
What is the geometry and hybridization of $ P{F_6}^ - $ . What orbitals are used to hybridize?
Answer
494.1k+ views
Hint: Phosphorus is the central atom in the compound $ P{F_6}^ - $ . There are only five electrons in the outermost shell of the phosphorus atom and the negative charge is placed on the more electronegative atom which is fluorine in this case.
Complete answer:
The ground state electronic configuration of the central phosphorus atom in $ P{F_6}^ - $ is such that there are five electrons in the outermost shell. Two of these electrons are paired and present in the s-orbital. To exhibit a covalency of five or above, the electrons need to be unpaired using the vacant d-orbitals.
The negative charge goes on the fluorine atom as it is more electronegative than phosphorus. Each fluorine atom shares one electron and pairs with the unpaired electron present in the atomic orbitals of phosphorus. The fluoride ion contains eight electrons and simply donates a pair of electrons in the vacant d-orbital of the phosphorus atom. As a result, six atomic orbitals of phosphorus are involved in the formation of $ P{F_6}^ - $ .
The six atomic orbitals undergo mixing to give six equivalent hybrid orbitals with better overlap, lesser energy and more directional character. These six hybrid orbitals arrange themselves in such a manner to create six equivalent positions for all fluorine atoms. The hybrid orbitals are therefore equal in length and mutually perpendicular to each other. Such a geometry is called an octahedral geometry.
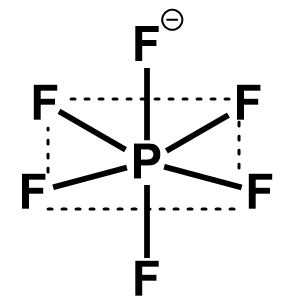
$ \Rightarrow $ The six atomic orbitals on phosphorus that undergo hybridization are $ s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z},{d_{{z^2}}}{\text{ and }}{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ . Thus the hybridization of $ P{F_6}^ - $ is $ s{p_3}{d_2} $ and the geometry is octahedral.
Note:
The structure of $ P{F_6}^ - $ can be compared to $ S{F_6} $ which has an equal number of electrons and undergoes similar hybridization to give an octahedral geometry. The orbitals present in the $ z$ - plane are used to form axial orbitals and the remaining orbital forms a square planar geometry in the $ x - y $ plane.
Complete answer:
The ground state electronic configuration of the central phosphorus atom in $ P{F_6}^ - $ is such that there are five electrons in the outermost shell. Two of these electrons are paired and present in the s-orbital. To exhibit a covalency of five or above, the electrons need to be unpaired using the vacant d-orbitals.
The negative charge goes on the fluorine atom as it is more electronegative than phosphorus. Each fluorine atom shares one electron and pairs with the unpaired electron present in the atomic orbitals of phosphorus. The fluoride ion contains eight electrons and simply donates a pair of electrons in the vacant d-orbital of the phosphorus atom. As a result, six atomic orbitals of phosphorus are involved in the formation of $ P{F_6}^ - $ .
The six atomic orbitals undergo mixing to give six equivalent hybrid orbitals with better overlap, lesser energy and more directional character. These six hybrid orbitals arrange themselves in such a manner to create six equivalent positions for all fluorine atoms. The hybrid orbitals are therefore equal in length and mutually perpendicular to each other. Such a geometry is called an octahedral geometry.

$ \Rightarrow $ The six atomic orbitals on phosphorus that undergo hybridization are $ s,{p_x},{p_y},{p_z},{d_{{z^2}}}{\text{ and }}{d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}} $ . Thus the hybridization of $ P{F_6}^ - $ is $ s{p_3}{d_2} $ and the geometry is octahedral.
Note:
The structure of $ P{F_6}^ - $ can be compared to $ S{F_6} $ which has an equal number of electrons and undergoes similar hybridization to give an octahedral geometry. The orbitals present in the $ z$ - plane are used to form axial orbitals and the remaining orbital forms a square planar geometry in the $ x - y $ plane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




