
Function of ER is/are:
a) Attachment site of ribosomes
b) Storage of genetic material
c) Removal of newly synthesized on RNA
d) None of the above
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions like in folding, synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins.
Complete step by step answer:
- Endoplasmic reticulum often shows ribosomes attached to their outer surface. The endoplasmic reticulum bearing ribosomes on the surface is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) .
- When the ribosomes are absent, the Endoplasmic reticulum looks more smooth and is termed as smooth endoplasmic reticulum(SER) .
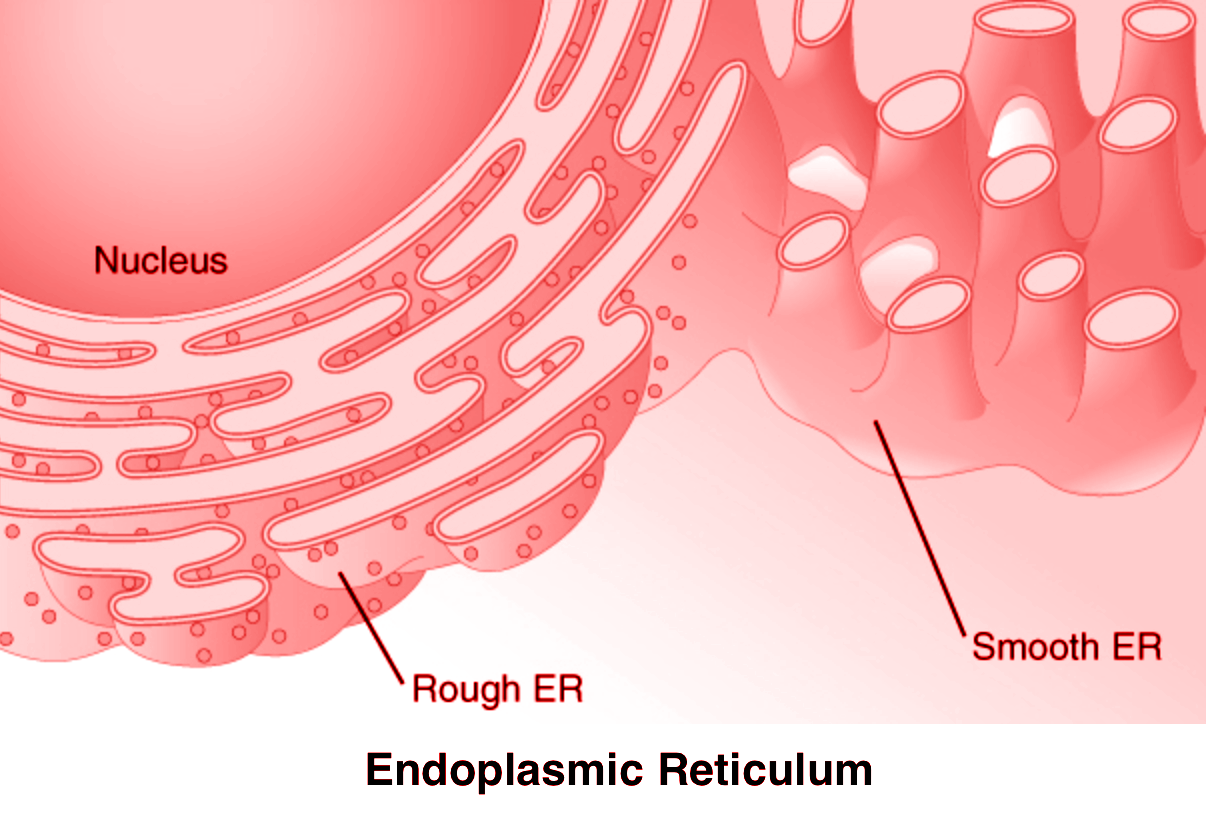
- In general, rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) can be seen in the cells which are actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Also, they are complex and continuous with the outer membrane of the nucleus.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is the major site for the synthesis of liquid. In animal cells, liquid- like steroidal hormones are synthesized in a smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) .
So, the correct answer is, ”attachment site of ribosomes”.
Additional information:
- Endoplasmic reticulum make and package proteins and lipids.
- It is much like an assembly line.
- Found in Eukaryotic organisms.
- Forms an interconnected network of flat and membrane endorsed sacs or tubes known as cisternae.
- Largest organelle in a Eukaryotic cell.
- It provides a separate chemical environment which allows for correct protein folding.
Note: The organelle was named by Keith Porter in 1953 based on observations made with the electron microscope on tissue cultured cells.
- They have a special encapsulated protein that balances its structure.
- The products of the endoplasmic reticulum move to Golgi bodies for the act of packing and additional processing before being secreted.
Complete step by step answer:
- Endoplasmic reticulum often shows ribosomes attached to their outer surface. The endoplasmic reticulum bearing ribosomes on the surface is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) .
- When the ribosomes are absent, the Endoplasmic reticulum looks more smooth and is termed as smooth endoplasmic reticulum(SER) .

- In general, rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) can be seen in the cells which are actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Also, they are complex and continuous with the outer membrane of the nucleus.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is the major site for the synthesis of liquid. In animal cells, liquid- like steroidal hormones are synthesized in a smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) .
So, the correct answer is, ”attachment site of ribosomes”.
Additional information:
- Endoplasmic reticulum make and package proteins and lipids.
- It is much like an assembly line.
- Found in Eukaryotic organisms.
- Forms an interconnected network of flat and membrane endorsed sacs or tubes known as cisternae.
- Largest organelle in a Eukaryotic cell.
- It provides a separate chemical environment which allows for correct protein folding.
Note: The organelle was named by Keith Porter in 1953 based on observations made with the electron microscope on tissue cultured cells.
- They have a special encapsulated protein that balances its structure.
- The products of the endoplasmic reticulum move to Golgi bodies for the act of packing and additional processing before being secreted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




