
Give (i) an oblique sketch and (ii) an isometric sketch for each of the following:
(a) A cuboid of dimensions 5 cm,3 cm, and 2 cm. (Is your sketch unique?)
(b) A cube with an edge 4 cm long.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We know that an oblique sketch has a more focus on the front side of an object or the face. This means that we can draw, say a cube, even if all its faces are not visible. An oblique sketch is drawn using the 45-degrees angle to render the third dimension. To draw the oblique sketch of the cuboid, we will first draw a rectangle of length 5 cm and breadth 3 cm. Now, we will sketch the back face which is offset with respect to the front face. Since the other dimension is 2 cm or thickness is 2 cm, we will draw the back face 2 cm diagonally from the left-most bottom edge. Now, we will join the edges. We can either redraw the internal edges as dotted lines or erase it off. To draw an isometric sketch, first, we have to join 5 dots vertically and 3 dots horizontally. Now, from the corners, we draw a line segment of length 2 cm. Now, we join all the edges. We have to either remove the internal lines or make it dotted. Similarly, we will draw a cube.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We need to draw oblique and isometric sketches of the given shapes.
(i) We know that an oblique sketch has a more focus on the front side of an object or the face. This means that we can draw, say a cube, even if all its faces are not visible. In other words, an oblique sketch is a 2-dimensional view of a shape. An oblique sketch is drawn using the 45-degrees angle to render the third dimensions
Let us draw the oblique sketches of the following.
(a) A cuboid of dimensions 5 cm,3 cm and 2 cm.
We will first draw a rectangle of length 5 cm and breadth 3 cm. This is shown below:

Now, we will sketch the back face which is offset with respect to the front face. Since the other dimension is 2 cm or thickness is 2 cm, we will draw the back face 2 cm diagonally from the left-most bottom edge. This is shown below:

Now, we will join the edges as follows:

Now, we can either redraw the internal edges as dotted lines or erase it off.


The oblique sketch of a cuboid is not unique. Either of the three faces can come in front which is shown below.


(ii) Now, let’s draw the isometric sketch of the given cuboid. We know that Isometric Sketch focuses on the edge of an object. It is drawn using 30 degrees angles.
First, we have to join 5 dots vertically and 3 dots horizontally as shown below. Each corner of the grid is considered as a dot.

Now, from the corners, we draw a line segment of length 2 cm.

Now, we join all the edges.

