
Function of companion cells is
A) providing energy to sieve elements for active transport
B) providing water to phloem
C) loading of sucrose into sieve elements by passive transport
D) loading of sucrose into sieve elements
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Companion cells Modified parenchyma, connected to strainer cells by plasmodesmata. Dissimilar to strainer cells, buddy cells are nucleated and have numerous mitochondria. Partner cells may direct movement.
Complete Answer:
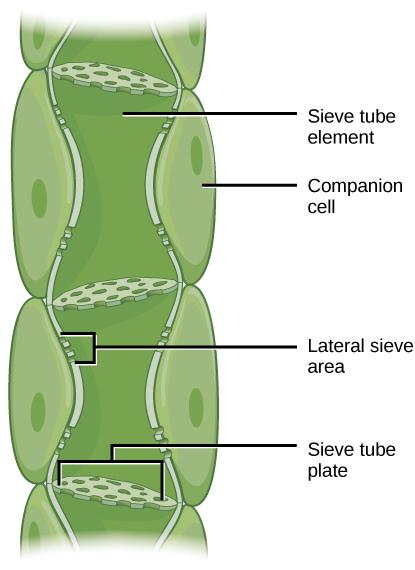
- Companion cell: companion cell A sort of cell found inside the phloem of blossoming plants. Each buddy cell is typically firmly connected with a sifter component.
- Its capacity is unsure, however it seems to manage the action of the neighboring sifter component and to partake in stacking and emptying sugar into the strainer component.
- In gymnosperms a comparative capacity is ascribed to aluminous cells, which are found firmly connected with gymnosperm strainer components.
Companion cell types:
1) Sieve-tube
2) Phloem
3) Plasmodesmata
1) Sieve tube: in blooming plants, lengthened living cells (strainer tube components) of the phloem, the cores of which have divided and vanished and the cross over end dividers of which h are punctured by strainer like gatherings of pores (sifter plates). They are the conductors of food (generally sugar) transport.
2) Phloem: Phloem is the vascular tissue answerable for the vehicle of sugars from source tissues (ex. photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or creating blossoms). Different particles, for example, proteins and mRNAs are likewise shipped all through the plant by means of
3) Plasmodesmata: Plasmodesmata (solitary: plasmodia) are tiny channels which cross the cell dividers of plant cells and some algal cells, empowering transport and correspondence between them.
Correct answer is option: (D) loading of sucrose into sieve elements.
Note: Companion cell a sort of cell found inside the phloem of blooming plants. Each companion cell is typically firmly connected with a sifter component. Its capacity is unsure, however it seems to direct the action of the contiguous sifter component and to partake in stacking and emptying sugar into the strainer component.
Complete Answer:
- Companion cell: companion cell A sort of cell found inside the phloem of blossoming plants. Each buddy cell is typically firmly connected with a sifter component.
- Its capacity is unsure, however it seems to manage the action of the neighboring sifter component and to partake in stacking and emptying sugar into the strainer component.
- In gymnosperms a comparative capacity is ascribed to aluminous cells, which are found firmly connected with gymnosperm strainer components.
Companion cell types:
1) Sieve-tube
2) Phloem
3) Plasmodesmata
1) Sieve tube: in blooming plants, lengthened living cells (strainer tube components) of the phloem, the cores of which have divided and vanished and the cross over end dividers of which h are punctured by strainer like gatherings of pores (sifter plates). They are the conductors of food (generally sugar) transport.
2) Phloem: Phloem is the vascular tissue answerable for the vehicle of sugars from source tissues (ex. photosynthetic leaf cells) to sink tissues (ex. non-photosynthetic root cells or creating blossoms). Different particles, for example, proteins and mRNAs are likewise shipped all through the plant by means of
3) Plasmodesmata: Plasmodesmata (solitary: plasmodia) are tiny channels which cross the cell dividers of plant cells and some algal cells, empowering transport and correspondence between them.

Correct answer is option: (D) loading of sucrose into sieve elements.
Note: Companion cell a sort of cell found inside the phloem of blooming plants. Each companion cell is typically firmly connected with a sifter component. Its capacity is unsure, however it seems to direct the action of the contiguous sifter component and to partake in stacking and emptying sugar into the strainer component.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




