
What is the $G_0$ (Quiescent) phase of cell cycle?
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Cell is a functional unit of every organism. Each cell has its own cell cycle. The cells are born or duplicated, carry out their life processes and then they die in the cell cycle. Quiescent phase is defined as the cellular state of a cell which is outside the replicative cycle.
Complete Answer:
The cells enter the Quiescent phase because of external factors like nutrient scarcity which is necessary for the cell proliferation.
The cells in the Quiescent phase have low RNA content and lack of cell proliferation markers.
A Cell spends all of its life in one of three phases-
- Interphase: Three phases are – S, $G_1$,$G_2$.
- Mitosis: Two parts, (1) Karyokinesis which means division of cell nucleus. (2) Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm.
- $G_0$ Phase: It is also called the Quiescent phase.
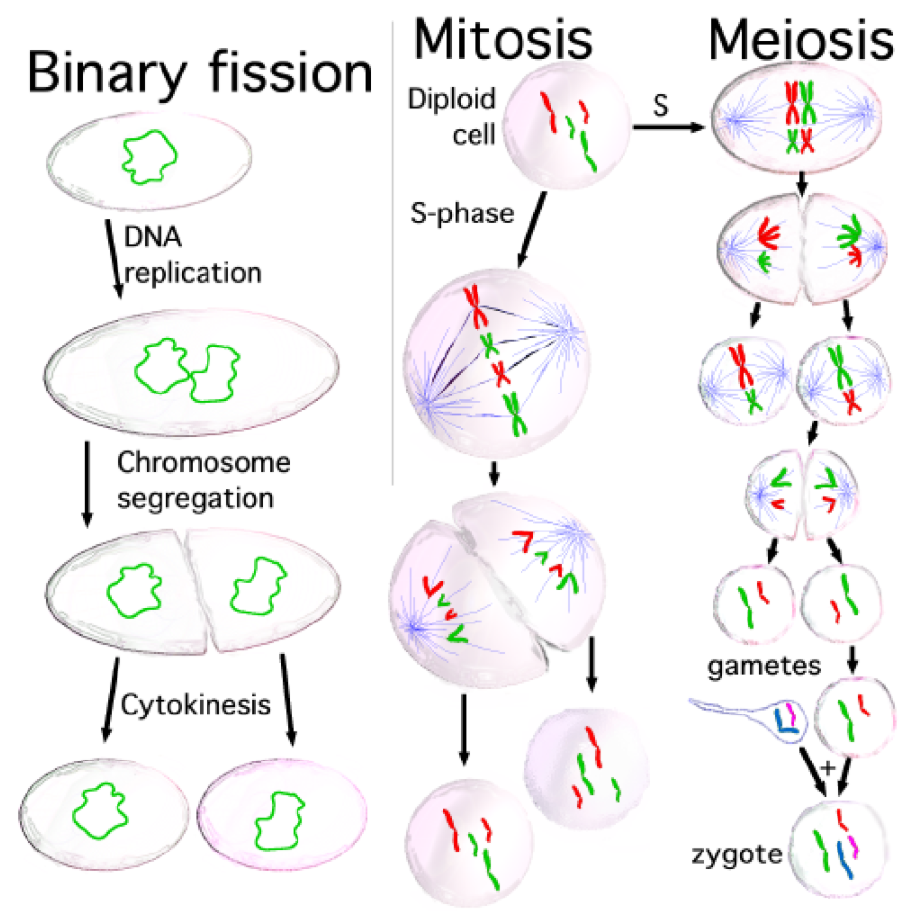
1) Interphase- In this phase the growth of cells occurs and The DNA is replicated.
- $G_1$ Phase- First gap
- S Phase- In this the DNA is replicated
- $G_2$ Phase
2) Mitosis – It is defined as division of the nucleus.
3) $G_0$ Phase – This is Inactive or resting stage of the cell cycle. The cells in the Quiescent phase do not divide.
Some cells do not appear to undergo division such as heart cells. These cells do not divide further and exit $G_1$ phase to enter an inactive stage known as quiescent stage. Cells in the $G_0$ phase are metabolically active but don’t proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism.
Some cells enter the $G_0$ phase temporarily until the external signal occurs for the arrival of $G_1$.
Note: Some cells that never or rarely divide like mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells exist in $G_0$ permanently. $G_0$ is also called a post mitotic stage because the cells are in a non dividing phase outside the cell cycle.
Complete Answer:
The cells enter the Quiescent phase because of external factors like nutrient scarcity which is necessary for the cell proliferation.
The cells in the Quiescent phase have low RNA content and lack of cell proliferation markers.
A Cell spends all of its life in one of three phases-
- Interphase: Three phases are – S, $G_1$,$G_2$.
- Mitosis: Two parts, (1) Karyokinesis which means division of cell nucleus. (2) Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm.
- $G_0$ Phase: It is also called the Quiescent phase.

1) Interphase- In this phase the growth of cells occurs and The DNA is replicated.
- $G_1$ Phase- First gap
- S Phase- In this the DNA is replicated
- $G_2$ Phase
2) Mitosis – It is defined as division of the nucleus.
3) $G_0$ Phase – This is Inactive or resting stage of the cell cycle. The cells in the Quiescent phase do not divide.
Some cells do not appear to undergo division such as heart cells. These cells do not divide further and exit $G_1$ phase to enter an inactive stage known as quiescent stage. Cells in the $G_0$ phase are metabolically active but don’t proliferate unless called on to do so depending on the requirement of the organism.
Some cells enter the $G_0$ phase temporarily until the external signal occurs for the arrival of $G_1$.
Note: Some cells that never or rarely divide like mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells exist in $G_0$ permanently. $G_0$ is also called a post mitotic stage because the cells are in a non dividing phase outside the cell cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




