
From the top and bottom of the tower the angle of elevation of the top of a cliff with height 400 m are observed to be $30{}^\circ $ and $60{}^\circ .$ Find the height of the tower.
Answer
519.3k+ views
Hint: We solve this question by using basic concepts of trigonometry. Here, angle of elevation means the angle considered from the plan surface upwards. We need to draw a diagram in order to represent this scenario. We have the angles of elevation by looking at the top of a cliff from the top and bottom of a tower as $30{}^\circ $ and $60{}^\circ $ respectively. Using the basic trigonometric angles and the height of the cliff, we calculate the height of the tower.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve this question, let us represent the question in the form of a diagram. We have drawn the figure as shown.
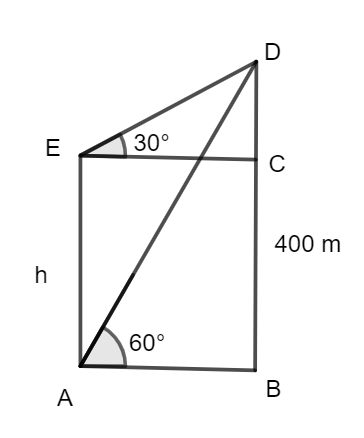
The height of the tower is assumed to be h. This is represented by the line segment AE in the figure. Also, the height of the cliff is 400 m which is given by the line segment DB. The angle of elevation of the cliff by looking from the top of the tower is $30{}^\circ $ and the angle of elevation of the cliff by looking from the bottom of the tower is $60{}^\circ $, which are given by the angles $\angle DEC$ and $\angle DAB$ respectively. We are required to find the value of h.
Using trigonometry in the $\Delta DAB,$ we can represent the angle in terms of sides as,
$\Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{DB}{AB}$
This is so because by the standard definition of tan, we know it is $\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}.$ We know the length of DB which is the height of the cliff given by 400 m and we know the value of the standard angle $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}.$ Using these in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{400}{AB}$
Cross-multiplying, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}AB=400$
Dividing both sides by $\sqrt{3},$
$\Rightarrow AB=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}$
This is the length of the base of the $\Delta DAB.$ As we can see, AB and CE are of same length, therefore
$\Rightarrow AB=CE=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}$
Next, we consider the $\Delta DEC,$ and apply the same formula,
$\Rightarrow \tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{DC}{CE}$
We know the standard value of $\tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}.$ Also, we can see from the figure that DC is nothing but difference in the heights of the cliff and the tower. This is given as
$\Rightarrow DC=400-h$
Using these in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{400-h}{CE}$
We also know that $CE=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}},$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{400-h}{\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}}$
Cross-multiplying,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}=400-h$
Multiplying the two $\sqrt{3}$ in the denominator we get a 3.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{400}{3}=400-h$
Multiplying both sides by 3,
$\Rightarrow 400=3\left( 400-h \right)$
Multiplying the terms in brackets on the right-hand side,
$\Rightarrow 400=1200-3h$
Adding 3h on both sides,
$\Rightarrow 400+3h=1200$
Subtracting 400 on both sides,
$\Rightarrow 3h=1200-400$
After subtracting the two terms on the right-hand side, we divide both sides by 3.
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{800}{3}=266.6667$
Hence, the height of the tower is 266.6667 m or $\dfrac{800}{3}$ m.
Note: We need to know the concept of angle of elevation and depression in order to solve such sums. It is important to know the values of some standard angle values of the basic trigonometric functions too. Observing the diagram is very important for such problems as they can help us get many minute details like AB being equal to CE and DC being the difference in height of the cliff and tower, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
In order to solve this question, let us represent the question in the form of a diagram. We have drawn the figure as shown.

The height of the tower is assumed to be h. This is represented by the line segment AE in the figure. Also, the height of the cliff is 400 m which is given by the line segment DB. The angle of elevation of the cliff by looking from the top of the tower is $30{}^\circ $ and the angle of elevation of the cliff by looking from the bottom of the tower is $60{}^\circ $, which are given by the angles $\angle DEC$ and $\angle DAB$ respectively. We are required to find the value of h.
Using trigonometry in the $\Delta DAB,$ we can represent the angle in terms of sides as,
$\Rightarrow \tan 60{}^\circ =\dfrac{DB}{AB}$
This is so because by the standard definition of tan, we know it is $\dfrac{\text{perpendicular}}{\text{base}}.$ We know the length of DB which is the height of the cliff given by 400 m and we know the value of the standard angle $\tan 60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3}.$ Using these in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{400}{AB}$
Cross-multiplying, we get,
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{3}AB=400$
Dividing both sides by $\sqrt{3},$
$\Rightarrow AB=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}$
This is the length of the base of the $\Delta DAB.$ As we can see, AB and CE are of same length, therefore
$\Rightarrow AB=CE=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}$
Next, we consider the $\Delta DEC,$ and apply the same formula,
$\Rightarrow \tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{DC}{CE}$
We know the standard value of $\tan 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}.$ Also, we can see from the figure that DC is nothing but difference in the heights of the cliff and the tower. This is given as
$\Rightarrow DC=400-h$
Using these in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{400-h}{CE}$
We also know that $CE=\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}},$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{400-h}{\dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}}$
Cross-multiplying,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times \dfrac{400}{\sqrt{3}}=400-h$
Multiplying the two $\sqrt{3}$ in the denominator we get a 3.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{400}{3}=400-h$
Multiplying both sides by 3,
$\Rightarrow 400=3\left( 400-h \right)$
Multiplying the terms in brackets on the right-hand side,
$\Rightarrow 400=1200-3h$
Adding 3h on both sides,
$\Rightarrow 400+3h=1200$
Subtracting 400 on both sides,
$\Rightarrow 3h=1200-400$
After subtracting the two terms on the right-hand side, we divide both sides by 3.
$\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{800}{3}=266.6667$
Hence, the height of the tower is 266.6667 m or $\dfrac{800}{3}$ m.
Note: We need to know the concept of angle of elevation and depression in order to solve such sums. It is important to know the values of some standard angle values of the basic trigonometric functions too. Observing the diagram is very important for such problems as they can help us get many minute details like AB being equal to CE and DC being the difference in height of the cliff and tower, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




