
G0 state of cell denotes
(a) Death of cell
(b) Permanent pause
(c) Exit of the cell from cell cycle
(d) Checkpoint before entering the next phase
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The phase G0 in the cell cycle is also called the resting phase. In the phase G1, cells reach the phase G0 from a cell cycle checkpoint. Cells then stay in phase G0 until they have a reason to split.
Complete answer:
The cell cycle consists basically of four phases G1, S, G2, and M. G0 phase also known as the extended G1 phase which is a period during which the cell exits from the cell cycle. The cell exists in a quiescent state at this stage and does not divide. If cells are not to be separated after the G1 process and begin to undergo differentiation into various cell types such cells are said to be in G0 state.
G0 is often referred to as a "post-mitotic" condition because cells in G0 are outside of the cell cycle in a non-dividing period. Cells in the G0 state remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless they are called upon to do so depending on the organism's requirement.
So, the correct answer is ‘Exit of the cell from cell cycle’.
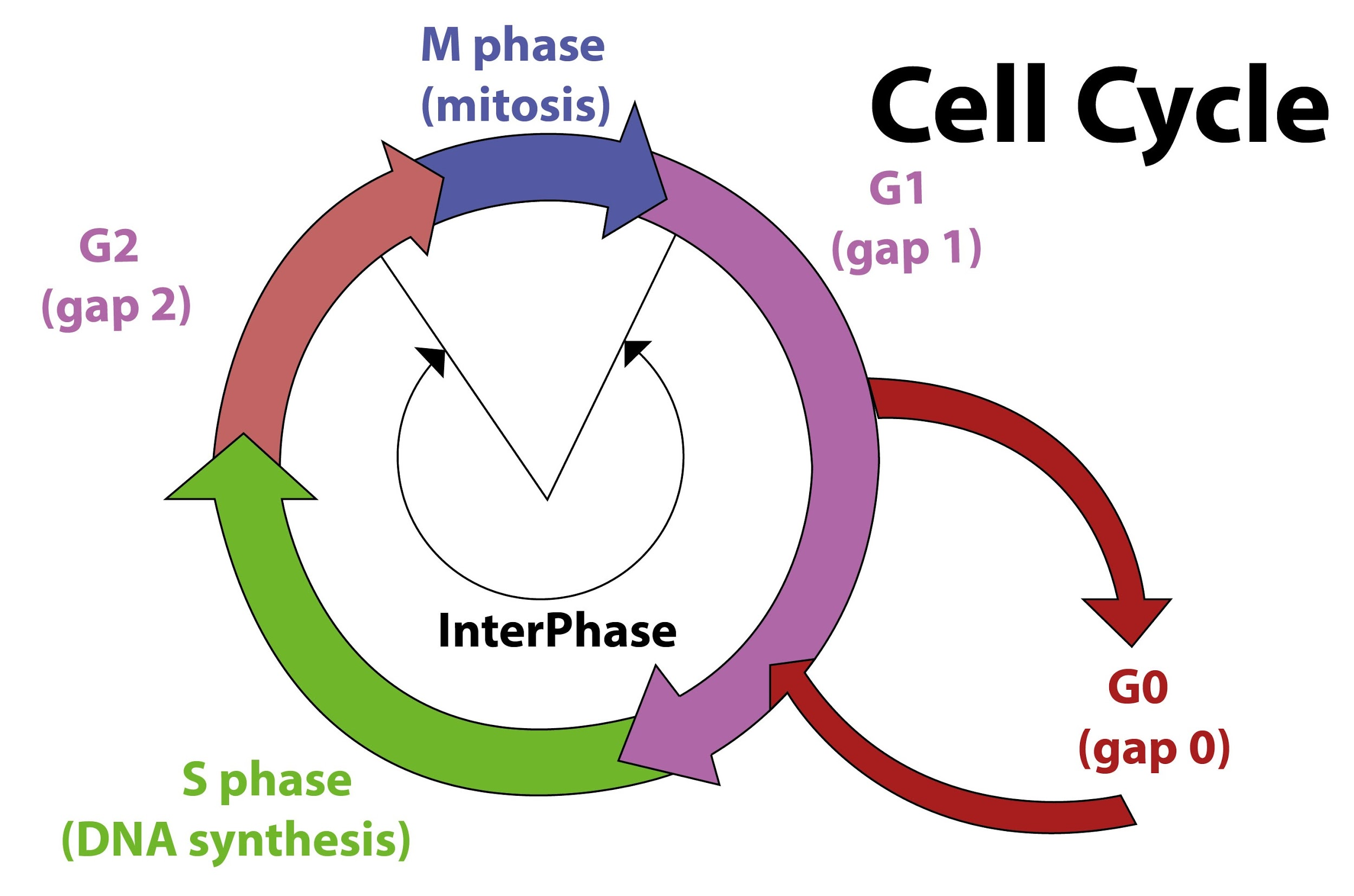
Note: While several cells that die along with the organism in the G0 phase, not all cells entering the G0 phase are doomed to die; this is mostly simply a consequence of the cell's lack of any ability to re-enter the cell cycle. Some cells temporarily join G0 before an external signal activates G1 initialization. Other cells, such as mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells, which never or rarely divide, remain permanently in G0.
Complete answer:
The cell cycle consists basically of four phases G1, S, G2, and M. G0 phase also known as the extended G1 phase which is a period during which the cell exits from the cell cycle. The cell exists in a quiescent state at this stage and does not divide. If cells are not to be separated after the G1 process and begin to undergo differentiation into various cell types such cells are said to be in G0 state.
G0 is often referred to as a "post-mitotic" condition because cells in G0 are outside of the cell cycle in a non-dividing period. Cells in the G0 state remain metabolically active but no longer proliferate unless they are called upon to do so depending on the organism's requirement.
So, the correct answer is ‘Exit of the cell from cell cycle’.

Note: While several cells that die along with the organism in the G0 phase, not all cells entering the G0 phase are doomed to die; this is mostly simply a consequence of the cell's lack of any ability to re-enter the cell cycle. Some cells temporarily join G0 before an external signal activates G1 initialization. Other cells, such as mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells, which never or rarely divide, remain permanently in G0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




