 0} \right) $
$ {V_C} = - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{8R}} $
To find the potential of the system given in the image, we must subtract the potential due to the cavity from the potential due to the complete sphere i.e. :
$ {V_{system}} = V - {V_c} $
$ {V_{system}} = - \dfrac{{11GM}}{{8R}} - \left( { - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{8R}}} \right) $
Hence the potential of the system is calculated as:
$ {V_{{\text{system}}}} = - \dfrac{{GM}}{R} $
Therefore, the correct answer will be option D.
Note:
In such questions, we must realize that the potential at the center of the cavity will not be equal to the potential due to the complete sphere and we must subtract the potential due to the removed sphere from the potential due to the complete sphere.
Formula used: $ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}(3{R^2} - {r^2}) $ where $ V $ is the potential due to inside a solid sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ at a distance $ r $ away from the center of the sphere.
Complete step by step solution:
We’ve been given that a spherical portion of radius $ R/2 $ is removed from a solid sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ . To solve such questions, we should first calculate the potential due to the complete sphere of mass $ M $ and radius $ R $ at the center of the cavity i.e. at a distance of $ R/2 $ . So, we can calculate the potential using the formula
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}(3{R^2} - {r^2}) $
So the potential due to the complete sphere can at $ r = \dfrac{R}{2} $ can be calculated as
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {3{R^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right) $
$ V = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {\dfrac{{11{R^2}}}{4}} \right) $
On cancelling $ {R^2} $ , we get
$ V = - \dfrac{{11GM}}{{8R}} $
To find the potential after removing the smaller sphere, we will now calculate the potential at the center of the cavity due to a sphere having the size and mass of the cavity. To find the mass of the sphere the size of the cavity, we will make use of the fact that the sphere has a uniform density given by:
$ \rho = \dfrac{M}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}}} $
So for a sphere of radius $ R/2 $ , the mass $ m $ can be calculated as:
$ m = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{R}{2}} \right)^3} $
$ \Rightarrow m = \rho \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \dfrac{{{R^3}}}{8} $
Rewriting the mass in terms of the bigger sphere of mass $ M $ , we can write
$ m = \dfrac{M}{8} $
So the potential due to a sphere the size of the cavity at the center of the cavity $ (r = 0) $ can be calculated as
$ {V_C} = - \dfrac{{GM}}{{2{R^3}}}\left( {3{R^2} - 0} \right) $
$ {V_C} = - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{8R}} $
To find the potential of the system given in the image, we must subtract the potential due to the cavity from the potential due to the complete sphere i.e. :
$ {V_{system}} = V - {V_c} $
$ {V_{system}} = - \dfrac{{11GM}}{{8R}} - \left( { - \dfrac{{3GM}}{{8R}}} \right) $
Hence the potential of the system is calculated as:
$ {V_{{\text{system}}}} = - \dfrac{{GM}}{R} $
Therefore, the correct answer will be option D.
Note:
In such questions, we must realize that the potential at the center of the cavity will not be equal to the potential due to the complete sphere and we must subtract the potential due to the removed sphere from the potential due to the complete sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




