
What is the function of leucoplast?
A. To store starch grains, oil drops and protein granules
B. To store nucleoprotein
C. To store glycoprotein
D. To synthesize glycogen
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Leucoplasts are storage organs that are observed in endosperms, roots, tubers, and other plant parts that are not involved in photosynthesis. The leucoplasts are the warehouse to store nutrients.
Complete answer:
Plastids are solely present in plant cells. Leucoplast is a colorless plastid that was discovered in the year 1883 by Andreas Franz Wilhelm Schimper, a German scientist.
Additional information:
Leucoplast: Leuco means ‘white’ and plasts means ‘molded’. Leucoplasts are unpigmented storage organelles in plants which store grains, protein granules, and oil droplets. Leucoplasts are commonly observed in plant parts which are non-photosynthetic like seeds, roots, and bulbs. The leucoplasts can be differentiated into 3 types depending on the plant’s needs. They are:
> Amyloplasts: The starch is produced and stored in amyloplasts. Amyloplasts are usually observed in vegetative plants like potatoes.
Proteinoplasts: The proteins can be stored in protoplasts and are usually found in seeds. They have crystalline proteins and may act as a site for enzymatic activity.
> Elaioplasts: The fats and lipids are stored in the plants by elaioplasts. The fats and lipids are stored within a fat droplet.
The different types of plastids are chloroplasts, chromoplasts, gerontoplasts, and leucoplasts. The function of leucoplasts is already mentioned in the above paragraph.
> Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts have green pigments called chloroplasts which are accountable for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are located in guard cells.
> Chromoplasts: Chromoplasts are accountable for the production as well as the storage of carotenoid pigments. They are majorly present in fruits that are ripened, flowers, and leaves to draw the attention of the pollinators.
> Gerontoplasts: When plants die, the chlorophyll will break down to form gerontoplasts.
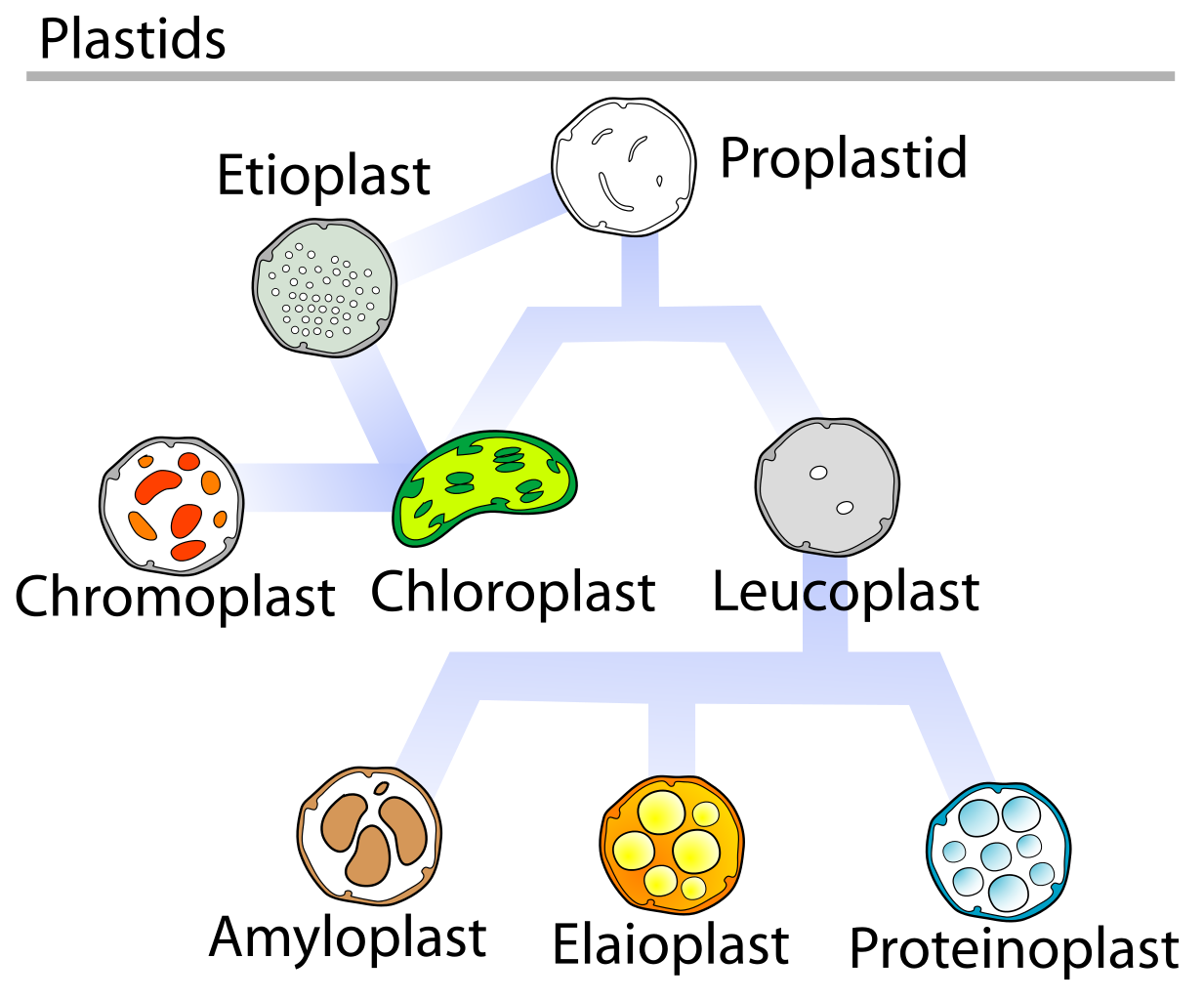
The figure represents different types of plastids.
Note: The chloroplast can be developed from leucoplasts if leucoplasts are exposed to light. Also, the leucoplasts can be developed from chloroplasts if the chloroplasts are exposed to the light. It is one of the few organelles that has its DNA.
Complete answer:
Plastids are solely present in plant cells. Leucoplast is a colorless plastid that was discovered in the year 1883 by Andreas Franz Wilhelm Schimper, a German scientist.
Additional information:
Leucoplast: Leuco means ‘white’ and plasts means ‘molded’. Leucoplasts are unpigmented storage organelles in plants which store grains, protein granules, and oil droplets. Leucoplasts are commonly observed in plant parts which are non-photosynthetic like seeds, roots, and bulbs. The leucoplasts can be differentiated into 3 types depending on the plant’s needs. They are:
> Amyloplasts: The starch is produced and stored in amyloplasts. Amyloplasts are usually observed in vegetative plants like potatoes.
Proteinoplasts: The proteins can be stored in protoplasts and are usually found in seeds. They have crystalline proteins and may act as a site for enzymatic activity.
> Elaioplasts: The fats and lipids are stored in the plants by elaioplasts. The fats and lipids are stored within a fat droplet.
The different types of plastids are chloroplasts, chromoplasts, gerontoplasts, and leucoplasts. The function of leucoplasts is already mentioned in the above paragraph.
> Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts have green pigments called chloroplasts which are accountable for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are located in guard cells.
> Chromoplasts: Chromoplasts are accountable for the production as well as the storage of carotenoid pigments. They are majorly present in fruits that are ripened, flowers, and leaves to draw the attention of the pollinators.
> Gerontoplasts: When plants die, the chlorophyll will break down to form gerontoplasts.

The figure represents different types of plastids.
Note: The chloroplast can be developed from leucoplasts if leucoplasts are exposed to light. Also, the leucoplasts can be developed from chloroplasts if the chloroplasts are exposed to the light. It is one of the few organelles that has its DNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




