
Germination is epigeal in -
(a)Zea mays
(b)Helianthus
(c)Mangifera
(d)Pisum
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The term ‘epi’ means below something. And since we are understanding about germination, there are plants that may germinate above or below the ground surface. Germination can occur above or below ground depending on the type of the plant seed.
Complete answer:
- Epigeal germination is the type where the cotyledons are above the soil surface as the hypocotyl elongates very rapidly. The epicotyl remains unchanged in length.
- Examples of epigeal germination are cotton, sunflower, castor, and bean (or common bean).
- As epigeal germination plants are more vulnerable to grazing and weather conditions, the plants produce a large number of seeds as an evolutionary strategy.
Additional Information: - Hypogeal germination is the type where the cotyledons stay below the ground, the epicotyl above the cotyledon grows, while the hypocotyl below the cotyledon remains the same in length.
- Examples of hypogeal germination include pea, mango, maize, and lily.
- Here, the plumule pushes the cotyledons out of the soil.
- The cotyledons are fleshy and as they stay below ground, they develop a survival strategy that they are resistant to cold temperatures or grazing.
- Hypogeal germination also occurs in plants where low nutrient soils and low sunlight conditions are favored. They are also resistant to flooding.
- Plants with hypogeal germination grow relatively slower while those with epigeal germination grow faster. This is also dependent on their resistance to flooding. Since epigeal plants are not resistant to flooding, rapid growth allows them to develop before the area is flooded again.
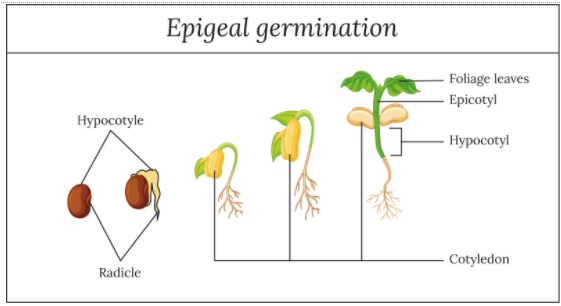
So, the correct answer is ‘Helianthus’.
Note: - Two species in the same genus can show different types of germination. For example, the runner bean or the Phaseolus coccineus shows hypogeal germination while the common bean Phaseolus vulgaris shows epigeal germination.
Complete answer:
- Epigeal germination is the type where the cotyledons are above the soil surface as the hypocotyl elongates very rapidly. The epicotyl remains unchanged in length.
- Examples of epigeal germination are cotton, sunflower, castor, and bean (or common bean).
- As epigeal germination plants are more vulnerable to grazing and weather conditions, the plants produce a large number of seeds as an evolutionary strategy.
Additional Information: - Hypogeal germination is the type where the cotyledons stay below the ground, the epicotyl above the cotyledon grows, while the hypocotyl below the cotyledon remains the same in length.
- Examples of hypogeal germination include pea, mango, maize, and lily.
- Here, the plumule pushes the cotyledons out of the soil.
- The cotyledons are fleshy and as they stay below ground, they develop a survival strategy that they are resistant to cold temperatures or grazing.
- Hypogeal germination also occurs in plants where low nutrient soils and low sunlight conditions are favored. They are also resistant to flooding.
- Plants with hypogeal germination grow relatively slower while those with epigeal germination grow faster. This is also dependent on their resistance to flooding. Since epigeal plants are not resistant to flooding, rapid growth allows them to develop before the area is flooded again.

So, the correct answer is ‘Helianthus’.
Note: - Two species in the same genus can show different types of germination. For example, the runner bean or the Phaseolus coccineus shows hypogeal germination while the common bean Phaseolus vulgaris shows epigeal germination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




