
What is the function of pyloric sphincter?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: Pyloric sphincter is a valve created by smooth muscles separating the stomach’s pyloric region from the first part of the small intestine, duodenum.
Complete answer:
Our digestive system is a complex machinery involving a number of organs, all functioning with the purpose of digestion of food, absorption of nutrients and disposal of waste. Throughout this system, organs maintain pH levels according to their needs. Some pH levels differ at such a scale that any kind of mix up in their juices can cause severe health issues. Two such organs are the stomach and the small intestine. While the pH of stomach ranges from 1.5 - 3.5, the pH level in the duodenum is maintained at 6. Any unintentional flow of fluids from one organ to the other can cause digestive problems.
The unidirectional flow of chyme (partially digested food along with stomach juices) from the stomach to duodenum is overlooked by the pyloric sphincter. This ring of smooth muscles allow chyme to move out from the stomach only when it experiences peristaltic pressure (contractions) from the fundic and body region of stomach indicating that the food has been appropriately mixed with the acids. The pyloric sphincter acts as a guard and allows the chyme to pass on to the duodenum bit by bit.
As all the chyme moves to the duodenum, the pressure in the latter increases due to peristalsis, forcing the pyloric sphincter shut. This does not allow the movement of intestinal juices into the stomach.
Note:
Though pyloric sphincter is a small mass of smooth muscle, it’s malfunctioning can cause problems like Bile reflux, which is similar to acid reflux and Gastroparesis, which causes difficulty in emptying the stomach.
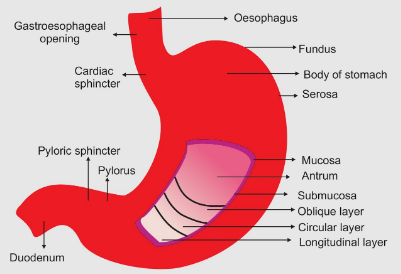
Complete answer:
Our digestive system is a complex machinery involving a number of organs, all functioning with the purpose of digestion of food, absorption of nutrients and disposal of waste. Throughout this system, organs maintain pH levels according to their needs. Some pH levels differ at such a scale that any kind of mix up in their juices can cause severe health issues. Two such organs are the stomach and the small intestine. While the pH of stomach ranges from 1.5 - 3.5, the pH level in the duodenum is maintained at 6. Any unintentional flow of fluids from one organ to the other can cause digestive problems.
The unidirectional flow of chyme (partially digested food along with stomach juices) from the stomach to duodenum is overlooked by the pyloric sphincter. This ring of smooth muscles allow chyme to move out from the stomach only when it experiences peristaltic pressure (contractions) from the fundic and body region of stomach indicating that the food has been appropriately mixed with the acids. The pyloric sphincter acts as a guard and allows the chyme to pass on to the duodenum bit by bit.
As all the chyme moves to the duodenum, the pressure in the latter increases due to peristalsis, forcing the pyloric sphincter shut. This does not allow the movement of intestinal juices into the stomach.
Note:
Though pyloric sphincter is a small mass of smooth muscle, it’s malfunctioning can cause problems like Bile reflux, which is similar to acid reflux and Gastroparesis, which causes difficulty in emptying the stomach.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




