
What is the general formula of a carboxylic acid?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Carboxylic acid is a homologous series of compounds that contain a carboxyl functional group (-COOH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. These compounds are acidic in nature and the general formula for this homologous series is - ${{\text{C}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2n+1}}}\text{COOH}$.
Complete answer:
A homologous series a series of chemical compounds that are having the same functional group and similar chemical properties and the successive members differ by a $-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ group.
Carboxylic acids also form a homologous series and like all homologous series, the carboxylic acids have a general formula and common properties that are listed below:
-The general formula for the carboxylic acids is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2n+1}}}\text{COOH}$.
-Compounds show a gradual variation in physical properties, such as boiling points.
-All have similar chemical properties
The functional group in the carboxylic acids is the carboxyl group, –COOH. The carboxyl group is made up of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a carbonyl group (-C=O). The structure is given below:
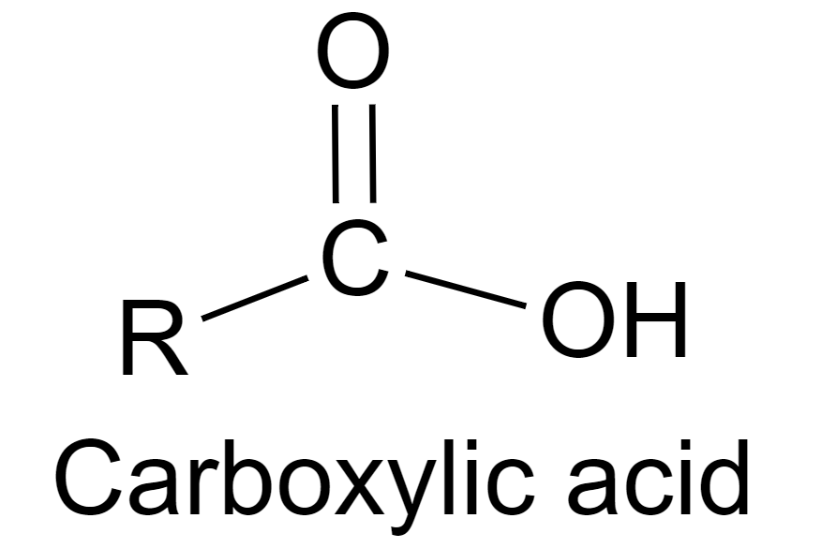
Due to this functional group, carboxylic acids possess acidic characters and typical properties such as they react with bases to form salt and water and with metals, they form salt and hydrogen.
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than other organic compounds but less acidic than mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Additional information:
Carboxylic acids occur widely in nature. Lactic acid found in sour milk products and citric acid found in citrus fruits is carboxylic acids.
Note:
Compounds formed by the replacement of the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxylic acids by certain other groups are known as carboxylic acid derivatives. This class of carboxylic acid derivatives includes many important compounds such as acyl halides, esters, acid anhydrides, and amides.
Complete answer:
A homologous series a series of chemical compounds that are having the same functional group and similar chemical properties and the successive members differ by a $-\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ group.
Carboxylic acids also form a homologous series and like all homologous series, the carboxylic acids have a general formula and common properties that are listed below:
-The general formula for the carboxylic acids is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{n}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2n+1}}}\text{COOH}$.
-Compounds show a gradual variation in physical properties, such as boiling points.
-All have similar chemical properties
The functional group in the carboxylic acids is the carboxyl group, –COOH. The carboxyl group is made up of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a carbonyl group (-C=O). The structure is given below:

Due to this functional group, carboxylic acids possess acidic characters and typical properties such as they react with bases to form salt and water and with metals, they form salt and hydrogen.
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than other organic compounds but less acidic than mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Additional information:
Carboxylic acids occur widely in nature. Lactic acid found in sour milk products and citric acid found in citrus fruits is carboxylic acids.
Note:
Compounds formed by the replacement of the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxylic acids by certain other groups are known as carboxylic acid derivatives. This class of carboxylic acid derivatives includes many important compounds such as acyl halides, esters, acid anhydrides, and amides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




