
Give an example where (a) the velocity of a particle is zero but its acceleration is not zero, (b) the velocity is opposite in direction to the acceleration, (c) the velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Acceleration, velocity and displacement are combined with a simple law. That is, the rate of change of velocity with respect to time is acceleration and the rate of change of position with respect to time is velocity.
Formula used: Distance covered by an acceleration object can be written as: \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Even if the velocity of an object becomes zero (for a moment) acceleration is considered to be non-zero. For example, in a pendulum, the velocity is zero as it reverses its direction. But it has to travel backwards due to the kinetic energy and the restoring force stored in it. At that instant of time, the acceleration is non-zero.
(b) Consider a ball moving with constant velocity (horizontally) in a downward direction with constant downward acceleration ‘-g’. Then, according to equation (1), the distance covered by the ball can also be written as \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]. But here, the acceleration is ‘-g’. Therefore, \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}( - g){t^2}\]. Negative sign is used because force is directed downwards. This is the example of the case when the velocity is opposite in direction to the acceleration.
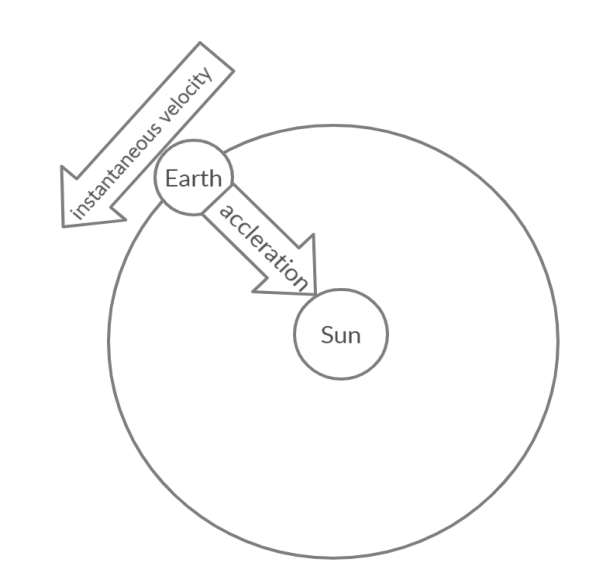
(c) Acceleration produced by the rate of change of velocity when the velocity is changing its direction is called centripetal acceleration. For example, the planetary motion. Consider the motion of earth around the sun. The force and the acceleration on earth is always towards the sun, not around the sun. In this case, the velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.
Note:
The situation where the velocity of a particle is zero with non-zero acceleration can also be thought of as an example when the ball is thrown vertically upwards. After sometime, it starts falling vertically downwards. When the ball reverses its direction, the velocity becomes zero but the acceleration is still not zero.
Formula used: Distance covered by an acceleration object can be written as: \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
(a) Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. Even if the velocity of an object becomes zero (for a moment) acceleration is considered to be non-zero. For example, in a pendulum, the velocity is zero as it reverses its direction. But it has to travel backwards due to the kinetic energy and the restoring force stored in it. At that instant of time, the acceleration is non-zero.
(b) Consider a ball moving with constant velocity (horizontally) in a downward direction with constant downward acceleration ‘-g’. Then, according to equation (1), the distance covered by the ball can also be written as \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]. But here, the acceleration is ‘-g’. Therefore, \[x = \dfrac{1}{2}( - g){t^2}\]. Negative sign is used because force is directed downwards. This is the example of the case when the velocity is opposite in direction to the acceleration.
(c) Acceleration produced by the rate of change of velocity when the velocity is changing its direction is called centripetal acceleration. For example, the planetary motion. Consider the motion of earth around the sun. The force and the acceleration on earth is always towards the sun, not around the sun. In this case, the velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.

Note:
The situation where the velocity of a particle is zero with non-zero acceleration can also be thought of as an example when the ball is thrown vertically upwards. After sometime, it starts falling vertically downwards. When the ball reverses its direction, the velocity becomes zero but the acceleration is still not zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




