
Full name of DDT is:
(A) 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane
(B) 1,1-dichloro-2,2-diphenyl trimethylethane
(C) 1,1-dichloro-2,2-diphenyl trichloroethane
(D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint – You can start by defining the full form of DDT and draw a well labeled of its molecular structure. Then move on to how DDT was discovered and where it is used. Especially remember to point out what harm it can do for us and the environment.
Complete step by step solution:
> The structure of DDT is shown below:
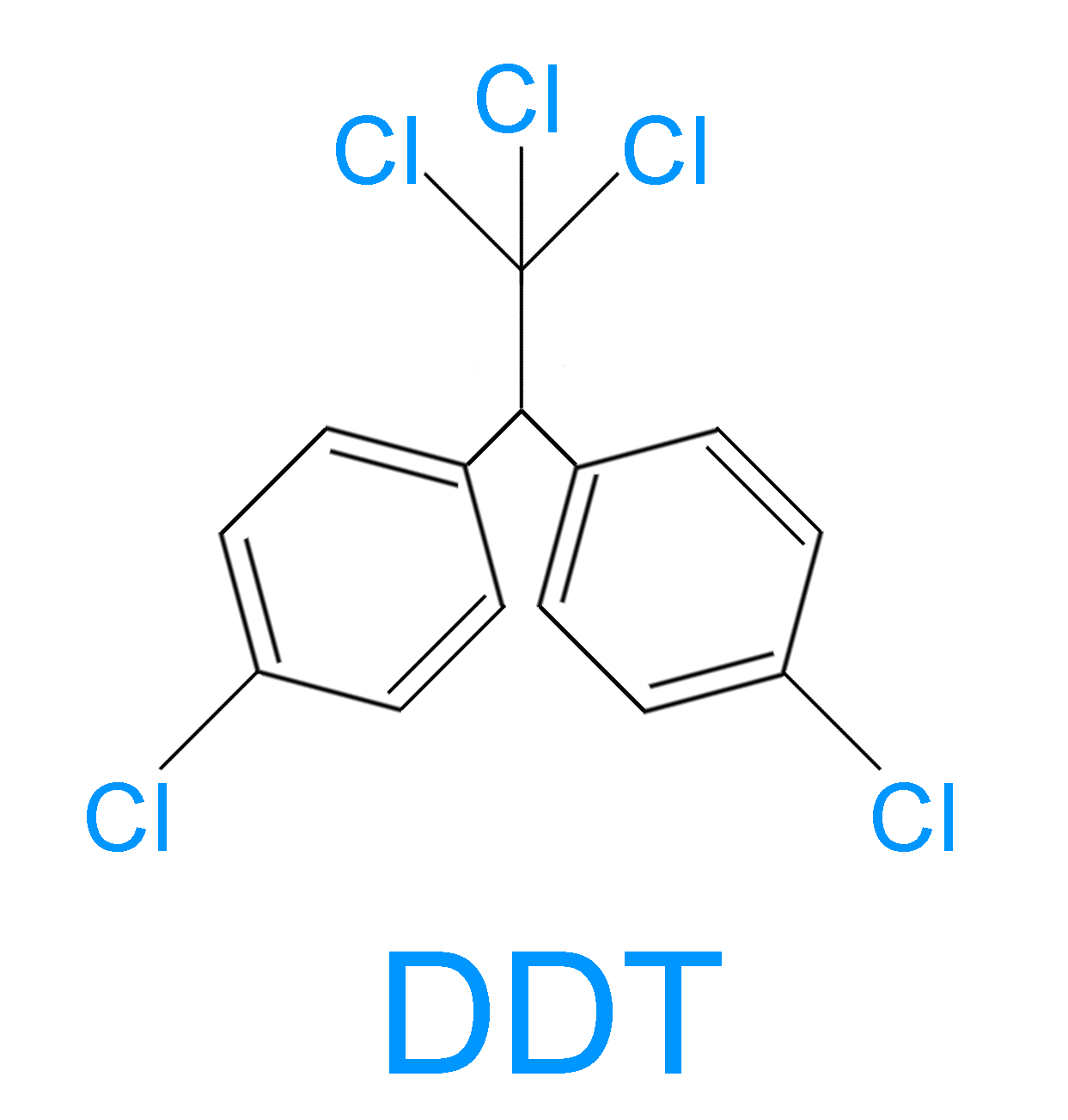
> DDT was synthesized for the first time in 1874 by an Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler. But it was only in 1939 that a Swiss chemist Paul Hermann discovered its use as an insecticide.
> DDT has a great significance in world history. In World War II when the world was engulfed in war, diseases like malaria wreaked havoc among the soldiers and civilians. So DDT came as a potential solution to reduce the number of mosquitos (the vectors for malaria causing pathogens).
> The reaction by which DDT is produced is as follows
$2{C_6}{H_5}Cl(chlorobenzene) + {C_2}HOC{l_3}(chloral)\xrightarrow{{}}{C_{14}}{H_9}C{l_5}(DDT) + {H_2}O$
> As you can see chlorobenzene and chloral are used as the raw material for the process of making 1,1-dichloro-2,2-diphenyl trichloroethane.
> DDT should be handled carefully, as DDT can disturb the endocrine system of humans. It is also considered as a carcinogen (substances that can potentially cause the formation of cancerous cells). In case of shorter periods of time it does not harm that much and is classified by the US National Toxicology Program as “moderately toxic”.
Therefore option (A) 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane is the correct answer.
Note - DDT became available for public sale in 1945 for use as an agricultural pesticide and household insecticide. By 1944 we started hearing concerns that excessive use of DDT might do more harm than good. It was reported that excessive use of DDT can not only kill insects but also kills fish, birds and other forms of life.
Complete step by step solution:
> The structure of DDT is shown below:

> DDT was synthesized for the first time in 1874 by an Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler. But it was only in 1939 that a Swiss chemist Paul Hermann discovered its use as an insecticide.
> DDT has a great significance in world history. In World War II when the world was engulfed in war, diseases like malaria wreaked havoc among the soldiers and civilians. So DDT came as a potential solution to reduce the number of mosquitos (the vectors for malaria causing pathogens).
> The reaction by which DDT is produced is as follows
$2{C_6}{H_5}Cl(chlorobenzene) + {C_2}HOC{l_3}(chloral)\xrightarrow{{}}{C_{14}}{H_9}C{l_5}(DDT) + {H_2}O$
> As you can see chlorobenzene and chloral are used as the raw material for the process of making 1,1-dichloro-2,2-diphenyl trichloroethane.
> DDT should be handled carefully, as DDT can disturb the endocrine system of humans. It is also considered as a carcinogen (substances that can potentially cause the formation of cancerous cells). In case of shorter periods of time it does not harm that much and is classified by the US National Toxicology Program as “moderately toxic”.
Therefore option (A) 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane is the correct answer.
Note - DDT became available for public sale in 1945 for use as an agricultural pesticide and household insecticide. By 1944 we started hearing concerns that excessive use of DDT might do more harm than good. It was reported that excessive use of DDT can not only kill insects but also kills fish, birds and other forms of life.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




