
Give an example of each Isolated diene.
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: A diene is a covalent molecule in organic chemistry that includes two double bonds, generally between carbon atoms. They have two alkene units and the usual systematic naming prefix di. Dienes are found in both natural and manufactured compounds and are utilised in organic synthesis as a component of larger molecules. In the polymer industry, conjugated dienes are commonly employed as monomers. Nutritionists are interested in polyunsaturated fats.
Completed answer:
Due to variables such as charge delocalization through resonance and hybridization energy, conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated) are more stable than non conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated). This might also explain why allylic radicals are far more stable than secondary or tertiary carbocations. This is owing to the pi orbitals' positions and their propensity to overlap, which strengthens the single bond between the two double bonds. Two double bonds are separated by more than one single bond in nonconjugated (isolated) dienes. Two double bonds are separated by more than one single bond in a diene. Because greater electron density is delocalized, the molecule becomes more stable. Non-conjugated and cumulated dienes are less stable than conjugated dienes.
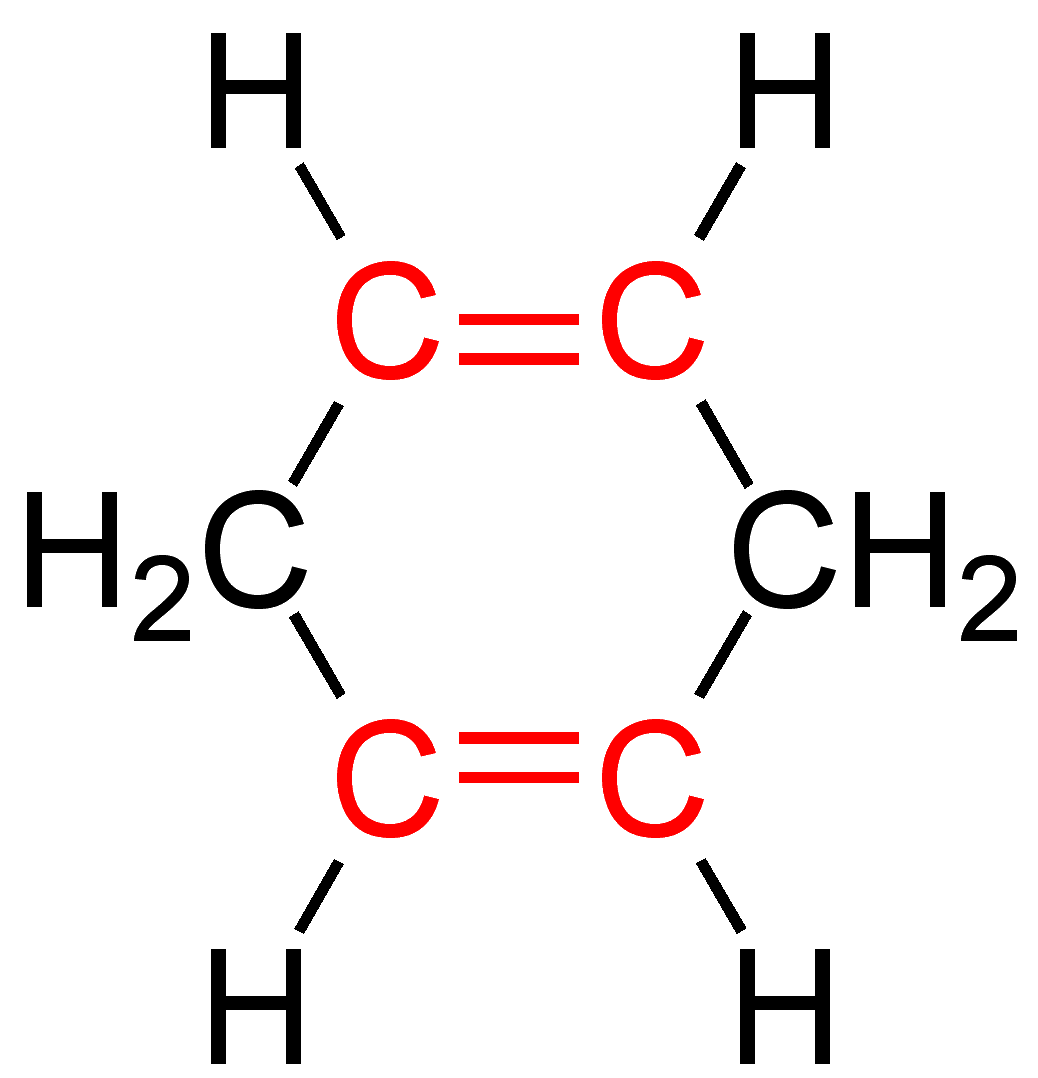
The double bonds in unconjugated dienes are separated by two or more single bonds. They are less stable than isomeric conjugated dienes in most cases. An isolated diene is another name for this substance.
Note:
Butadiene is produced on a large scale by thermal cracking of butanes. Dicyclopentadiene is made from coal tars in a similar non-selective method. Dehydrohalogenation and condensations, for example, are more focused and sensitive processes used in the laboratory. The Whiting reaction is one of several techniques that have been devised. The oligomerization and dimerization of conjugated dienes give rise to non conjugated dienes. Dimerization of 1,3-butadiene produces 1,5-cyclooctadiene and vinylcyclohexene, for example. Acetyl CoA is used to biosynthesize diene-containing fatty acids.
Completed answer:
Due to variables such as charge delocalization through resonance and hybridization energy, conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated) are more stable than non conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated). This might also explain why allylic radicals are far more stable than secondary or tertiary carbocations. This is owing to the pi orbitals' positions and their propensity to overlap, which strengthens the single bond between the two double bonds. Two double bonds are separated by more than one single bond in nonconjugated (isolated) dienes. Two double bonds are separated by more than one single bond in a diene. Because greater electron density is delocalized, the molecule becomes more stable. Non-conjugated and cumulated dienes are less stable than conjugated dienes.

The double bonds in unconjugated dienes are separated by two or more single bonds. They are less stable than isomeric conjugated dienes in most cases. An isolated diene is another name for this substance.
Note:
Butadiene is produced on a large scale by thermal cracking of butanes. Dicyclopentadiene is made from coal tars in a similar non-selective method. Dehydrohalogenation and condensations, for example, are more focused and sensitive processes used in the laboratory. The Whiting reaction is one of several techniques that have been devised. The oligomerization and dimerization of conjugated dienes give rise to non conjugated dienes. Dimerization of 1,3-butadiene produces 1,5-cyclooctadiene and vinylcyclohexene, for example. Acetyl CoA is used to biosynthesize diene-containing fatty acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




