
Give an account of the nervous system in cockroaches.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: By activating the running response in the motor centers of the thoracic ganglia, the nervous system promotes cockroach survival. Cockroach nervous system consists of CNS (Central Nervous system), PNS (peripheral Nervous System), and Sympathetic Nervous system.
Complete answer:
- The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmented ganglia connected on the ventral side with coupled longitudinal connectors.
- In the thorax lie three ganglia, and in the abdomen there are six. The cockroach's nervous system is spread all over the body.
- The head holds a small part of the nervous system and the rest is located along the ventral part of your body. So it is clearly understood that it is going to live for as long as one week if the chef of the cockroach is cut off.
- In the region of the head, the brain is a super esophageal ganglion, supplying antennae and compound eyes with nerves.
- The sensory organs in Cockroach include antennae, pupils, maxillary-palps, labial palps, and cerci etc. On the dorsal surface of the head are the compound eyes.
- Around 2000 hexagonal ommatidia are present in each eye. A cockroach may get several images of an object using ommatidia. This form of vision is known for its sensitivity as a mosaic vision, but less detail is usual during the night.
- The main characteristics of the central nervous system (CNS) in cockroaches are its segmented nature and the decentralisation of control processes.
- Brain, thoracic, and abdominal ganglia are connected together by a pair of interganglionic connectors to form the ventral nerve cord (VNC).
The diagram of nervous system of cockroach is given below:
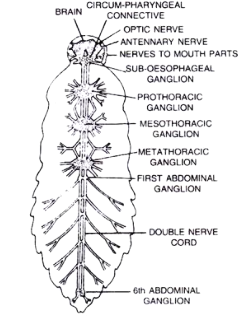
Nervous system of cockroach
Note: Cockroach's nervous system can be split into 3 parts. The cockroach's central nervous system comprises supra-esophagus or cerebrum ganglia, sub-esophagus ganglia and circum oesophageal connectives in the head, and double ventral ganglionated nerve cords throughout the thorax and abdomen.
Complete answer:
- The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmented ganglia connected on the ventral side with coupled longitudinal connectors.
- In the thorax lie three ganglia, and in the abdomen there are six. The cockroach's nervous system is spread all over the body.
- The head holds a small part of the nervous system and the rest is located along the ventral part of your body. So it is clearly understood that it is going to live for as long as one week if the chef of the cockroach is cut off.
- In the region of the head, the brain is a super esophageal ganglion, supplying antennae and compound eyes with nerves.
- The sensory organs in Cockroach include antennae, pupils, maxillary-palps, labial palps, and cerci etc. On the dorsal surface of the head are the compound eyes.
- Around 2000 hexagonal ommatidia are present in each eye. A cockroach may get several images of an object using ommatidia. This form of vision is known for its sensitivity as a mosaic vision, but less detail is usual during the night.
- The main characteristics of the central nervous system (CNS) in cockroaches are its segmented nature and the decentralisation of control processes.
- Brain, thoracic, and abdominal ganglia are connected together by a pair of interganglionic connectors to form the ventral nerve cord (VNC).
The diagram of nervous system of cockroach is given below:

Nervous system of cockroach
Note: Cockroach's nervous system can be split into 3 parts. The cockroach's central nervous system comprises supra-esophagus or cerebrum ganglia, sub-esophagus ganglia and circum oesophageal connectives in the head, and double ventral ganglionated nerve cords throughout the thorax and abdomen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




