
Ginger is an underground stem. It is distinguished from the root because
A) It lacks chlorophyll
B) It stores food
C) It has nodes and internodes
D) It has xylem and vessels
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: At some specific locations, ginger bears buds. When it gets favourable conditions, leaves and flowers arise from the buds at those places. Such buds are not found in the underground roots.
Complete answer:
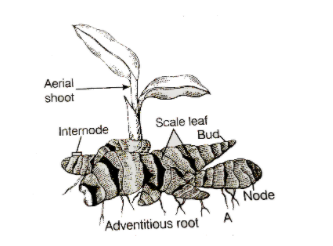
Underground stems are actually the modified plant structures that exist under the surface of the soil but the tissue from which these structures have been derived is the stem tissue. As these are derived from stem tissues, they possess the most basic feature of stem i.e. the presence of nodes and internodes and this feature distinguishes the underground stems from the underground roots. Ginger is considered as an underground stem and not root because it bears nodes and internodes at specific locations that are absent in the roots. Here, the nodes and internodes present in the ginger has been shown below –
Additional information
Being an underground part, they can’t perform photosynthetic processes so usually they function as storage tissues for food and nutrients. Besides these functions, they also help in asexual reproduction by promoting propagation of new clones and perennation i.e. survival from one growing season to the next.
Two axes of growth are found in the plants that can be observed when the seed starts to germinate. Out of these two, the one structure that develops upward in the soil is called stem while the second one that develops downward is called root. The former structure i.e. the stem is modified during the further growth process to transport water and nutrients to and from the leaves and flowers while the later one is modified to have root hairs and its branches to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
The leaves and flowers are formed from the stem at some specific locations where buds are present. These locations are nodes and internodes. These are not found in the roots and thus serve as a basic differentiating feature for the stems
So, the correct answer is ‘It has nodes and internodes’.
Note:Underground stems are modified in different plants as per their growing environment and requirements. These can be in the form of a bulb, corm, stolon, rhizome, or tuber. The ginger is an example of a rhizome where leaves are found in reduced form as scales. We consume a number of underground stems like potato, onion, yam, ginger, etc.
Complete answer:
Underground stems are actually the modified plant structures that exist under the surface of the soil but the tissue from which these structures have been derived is the stem tissue. As these are derived from stem tissues, they possess the most basic feature of stem i.e. the presence of nodes and internodes and this feature distinguishes the underground stems from the underground roots. Ginger is considered as an underground stem and not root because it bears nodes and internodes at specific locations that are absent in the roots. Here, the nodes and internodes present in the ginger has been shown below –

Additional information
Being an underground part, they can’t perform photosynthetic processes so usually they function as storage tissues for food and nutrients. Besides these functions, they also help in asexual reproduction by promoting propagation of new clones and perennation i.e. survival from one growing season to the next.
Two axes of growth are found in the plants that can be observed when the seed starts to germinate. Out of these two, the one structure that develops upward in the soil is called stem while the second one that develops downward is called root. The former structure i.e. the stem is modified during the further growth process to transport water and nutrients to and from the leaves and flowers while the later one is modified to have root hairs and its branches to absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
The leaves and flowers are formed from the stem at some specific locations where buds are present. These locations are nodes and internodes. These are not found in the roots and thus serve as a basic differentiating feature for the stems
So, the correct answer is ‘It has nodes and internodes’.
Note:Underground stems are modified in different plants as per their growing environment and requirements. These can be in the form of a bulb, corm, stolon, rhizome, or tuber. The ginger is an example of a rhizome where leaves are found in reduced form as scales. We consume a number of underground stems like potato, onion, yam, ginger, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




