
What functional groups are there in aspartame?
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint :We know that the Aspartame is used as a substitute of sugar as an artificial sweetener in foods and beverages. The aspartame contains two amino acids which are joined together by a peptide bond. It’s used in food products. It is a non-saccharide and is a dipeptide of phenylalanine and aspartic acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Aspartame is an artificial sweetener which is non-saccharides which is $ 200 $ times sweeter than the sucrose. It is commonly used as a sugar substitute added in food and beverages. Aspartame is a methyl ester of aspartic acid. Aspartame is a formed in $ 1965 $ and approved for use in food products by FDA in $ 1981. $
We must remember that the aspartame is not a carbohydrate but is $ 200 $ times sweeter than sucrose. It is usually used as a sugar substitute i.e. artificial sweetener in foods and beverages. Aspartame is a non-caloric sweetener too. It is a methyl ester of a dipeptide formed from two amino acids aspartic acid and phenylalanine. It is a white colorless powder used in food stuff throughout the world. Aspartame breaks down and loses its sweetness over time if it’s stored in liquids at temperature more than $ {{30}^{o}}C $ . It is very stable in a dry state. But in solution, it degrades into diketopiperazine. This compound can’t be usable in foods at higher temperature. The structural formula of aspartame is:
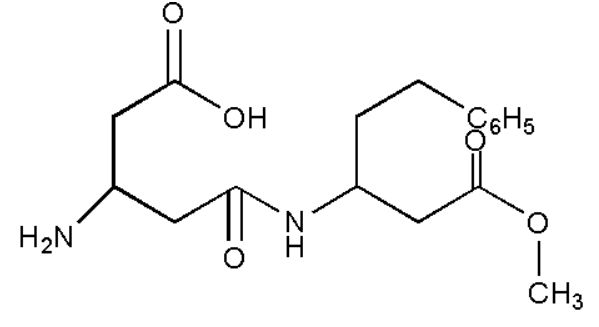
The functional groups in aspartame are carboxyl, primary amine, amide, ester, and phenyl. From left to right, the functional groups are
-A carboxyl group, $ -COOH $
-An amine, $ -NH $
-An amide group, $ -CONH- $
-An ester group, $ -COOR $
-A phenyl group $ -{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}} $
Note :
Remember that we must remember that aspartame intake has various side effects. This mainly because of degradation of aspartame at high temperature. Brain tumor is caused by the aspartame methanol which is a breakdown product.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Aspartame is an artificial sweetener which is non-saccharides which is $ 200 $ times sweeter than the sucrose. It is commonly used as a sugar substitute added in food and beverages. Aspartame is a methyl ester of aspartic acid. Aspartame is a formed in $ 1965 $ and approved for use in food products by FDA in $ 1981. $
We must remember that the aspartame is not a carbohydrate but is $ 200 $ times sweeter than sucrose. It is usually used as a sugar substitute i.e. artificial sweetener in foods and beverages. Aspartame is a non-caloric sweetener too. It is a methyl ester of a dipeptide formed from two amino acids aspartic acid and phenylalanine. It is a white colorless powder used in food stuff throughout the world. Aspartame breaks down and loses its sweetness over time if it’s stored in liquids at temperature more than $ {{30}^{o}}C $ . It is very stable in a dry state. But in solution, it degrades into diketopiperazine. This compound can’t be usable in foods at higher temperature. The structural formula of aspartame is:

The functional groups in aspartame are carboxyl, primary amine, amide, ester, and phenyl. From left to right, the functional groups are
-A carboxyl group, $ -COOH $
-An amine, $ -NH $
-An amide group, $ -CONH- $
-An ester group, $ -COOR $
-A phenyl group $ -{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}} $
Note :
Remember that we must remember that aspartame intake has various side effects. This mainly because of degradation of aspartame at high temperature. Brain tumor is caused by the aspartame methanol which is a breakdown product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