We have to either remove the internal lines or make it dotted.
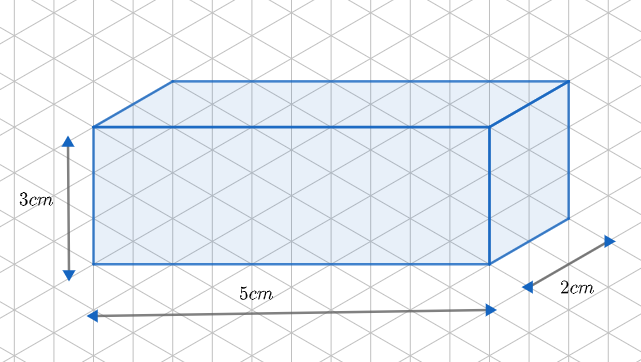
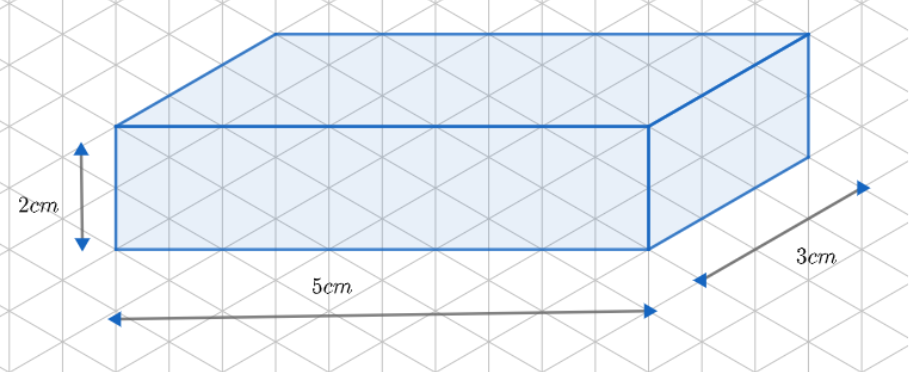
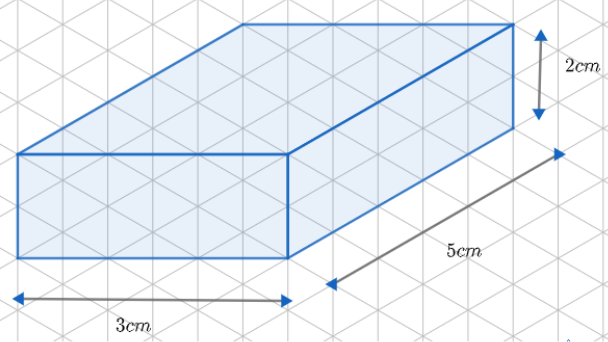
Similar to oblique sketches, we can have different isometric sketches of the cuboid.
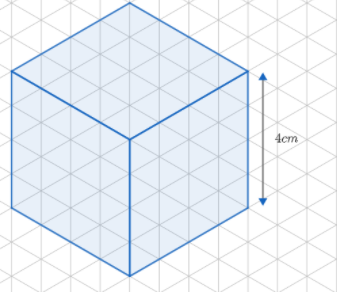
(b) Similar to the cuboid, we will draw the cube side 4 cm.
(i) Oblique sketch
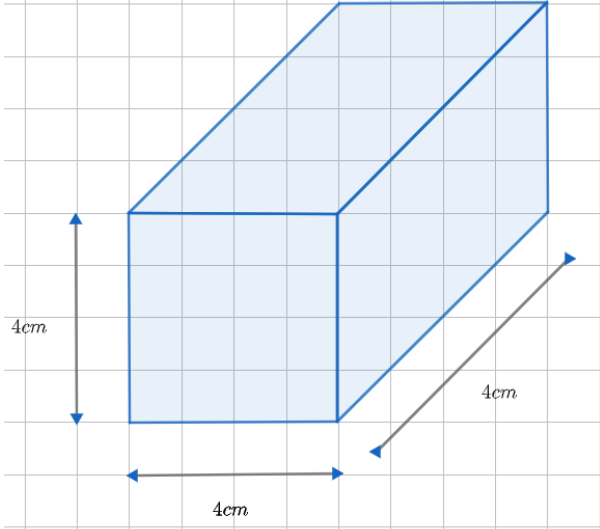
(ii) Isometric sketch
Note: There are some rules to be followed when an isometric sketch is drawn. In the isometric drawing, we will keep the vertical lines as vertically, whereas the horizontal lines are drawn at an angle of 30-degree to the horizontal plane. The angle between all the three axes of the coordinate plane must be equal to 120 degrees.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We need to draw oblique and isometric sketches of the given shapes.
(i) We know that an oblique sketch has a more focus on the front side of an object or the face. This means that we can draw, say a cube, even if all its faces are not visible. In other words, an oblique sketch is a 2-dimensional view of a shape. An oblique sketch is drawn using the 45-degrees angle to render the third dimensions
Let us draw the oblique sketches of the following.
(a) A cuboid of dimensions 5 cm,3 cm and 2 cm.
We will first draw a rectangle of length 5 cm and breadth 3 cm. This is shown below:

Now, we will sketch the back face which is offset with respect to the front face. Since the other dimension is 2 cm or thickness is 2 cm, we will draw the back face 2 cm diagonally from the left-most bottom edge. This is shown below:

Now, we will join the edges as follows:

Now, we can either redraw the internal edges as dotted lines or erase it off.


The oblique sketch of a cuboid is not unique. Either of the three faces can come in front which is shown below.


(ii) Now, let’s draw the isometric sketch of the given cuboid. We know that Isometric Sketch focuses on the edge of an object. It is drawn using 30 degrees angles.
First, we have to join 5 dots vertically and 3 dots horizontally as shown below. Each corner of the grid is considered as a dot.

Now, from the corners, we draw a line segment of length 2 cm.

Now, we join all the edges.

We have to either remove the internal lines or make it dotted.

Similar to oblique sketches, we can have different isometric sketches of the cuboid.


(b) Similar to the cuboid, we will draw the cube side 4 cm.
(i) Oblique sketch

(ii) Isometric sketch

Note: There are some rules to be followed when an isometric sketch is drawn. In the isometric drawing, we will keep the vertical lines as vertically, whereas the horizontal lines are drawn at an angle of 30-degree to the horizontal plane. The angle between all the three axes of the coordinate plane must be equal to 120 degrees.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




