
Give a brief account of the mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint: Chemical transmission causes depolarization of the membrane and initiates an action potential. A faster method of nerve conduction than the chemical method of transmission is electrical transmission.
Complete answer:
A synapse is a junction between two neurons. It is present between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of the next neuron separated by a cleft.
There are two ways of synaptic transmission.
(1) Chemical transmission
(2) Electrical transmission
The mechanism of synaptic transmission at the electrical synapse:
-In this case, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are in proximity.
-The impulse in the form of an electric current directly flows from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron.
-Transmission is faster than the chemical synapse.
The mechanism of synaptic transmission at the chemical synapse:
-the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons are separated by the synaptic cleft.
-When an impulse arrives at the axon terminal, the calcium ions present in the synaptic cleft enter the synaptic knobs present at the axon terminals of the presynaptic neuron.
-The synaptic vesicles present in the synaptic knobs present in the presynaptic neuron move towards the plasma membrane and fuse with it.
-The vesicles release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. (Empty synaptic vesicles return to the cytoplasm of the presynaptic neuron where they are refilled.)
Note:
-The molecules of acetylcholine bind to the protein receptors present on the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic neurons.
-This binding opens the channels, and sodium ions enter the postsynaptic neuron, while potassium ions leave the postsynaptic membrane.
-This generates an action potential in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron, and hence, the impulse is transmitted to the postsynaptic neuron.
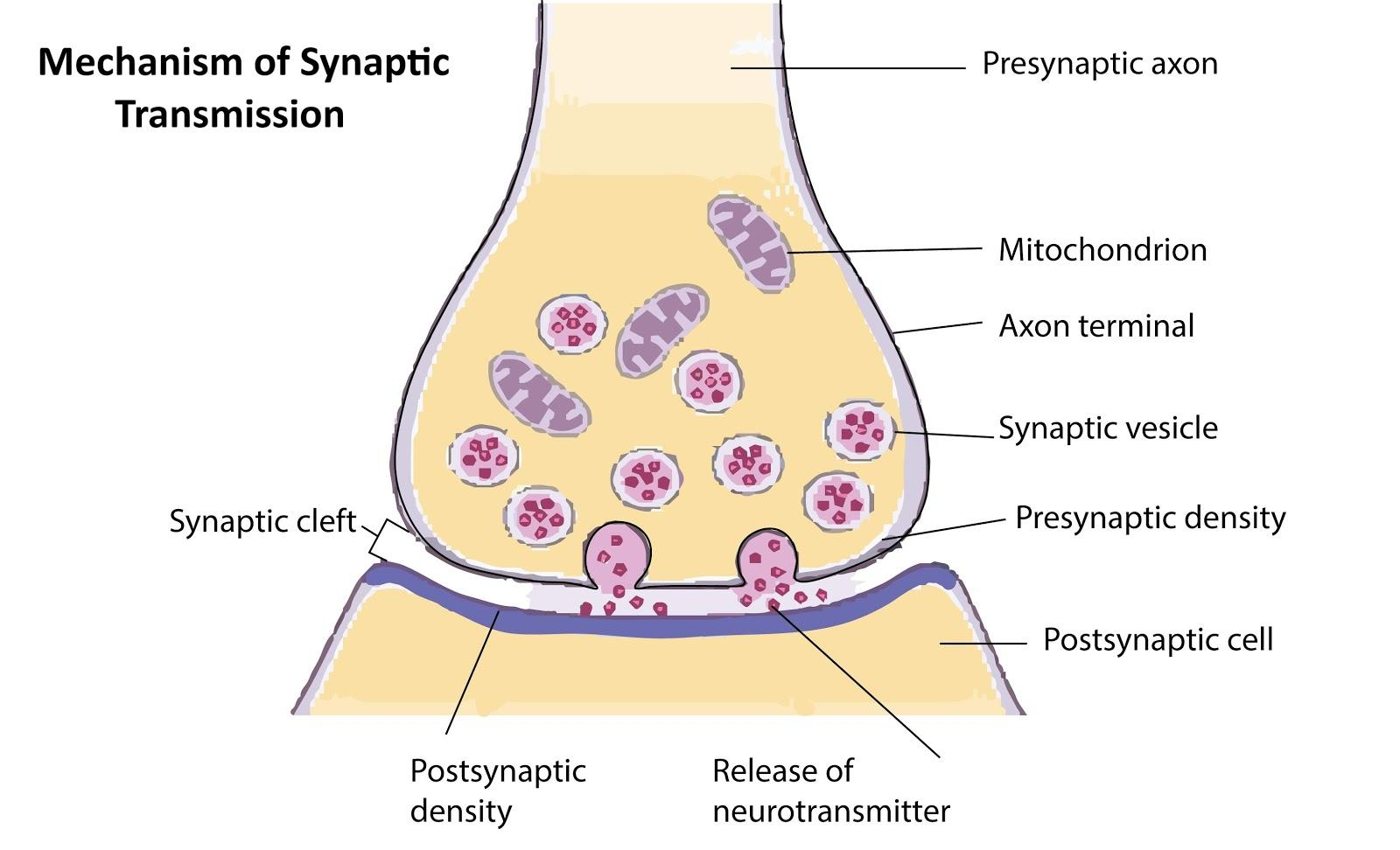
Complete answer:
A synapse is a junction between two neurons. It is present between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of the next neuron separated by a cleft.
There are two ways of synaptic transmission.
(1) Chemical transmission
(2) Electrical transmission
The mechanism of synaptic transmission at the electrical synapse:
-In this case, the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are in proximity.
-The impulse in the form of an electric current directly flows from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron.
-Transmission is faster than the chemical synapse.
The mechanism of synaptic transmission at the chemical synapse:
-the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons are separated by the synaptic cleft.
-When an impulse arrives at the axon terminal, the calcium ions present in the synaptic cleft enter the synaptic knobs present at the axon terminals of the presynaptic neuron.
-The synaptic vesicles present in the synaptic knobs present in the presynaptic neuron move towards the plasma membrane and fuse with it.
-The vesicles release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. (Empty synaptic vesicles return to the cytoplasm of the presynaptic neuron where they are refilled.)
Note:
-The molecules of acetylcholine bind to the protein receptors present on the plasma membrane of the postsynaptic neurons.
-This binding opens the channels, and sodium ions enter the postsynaptic neuron, while potassium ions leave the postsynaptic membrane.
-This generates an action potential in the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron, and hence, the impulse is transmitted to the postsynaptic neuron.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




