
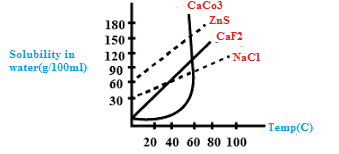
From the given graph predict the compound which would be most easily purified by crystallization from aqueous solution.
This graph is drawn on paint.
A) $ZnS$
B) $CaC{O_3}$
C) $Ca{F_2}$
D) $NaCl$

Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint: We know Recrystallization, otherwise called partial crystallization, is a methodology for decontaminating an unclean compound in a dissolvable. The technique for refinement depends on the rule that the dissolvability of most solids increases with expanded temperature. This implies that as temperature builds the measure of solute that can be broken up in dissolvable increments.
Complete answer:
Dissolvability is the capacity of a strong, fluid, or vaporous synthetic substance (alluded to as the solute) to break down in dissolvable (normally a fluid) and structure a solution. The dissolvability of a substance generally relies upon the dissolvable utilized, just as temperature and pressing factor.
We know that Just Zinc sulfide dissolvability of water is more than sodium chloride so Zinc sulfide is recrystallised from solution. Thus, option A is correct.
Note:
A polluted compound is broken up (the contaminations should likewise be dissolvable in the dissolvable), to set up a profoundly assembled arrangement at a high temperature. The arrangement is cooled. Diminishing the temperature causes the solvency of the pollution in the arrangement and the substance being sanitized to diminish. The polluted substance at that point takes shape before the debasements, expecting that there was more unclean substance than there were contaminations. The tainted substance will take shape in a cleaner structure in light of the fact that the pollution will not solidify yet, hence abandoning the contaminations in the arrangement. A filtration cycle ought to be used to detach the more unadulterated jewels now. The framework can be repeated. Dissolvability twists can be used to anticipate the aftereffect of a recrystallisation system.
Complete answer:
Dissolvability is the capacity of a strong, fluid, or vaporous synthetic substance (alluded to as the solute) to break down in dissolvable (normally a fluid) and structure a solution. The dissolvability of a substance generally relies upon the dissolvable utilized, just as temperature and pressing factor.
We know that Just Zinc sulfide dissolvability of water is more than sodium chloride so Zinc sulfide is recrystallised from solution. Thus, option A is correct.
Note:
A polluted compound is broken up (the contaminations should likewise be dissolvable in the dissolvable), to set up a profoundly assembled arrangement at a high temperature. The arrangement is cooled. Diminishing the temperature causes the solvency of the pollution in the arrangement and the substance being sanitized to diminish. The polluted substance at that point takes shape before the debasements, expecting that there was more unclean substance than there were contaminations. The tainted substance will take shape in a cleaner structure in light of the fact that the pollution will not solidify yet, hence abandoning the contaminations in the arrangement. A filtration cycle ought to be used to detach the more unadulterated jewels now. The framework can be repeated. Dissolvability twists can be used to anticipate the aftereffect of a recrystallisation system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




