
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum? What structure of the rough ER is necessary for this function?
Answer
479.4k+ views
Hint: The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that transports proteins and other substances within a cell. Ribosomes are organelles that build proteins. The ribosomes that assemble proteins that will be part of the cell membrane or exported from the cell connect to the endoplasmic reticulum, giving it a rough look.
Complete answer:
Protein synthesis is aided by ribosomes on the RER.
Protein synthesis takes place in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes on the surface of the ER give it a rough appearance. The proteins that have been produced are secreted to various locations.
Ribosomes are the actual sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes complete the polymerization of lengthy polypeptide chains.
The endoplasmic reticulum can be smooth or rough, and its main job is to make proteins that help the rest of the cell function. Ribosomes, which are small, spherical organelles that make those proteins, are found in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. When proteins are produced incorrectly, they can sometimes linger in the endoplasmic reticulum.
They're held, and the endoplasmic reticulum enlarges because it's constipated in some ways, and the proteins don't get to where they're supposed to go. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum, on the other hand, is devoid of ribosomes.
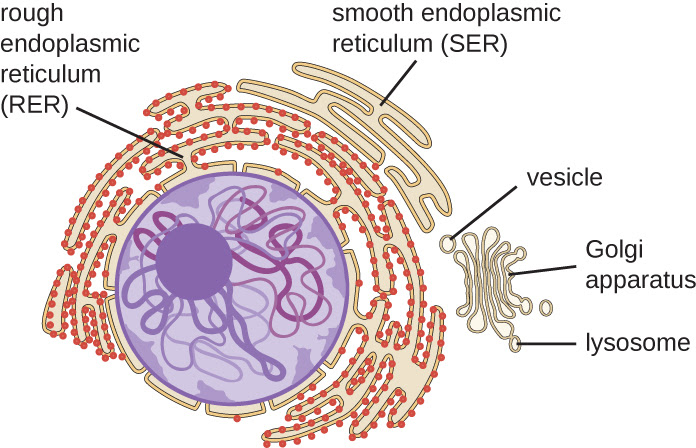
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also creates other compounds that the cell needs. The endoplasmic reticulum is a workhorse organelle that produces proteins and chemicals required by the rest of the cell.
Note:
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a subgroup of the endoplasmic reticulum and is part of the cell's endomembrane system (ER). This organelle is principally responsible for the synthesis, folding, and modification of proteins, particularly those that must be supplied to other organelles within the cell or secreted.
Complete answer:
Protein synthesis is aided by ribosomes on the RER.
Protein synthesis takes place in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes on the surface of the ER give it a rough appearance. The proteins that have been produced are secreted to various locations.
Ribosomes are the actual sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes complete the polymerization of lengthy polypeptide chains.
The endoplasmic reticulum can be smooth or rough, and its main job is to make proteins that help the rest of the cell function. Ribosomes, which are small, spherical organelles that make those proteins, are found in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. When proteins are produced incorrectly, they can sometimes linger in the endoplasmic reticulum.
They're held, and the endoplasmic reticulum enlarges because it's constipated in some ways, and the proteins don't get to where they're supposed to go. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum, on the other hand, is devoid of ribosomes.

The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also creates other compounds that the cell needs. The endoplasmic reticulum is a workhorse organelle that produces proteins and chemicals required by the rest of the cell.
Note:
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a subgroup of the endoplasmic reticulum and is part of the cell's endomembrane system (ER). This organelle is principally responsible for the synthesis, folding, and modification of proteins, particularly those that must be supplied to other organelles within the cell or secreted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




