
What is the geometry of the manganate ion, $ ~Mn{{O}_{4}}^{2-}? $
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: The three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make up a molecule is known as molecular geometry. It comprises the molecule's overall form, as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles, and any other geometrical factors that define each atom's location. The reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, colour, magnetism, and biological activity of a material are all influenced by molecular geometry.
Complete answer:
A central atom is placed in the middle of a tetrahedral molecular geometry, with four substituents located at the corners of the tetrahedron. When all four substituents are the same, as in methane and its heavier equivalents, the bond angles are $ 109.5{}^\circ $ . Point group Td includes methane and other fully symmetrical tetrahedral molecules, although most tetrahedral molecules have lesser symmetry. Chiral tetrahedral molecules are possible.
Now let us draw for $ ~Mn{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $
We have Mn, therefore manganate is a sulphate ion counterpart for which VSEPR may be used directly.
Determine which atom in the structure is the centre atom. Normally, this is the least electronegative atom (Mn). Make a skeletal structure with the other atoms single-bonded to the central one. Make an octet for each atom by wrapping electron pairs around it. Count how many valence electrons there are in your test structure (32). Count how many valence electrons you have accessible now. Four electrons are absent from the trial structure. As a result, Create a new structure with one double bond for each missing pair of electrons and an octet for each O atom:
The octet of the Mn atom can be "extended." Determine the molecular geometry using VSEPR theory. Around the Mn atom, there are four bonding electron domains and no lone pairs.
$ A{{X}_{4}} $ is a kind of molecule.
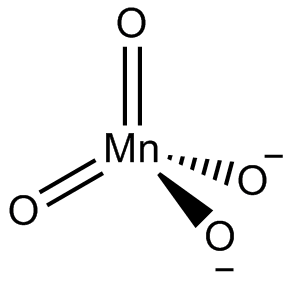
Hence The molecular geometry is tetrahedral.
Note:
A manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity containing manganese as the centre atom in inorganic nomenclature. However, because it includes manganese in the +6 oxidation state, the term is typically used to the tetraoxidomanganate(2-) anion, $ Mn{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ , also known as manganate(VI). Manganates are the only manganese(VI) compounds that have been discovered.
Complete answer:
A central atom is placed in the middle of a tetrahedral molecular geometry, with four substituents located at the corners of the tetrahedron. When all four substituents are the same, as in methane and its heavier equivalents, the bond angles are $ 109.5{}^\circ $ . Point group Td includes methane and other fully symmetrical tetrahedral molecules, although most tetrahedral molecules have lesser symmetry. Chiral tetrahedral molecules are possible.
Now let us draw for $ ~Mn{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $
We have Mn, therefore manganate is a sulphate ion counterpart for which VSEPR may be used directly.
Determine which atom in the structure is the centre atom. Normally, this is the least electronegative atom (Mn). Make a skeletal structure with the other atoms single-bonded to the central one. Make an octet for each atom by wrapping electron pairs around it. Count how many valence electrons there are in your test structure (32). Count how many valence electrons you have accessible now. Four electrons are absent from the trial structure. As a result, Create a new structure with one double bond for each missing pair of electrons and an octet for each O atom:
The octet of the Mn atom can be "extended." Determine the molecular geometry using VSEPR theory. Around the Mn atom, there are four bonding electron domains and no lone pairs.
$ A{{X}_{4}} $ is a kind of molecule.

Hence The molecular geometry is tetrahedral.
Note:
A manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity containing manganese as the centre atom in inorganic nomenclature. However, because it includes manganese in the +6 oxidation state, the term is typically used to the tetraoxidomanganate(2-) anion, $ Mn{{O}_{4}}^{2-} $ , also known as manganate(VI). Manganates are the only manganese(VI) compounds that have been discovered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




